Views :
1,086

-
(2017) Digital Domain Holdings Reports $64 Million in Losses
http://variety.com/2017/biz/asia/losses-at-digital-domain-holdings-double-1202020056/
Digital Domain Holdings, the Hong Kong-based visual effects and virtual reality group, saw losses in 2016 more than double to $64.3 million.
The core Digital Domain 3.0 business provided VFX for films including “Beauty and the Beast,” “Deadpool” and “X-Men: Apocalypse” during the year.
Revenues across the group increased 45% from $68 million (HK$527 million) in 2015 to $98.5 million (HK$763 million) last year. Net losses, which totaled $23.1 million (HK$179 million) in 2015, reached $64.3 million (HK$498 million) in 2016.
The company pointed to content development and research and development costs for virtual reality content and games, 360° and virtual humans, and a more than fourfold increase in amortization of intangible assets, as causes of the financial pain.
-
Autodesk announces new products to replace 123D
We’re incredibly proud of these products, and even more proud of what you all have MADE with them. But we recognize that the portfolio has become complex. We are making some changes to simplify our Autodesk portfolio and workflows for people everywhere who love to make things. We are consolidating these tools and features into key apps such as Tinkercad, Fusion 360, and ReMake.
Today, we are sharing the news that in early 2017, after we complete this consolidation, we’ll be shutting down 123Dapp.com
-
5 Thought Experiments That Will Melt Your Brain
1- the basic concept of the “Swampman” thought experiment posited by the philosopher Donald Davidson in the late-1980s. In this experiment a man is traveling through a swamp and killed by a bolt of lightning, but — by sheer chance — another bolt of lightning strikes a nearby swamp and rearranges all the organic particles to create an exact replica (including all the memories and such) of the man who was killed. The new Swampman wakes up and lives the rest of the deceased man’s life.
2- Achilles and the tortoise are racing at constant speeds: Very fast and very slow, respectively. At some point in the race, Achilles reaches the tortoise’s original starting point. But in the time it took Achilles to get there, the tortoise has moved forward. So, then Achilles’s next task would be to make up the new gap between himself and the tortoise, however by the time he did that, the tortoise would have again moved forward by some smaller amount. The process then repeats itself again and again. Achilles is always faced with a new (if smaller) gap to overcome. The takeaway: The great Achilles loses a race to a big dumb lumbering tortoise and no deficit is ever surmountable.
3- let’s say you just froze time at some point along an arrow’s trajectory . At that particular instant, the arrow is suspended in space in a single location. In any one instant of time, no motion is occurring. The arrow can only be in one place or the other and never in-between. So, how does it get from one instant to another if there is never a moment when it is in between the two places?
4- the question at hand is would a blind person who learned to distinguish basic shapes by touch be able to distinguish those objects when he suddenly received the power of sight? In other words, does information from one sensation translate to another, or do we associate them only in our minds?
https://news.psu.edu/story/141360/2006/04/17/research/probing-question-if-blind-person-gained-sight-could-they-recognize
5- You are on a bridge overlooking a set of trolley tracks and you notice that five people have been tied down to the tracks by a devious (and presumably moustache-twirling) villain. Then you see an out-of-control trolley barreling down the tracks that will certainly kill the unfortunate people unless someone intervenes. you realize that you are sharing your bridge with a gigantic fat man, who — if you were to push him in front of the trolley — would have enough girth to stop the trolley and save the five bound people, though he will certainly be killed.You are now faced with the following options: 1) Do nothing and the five people will die, or 2) Push the fat man in front of the trolley and sacrifice him for the five people. In either scenario, are you at all culpable in these innocent people’s deaths? Should the law make any distinction?
-
Photography basics: Shutter angle and shutter speed and motion blur
http://www.shutterangle.com/2012/cinematic-look-frame-rate-shutter-speed/
https://www.cinema5d.com/global-vs-rolling-shutter/
https://www.wikihow.com/Choose-a-Camera-Shutter-Speed
https://www.provideocoalition.com/shutter-speed-vs-shutter-angle/
Shutter is the device that controls the amount of light through a lens. Basically in general it controls the amount of time a film is exposed.
Shutter speed is how long this device is open for, which also defines motion blur… the longer it stays open the blurrier the image captured.
The number refers to the amount of light actually allowed through.
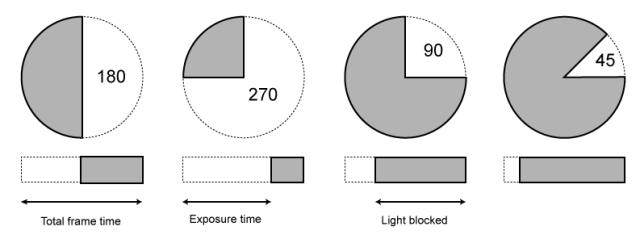
As a reference, shooting at 24fps, at 180 shutter angle or 1/48th of shutter speed (0.0208 exposure time) will produce motion blur which is similar to what we perceive at naked eye
Talked of as in (shutter) angles, for historical reasons, as the original exposure mechanism was controlled through a pie shaped mirror in front of the lens.
A shutter of 180 degrees is blocking/allowing light for half circle. (half blocked, half open). 270 degrees is one quarter pie shaped, which would allow for a higher exposure time (3 quarter pie open, vs one quarter closed) 90 degrees is three quarter pie shaped, which would allow for a lower exposure (one quarter open, three quarters closed)
The shutter angle can be converted back and fort with shutter speed with the following formulas:
https://www.provideocoalition.com/shutter-speed-vs-shutter-angle/shutter angle =
(360 * fps) * (1/shutter speed)
or
(360 * fps) / shutter speedshutter speed =
(360 * fps) * (1/shutter angle)
or
(360 * fps) / shutter angleFor example here is a chart from shutter angle to shutter speed at 24 fps:
270 = 1/32
180 = 1/48
172.8 = 1/50
144 = 1/60
90 = 1/96
72 = 1/120
45 = 1/198
22.5 = 1/348
11 = 1/696
8.6 = 1/1000The above is basically the relation between the way a video camera calculates shutter (fractions of a second) and the way a film camera calculates shutter (in degrees).
Smaller shutter angles show strobing artifacts. As the camera only ever sees at least half of the time (for a typical 180 degree shutter). Due to being obscured by the shutter during that period, it doesn’t capture the scene continuously.
This means that fast moving objects, and especially objects moving across the frame, will exhibit jerky movement. This is called strobing. The defect is also very noticeable during pans. Smaller shutter angles (shorter exposure) exhibit more pronounced strobing effects.
Larger shutter angles show more motion blur. As the longer exposure captures more motion.
Note that in 3D you want to first sum the total of the shutter open and shutter close values, than compare that to the shutter angle aperture, ie:
shutter open -0.0625
shutter close 0.0625
Total shutter = 0.0625+0.0625 = 0.125
Shutter angle = 360*0.125 = 45shutter open -0.125
shutter close 0.125
Total shutter = 0.125+0.125 = 0.25
Shutter angle = 360*0.25 = 90shutter open -0.25
shutter close 0.25
Total shutter = 0.25+0.25 = 0.5
Shutter angle = 360*0.5 = 180shutter open -0.375
shutter close 0.375
Total shutter = 0.375+0.375 = 0.75
Shutter angle = 360*0.75 = 270Faster frame rates can resolve both these issues.
Categories
- 3Dprinting (167)
- A.I. (521)
- animation (328)
- blender (178)
- colour (220)
- commercials (45)
- composition (144)
- cool (357)
- design (606)
- Featured (46)
- hardware (289)
- IOS (106)
- jokes (133)
- lighting (268)
- modeling (102)
- music (182)
- photogrammetry (150)
- photography (736)
- production (1,217)
- python (77)
- quotes (475)
- reference (295)
- software (1,270)
- trailers (287)
- ves (504)
- VR (218)

