RANDOM POSTs
-
SPAR3D – Stable Point-Aware Reconstruction of 3D Objects from Single Images
Read more: SPAR3D – Stable Point-Aware Reconstruction of 3D Objects from Single ImagesSPAR3D is a fast single-image 3D reconstructor with intermediate point cloud generation, which allows for interactive user edits and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
https://github.com/Stability-AI/stable-point-aware-3d
https://stability.ai/news/stable-point-aware-3d?utm_source=x&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=SPAR3D
-
Elon Musk finally admits Tesla’s HW3 might not support full self-driving
Read more: Elon Musk finally admits Tesla’s HW3 might not support full self-drivingThe CEO said when asked about Tesla achieving its promised unsupervised self-driving on HW3 vehicles:
We are not 100% sure. HW4 has several times the capability of HW3. It’s easier to get things to work on HW4 and it takes a lot of efforts to squeeze that into HW3. There is some chance that HW3 does not achieve the safety level that allows for unsupervised FSD.
-
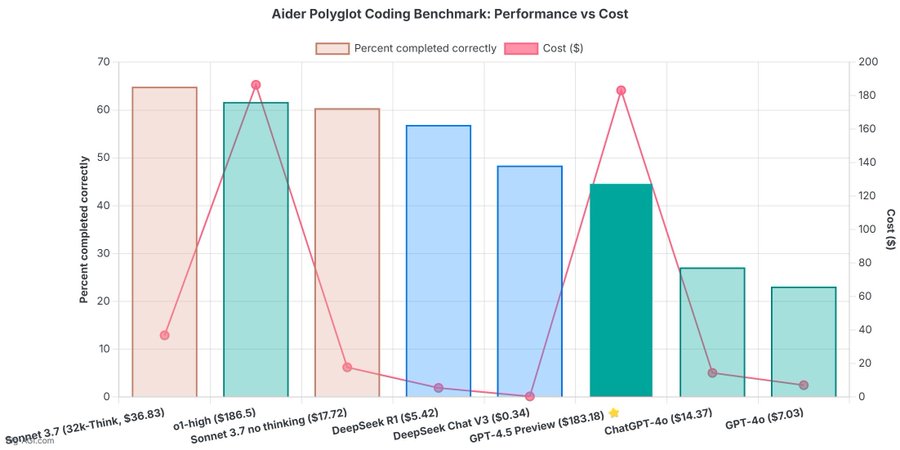
OpenAI 4.5 model arrives to mixed reviews
Read more: OpenAI 4.5 model arrives to mixed reviewsThe verdict is in: OpenAI’s newest and most capable traditional AI model, GPT-4.5, is big, expensive, and slow, providing marginally better performance than GPT-4o at 30x the cost for input and 15x the cost for output. The new model seems to prove that longstanding rumors of diminishing returns in training unsupervised-learning LLMs were correct and that the so-called “scaling laws” cited by many for years have possibly met their natural end.
-
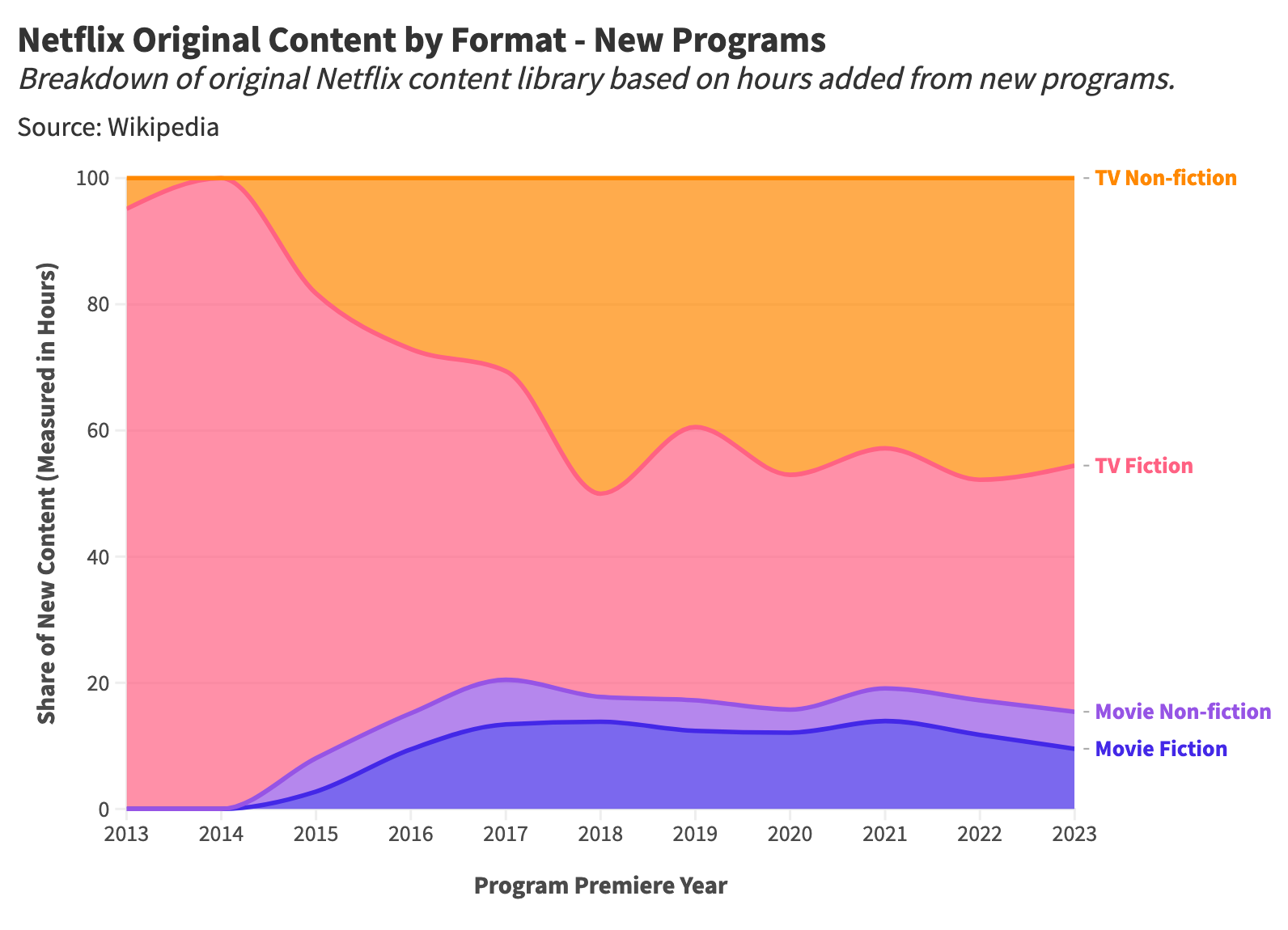
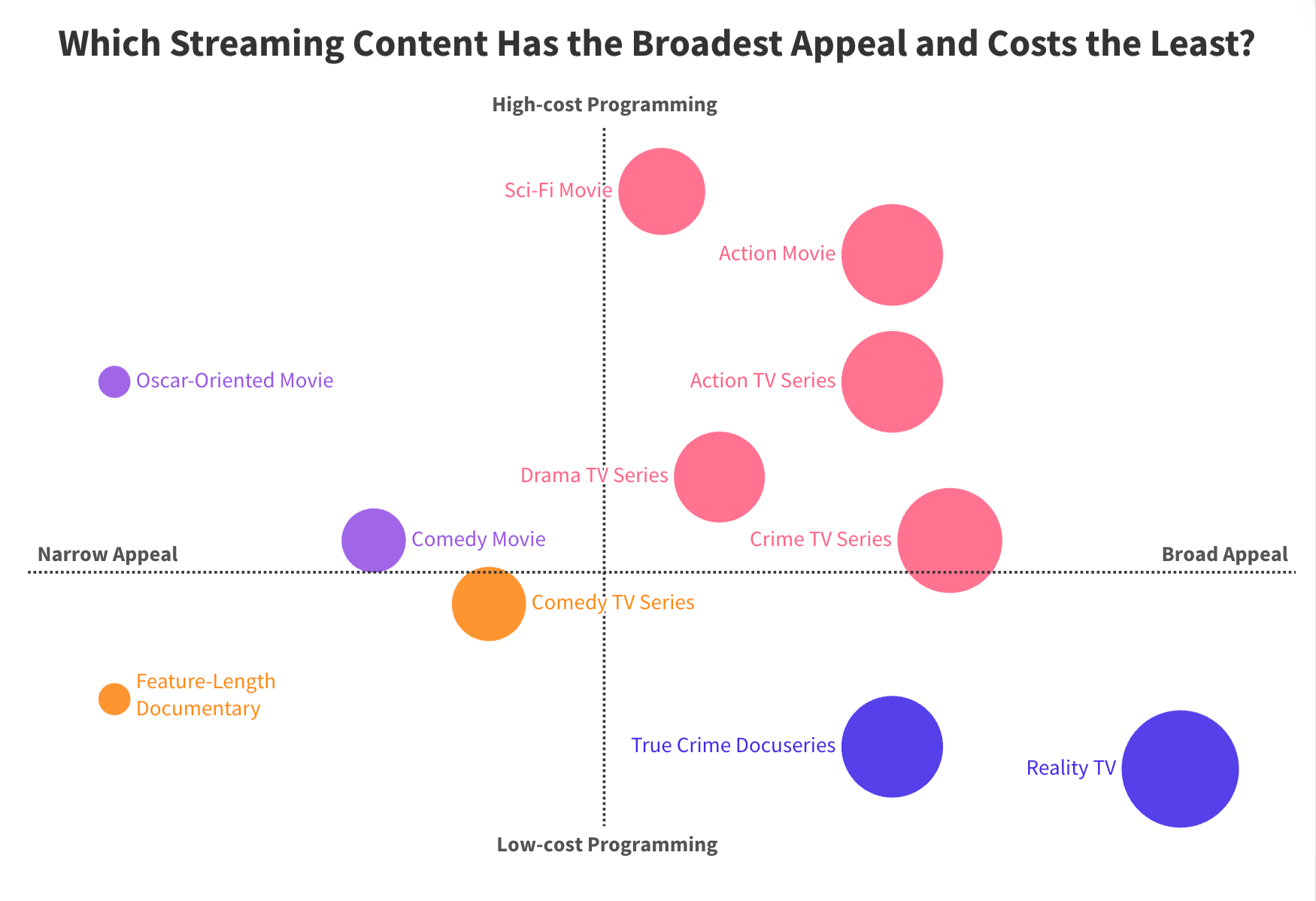
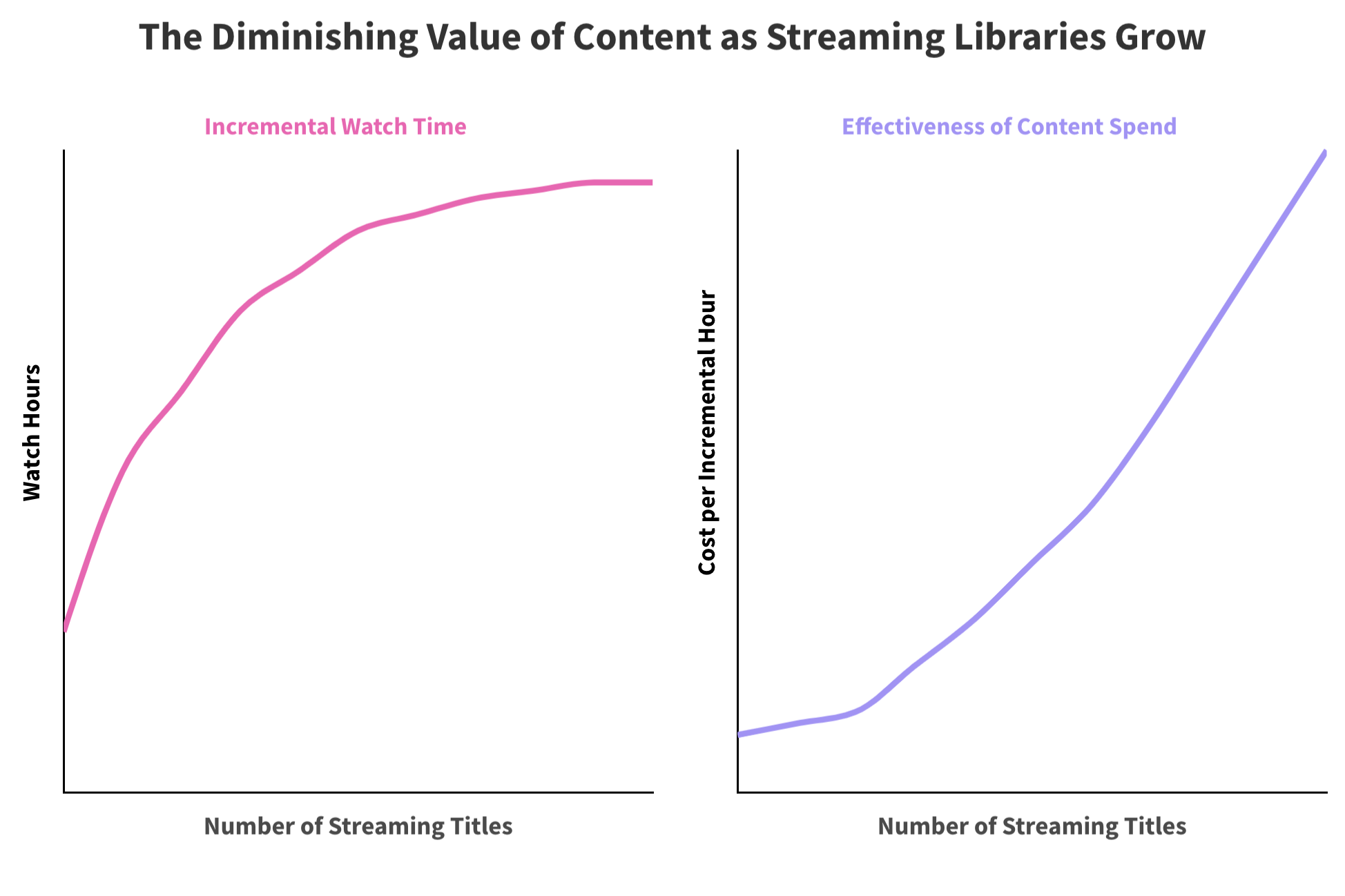
Daniel Parris – The Broken Economics of Streaming Services: A Stats Explainer
Read more: Daniel Parris – The Broken Economics of Streaming Services: A Stats Explainerhttps://www.statsignificant.com/p/the-broken-economics-of-streaming
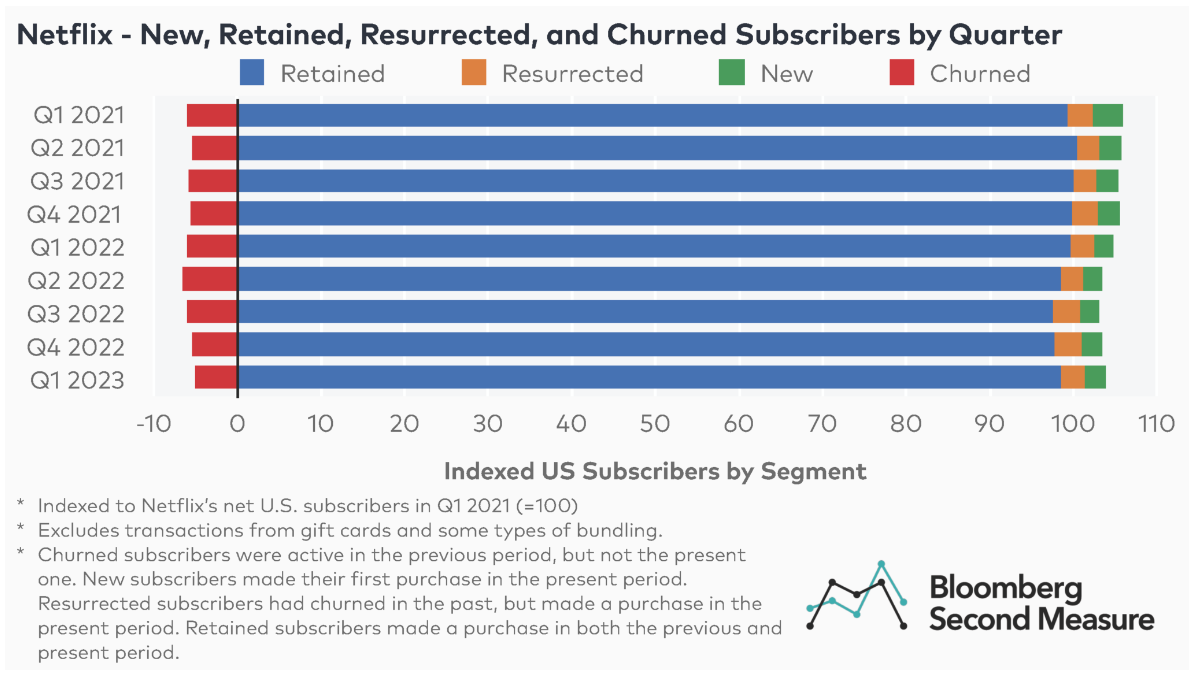
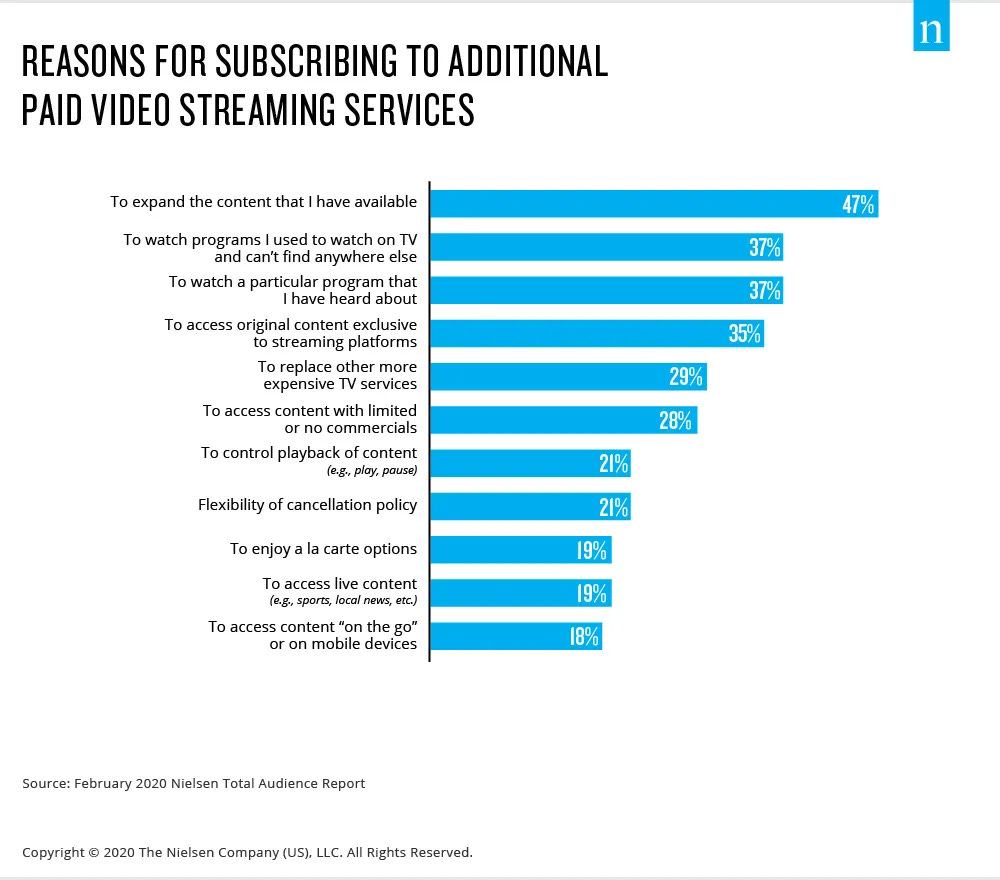
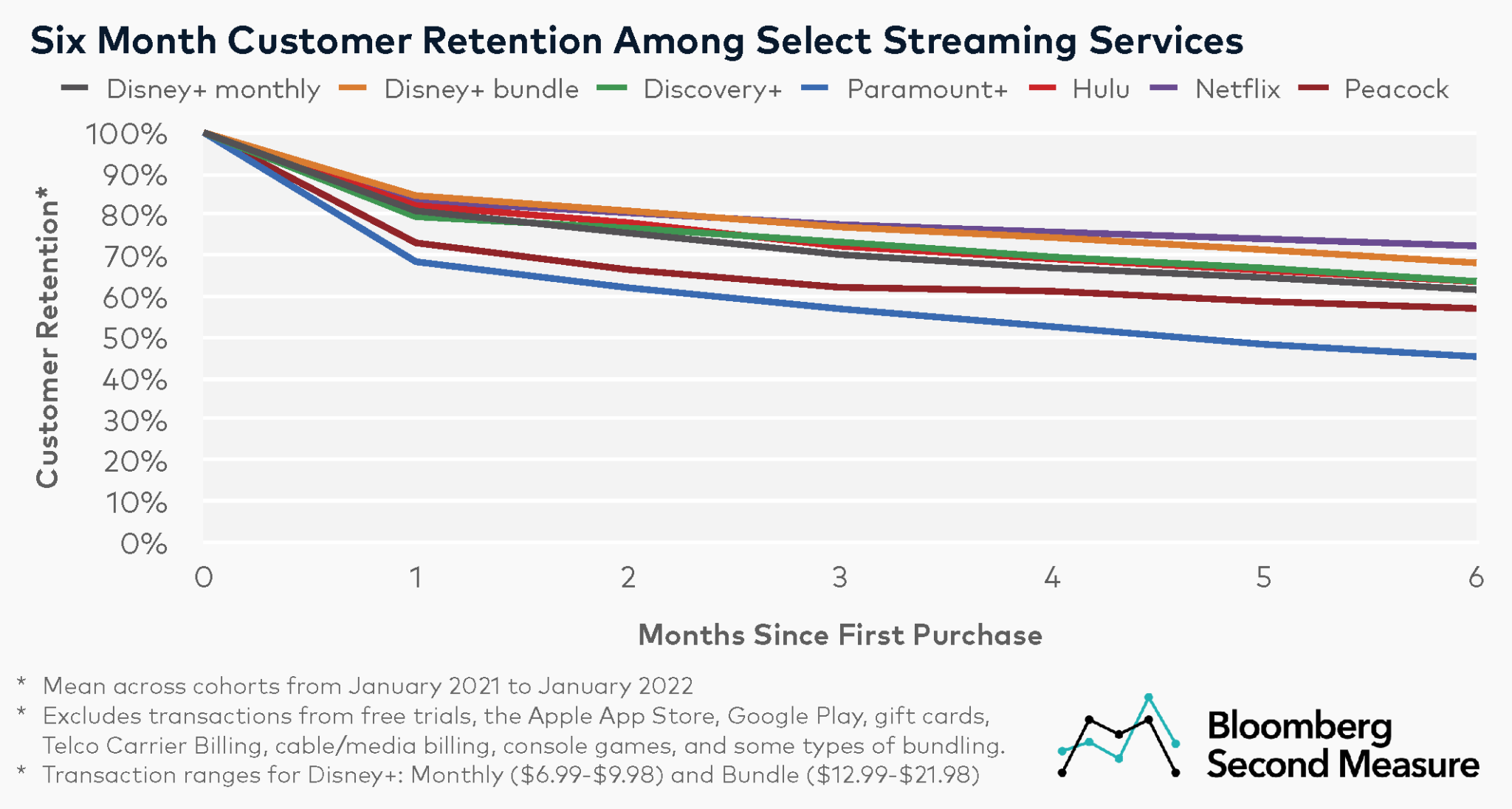
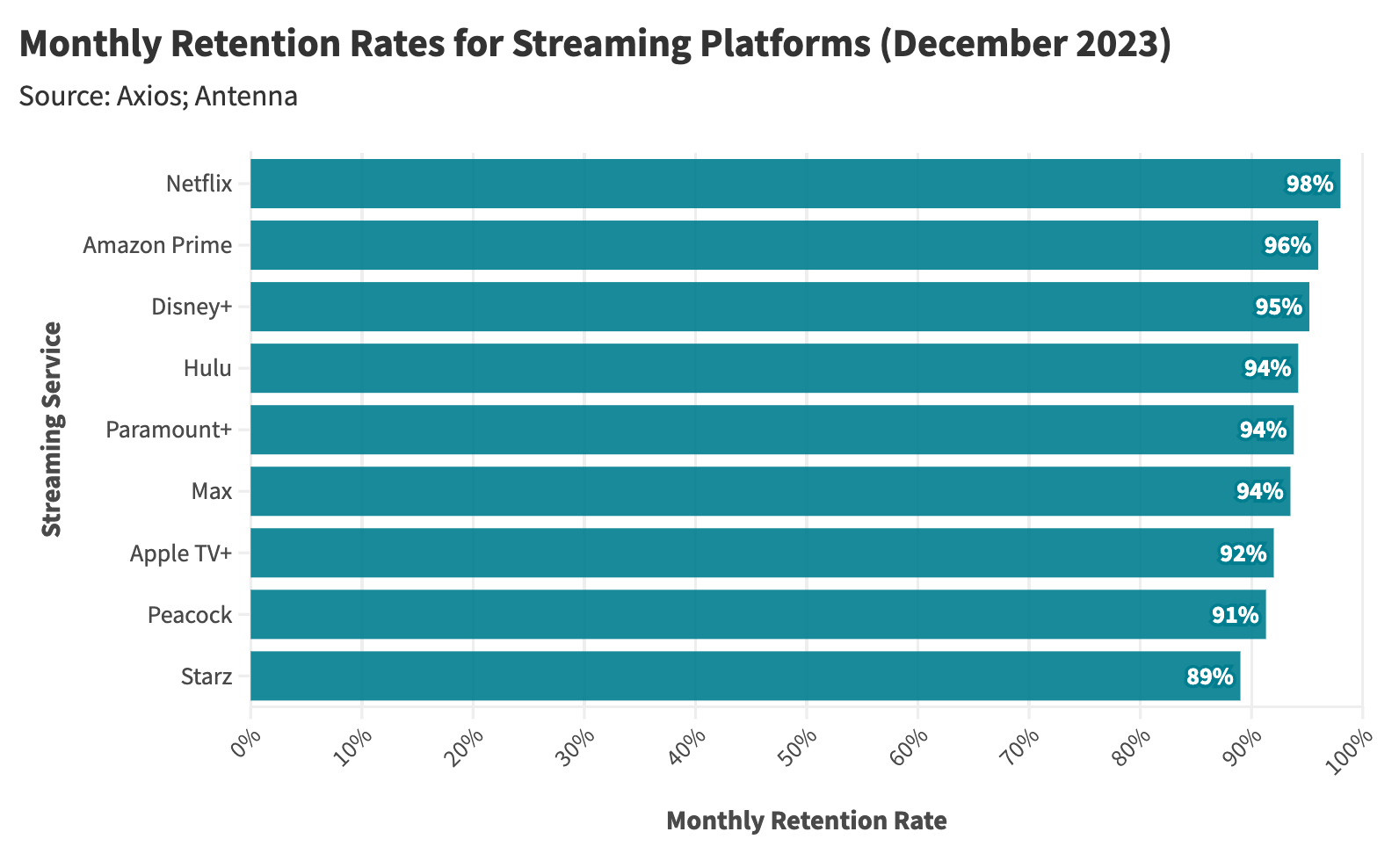
This report examines the financial instability in the streaming industry, focusing on the unsustainable economic models of platforms such as Paramount Plus.
Content Costs and Subscriber Retention
- Expenditure on Content: Streaming services invest heavily in content creation and acquisition to attract subscribers.
- Diminishing Returns: The escalating costs lead to diminishing returns as subscriber growth plateaus.
Competitive Landscape
- Continuous Production: High competition forces continuous, expensive content production to retain subscribers.
Future Projections
- Cable TV Model: The industry may shift towards models resembling traditional cable TV, incorporating advertising, subscription bundling, and higher prices to achieve financial sustainability.
NEWS TV NEWS
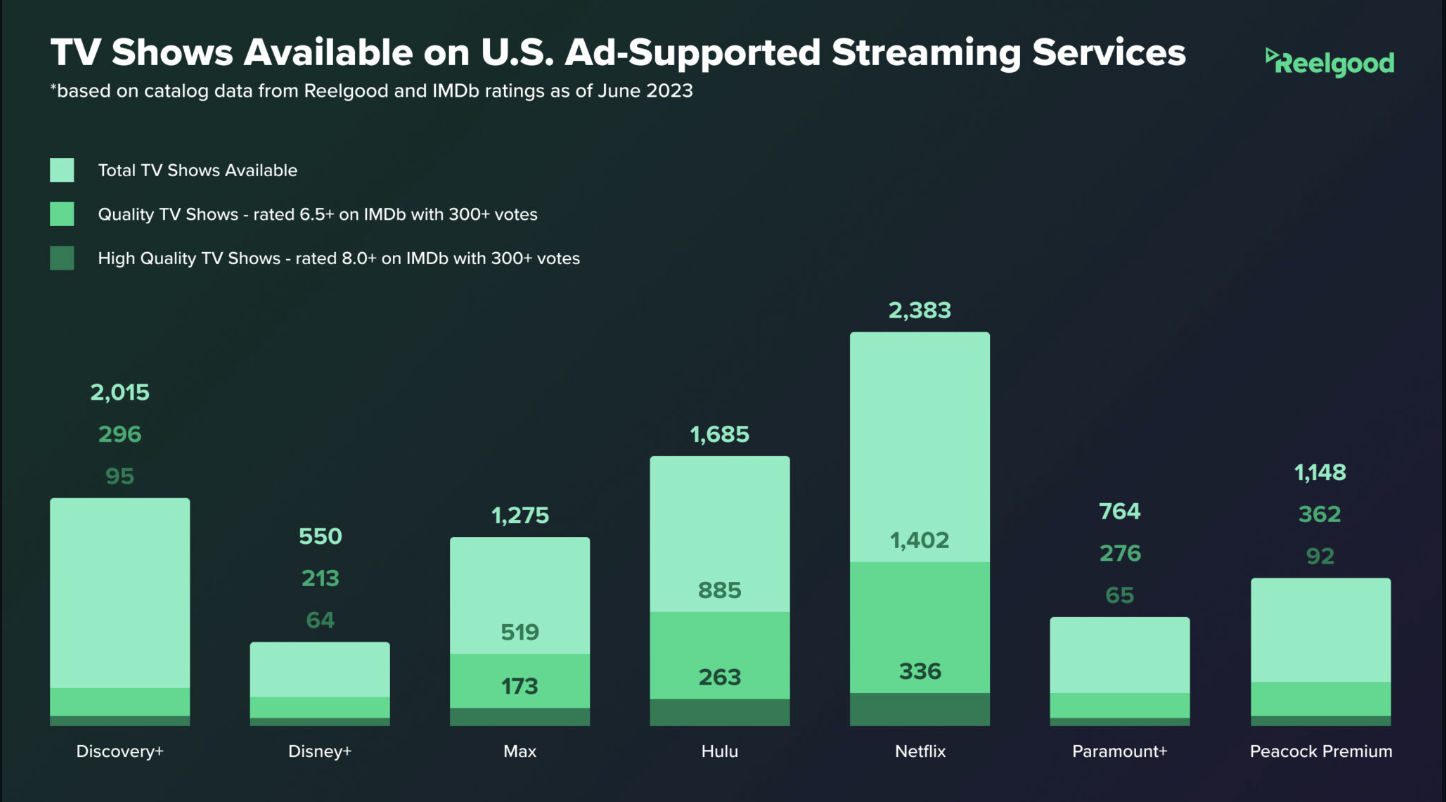
Hollywood’s Top TV Execs Are Happy About The Death Of Peak TV – Here’s Whyhttps://www.slashfilm.com/1593571/peak-tv-dead-hollywood-top-tv-execs-happy/
- Streaming services weren’t required to reveal their subscription numbers or actual viewership
- Shows just needed to look good on paper for investors and stockholders.
- Creators and actors soon learned they weren’t getting paid beyond an initial flat fee; royalties were now gone.
- 600 shows at once wasn’t good for anyone
- Thanks to the strikes, it all came crashing down

-
RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program
Read more: RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program5.10 of this tool includes excellent tools to clean up cr2 and cr3 used on set to support HDRI processing.
Converting raw to AcesCG 32 bit tiffs with metadata. -
Python and TCL: Tips and Tricks for Foundry Nuke
Read more: Python and TCL: Tips and Tricks for Foundry Nukewww.andreageremia.it/tutorial_python_tcl.html
https://www.gatimedia.co.uk/list-of-knobs-2

https://learn.foundry.com/nuke/developers/63/ndkdevguide/knobs-and-handles/knobtypes.html
http://www.andreageremia.it/tutorial_python_tcl.html
http://thoughtvfx.blogspot.com/2012/12/nuke-tcl-tips.html
Check final image quality
https://www.compositingpro.com/tech-check-compositing-shot-in-nuke/Local copy:
http://pixelsham.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/compositing_pro_tech_check_nuke_script.nkNuke tcl procedures
https://www.gatimedia.co.uk/nuke-tcl-proceduresKnobs
https://learn.foundry.com/nuke/developers/63/ndkdevguide/knobs-and-handles/knobtypes.html
(more…) -
Hunyuan video-to-video
Read more: Hunyuan video-to-videoThe open-source community has figured out how to run Hunyuan V2V using LoRAs.
You’ll need to install Kijai’s ComfyUI-HunyuanLoom and LoRAs, which you can either train yourself or find on Civitai.
1) you’ll need HunyuanLoom, after install, workflow found in the repo.
https://github.com/logtd/ComfyUI-HunyuanLoom
2) John Wick lora found here.
https://civitai.com/models/1131159/john-wick-hunyuan-video-lora
-
Advanced Computer Vision with Python OpenCV and Mediapipe
Read more: Advanced Computer Vision with Python OpenCV and Mediapipehttps://www.freecodecamp.org/news/advanced-computer-vision-with-python
https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/how-to-use-opencv-and-python-for-computer-vision-and-ai
Working for a VFX (Visual Effects) studio provides numerous opportunities to leverage the power of Python and OpenCV for various tasks. OpenCV is a versatile computer vision library that can be applied to many aspects of the VFX pipeline. Here’s a detailed list of opportunities to take advantage of Python and OpenCV in a VFX studio:
- Image and Video Processing:
- Preprocessing: Python and OpenCV can be used for tasks like resizing, color correction, noise reduction, and frame interpolation to prepare images and videos for further processing.
- Format Conversion: Convert between different image and video formats using OpenCV’s capabilities.
- Tracking and Matchmoving:
- Feature Detection and Tracking: Utilize OpenCV to detect and track features in image sequences, which is essential for matchmoving tasks to integrate computer-generated elements into live-action footage.
- Rotoscoping and Masking:
- Segmentation and Masking: Use OpenCV for creating and manipulating masks and alpha channels for various VFX tasks, like isolating objects or characters from their backgrounds.
- Camera Calibration:
- Intrinsic and Extrinsic Calibration: Python and OpenCV can help calibrate cameras for accurate 3D scene reconstruction and camera tracking.
- 3D Scene Reconstruction:
- Stereoscopy: Use OpenCV to process stereoscopic image pairs for creating 3D depth maps and generating realistic 3D scenes.
- Structure from Motion (SfM): Implement SfM techniques to create 3D models from 2D image sequences.
- Green Screen and Blue Screen Keying:
- Chroma Keying: Implement advanced keying algorithms using OpenCV to seamlessly integrate actors and objects into virtual environments.
- Particle and Fluid Simulations:
- Particle Tracking: Utilize OpenCV to track and manipulate particles in fluid simulations for more realistic visual effects.
- Motion Analysis:
- Optical Flow: Implement optical flow algorithms to analyze motion patterns in footage, useful for creating dynamic VFX elements that follow the motion of objects.
- Virtual Set Extension:
- Camera Projection: Use camera calibration techniques to project virtual environments onto physical sets, extending the visual scope of a scene.
- Color Grading:
- Color Correction: Implement custom color grading algorithms to match the color tones and moods of different shots.
- Automated QC (Quality Control):
- Artifact Detection: Develop Python scripts to automatically detect and flag visual artifacts like noise, flicker, or compression artifacts in rendered frames.
- Data Analysis and Visualization:
- Performance Metrics: Use Python to analyze rendering times and optimize the rendering process.
- Data Visualization: Generate graphs and charts to visualize render farm usage, project progress, and resource allocation.
- Automating Repetitive Tasks:
- Batch Processing: Automate repetitive tasks like resizing images, applying filters, or converting file formats across multiple shots.
- Machine Learning Integration:
- Object Detection: Integrate machine learning models (using frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch) to detect and track specific objects or elements within scenes.
- Pipeline Integration:
- Custom Tools: Develop Python scripts and tools to integrate OpenCV-based processes seamlessly into the studio’s pipeline.
- Real-time Visualization:
- Live Previsualization: Implement real-time OpenCV-based visualizations to aid decision-making during the preproduction stage.
- VR and AR Integration:
- Augmented Reality: Use Python and OpenCV to integrate virtual elements into real-world footage, creating compelling AR experiences.
- Camera Effects:
- Lens Distortion: Correct lens distortions and apply various camera effects using OpenCV, contributing to the desired visual style.
Interpolating frames from an EXR sequence using OpenCV can be useful when you have only every second frame of a final render and you want to create smoother motion by generating intermediate frames. However, keep in mind that interpolating frames might not always yield perfect results, especially if there are complex changes between frames. Here’s a basic example of how you might use OpenCV to achieve this:
import cv2 import numpy as np import os # Replace with the path to your EXR frames exr_folder = "path_to_exr_frames" # Replace with the appropriate frame extension and naming convention frame_template = "frame_{:04d}.exr" # Define the range of frame numbers you have start_frame = 1 end_frame = 100 step = 2 # Define the output folder for interpolated frames output_folder = "output_interpolated_frames" os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True) # Loop through the frame range and interpolate for frame_num in range(start_frame, end_frame + 1, step): frame_path = os.path.join(exr_folder, frame_template.format(frame_num)) next_frame_path = os.path.join(exr_folder, frame_template.format(frame_num + step)) if os.path.exists(frame_path) and os.path.exists(next_frame_path): frame = cv2.imread(frame_path, cv2.IMREAD_ANYDEPTH | cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) next_frame = cv2.imread(next_frame_path, cv2.IMREAD_ANYDEPTH | cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # Interpolate frames using simple averaging interpolated_frame = (frame + next_frame) / 2 # Save interpolated frame output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, frame_template.format(frame_num)) cv2.imwrite(output_path, interpolated_frame) print(f"Interpolated frame {frame_num}") # alternatively: print("Interpolated frame {}".format(frame_num))Please note the following points:
- The above example uses simple averaging to interpolate frames. More advanced interpolation methods might provide better results, such as motion-based algorithms like optical flow-based interpolation.
- EXR files can store high dynamic range (HDR) data, so make sure to use cv2.IMREAD_ANYDEPTH flag when reading these files.
- OpenCV might not support EXR format directly. You might need to use a library like exr to read and manipulate EXR files, and then convert them to OpenCV-compatible formats.
- Consider the characteristics of your specific render when using interpolation. If there are large changes between frames, the interpolation might lead to artifacts.
- Experiment with different interpolation methods and parameters to achieve the desired result.
- For a more advanced and accurate interpolation, you might need to implement or use existing algorithms that take into account motion estimation and compensation.
- Image and Video Processing:
-
Robert Alton on naive realism and quantum mechanics
Read more: Robert Alton on naive realism and quantum mechanicshttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e-Fo_k7RC8g
Any description of the universe is a description of the instrument you used to analyze the universe. Instruments including our brain.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.





