COMPOSITION
DESIGN
-
AI MidJourney – creating images with AI
Read more: AI MidJourney – creating images with AIhttps://www.deviantart.com/tag/midjourney
https://boingboing.net/2022/03/24/midjourney-sharpens-style-of-ai-art.html
https://www.resetera.com/threads/midjourney-is-lighting-up-the-ai-generated-art-community.586463/
https://www.artstation.com/artwork/G8Lead
Images courtesy of Midjourney’s users























COLOR
-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction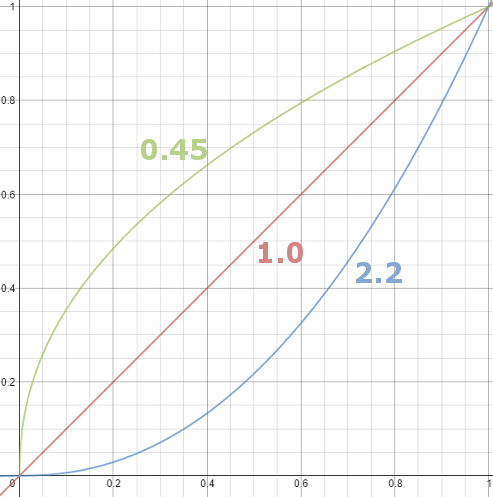
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.Our eyes, different camera or video recorder devices do not correctly capture luminance. (they are not linear)
Different display devices (monitor, phone screen, TV) do not display luminance correctly neither. So, one needs to correct them, therefore the gamma correction function.The human perception of brightness, under common illumination conditions (not pitch black nor blindingly bright), follows an approximate power function (note: no relation to the gamma function), with greater sensitivity to relative differences between darker tones than between lighter ones, consistent with the Stevens’ power law for brightness perception. If images are not gamma-encoded, they allocate too many bits or too much bandwidth to highlights that humans cannot differentiate, and too few bits or too little bandwidth to shadow values that humans are sensitive to and would require more bits/bandwidth to maintain the same visual quality.
https://blog.amerlux.com/4-things-architects-should-know-about-lumens-vs-perceived-brightness/
cones manage color receptivity, rods determine how large our pupils should be. The larger (more dilated) our pupils are, the more light enters our eyes. In dark situations, our rods dilate our pupils so we can see better. This impacts how we perceive brightness.
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
A gamma encoded image has to have “gamma correction” applied when it is viewed — which effectively converts it back into light from the original scene. In other words, the purpose of gamma encoding is for recording the image — not for displaying the image. Fortunately this second step (the “display gamma”) is automatically performed by your monitor and video card. The following diagram illustrates how all of this fits together:
Display gamma
The display gamma can be a little confusing because this term is often used interchangeably with gamma correction, since it corrects for the file gamma. This is the gamma that you are controlling when you perform monitor calibration and adjust your contrast setting. Fortunately, the industry has converged on a standard display gamma of 2.2, so one doesn’t need to worry about the pros/cons of different values.Gamma encoding of images is used to optimize the usage of bits when encoding an image, or bandwidth used to transport an image, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and color. Human response to luminance is also biased. Especially sensible to dark areas.
Thus, the human visual system has a non-linear response to the power of the incoming light, so a fixed increase in power will not have a fixed increase in perceived brightness.
We perceive a value as half bright when it is actually 18% of the original intensity not 50%. As such, our perception is not linear.You probably already know that a pixel can have any ‘value’ of Red, Green, and Blue between 0 and 255, and you would therefore think that a pixel value of 127 would appear as half of the maximum possible brightness, and that a value of 64 would represent one-quarter brightness, and so on. Well, that’s just not the case.
Pixar Color Management
https://renderman.pixar.com/color-management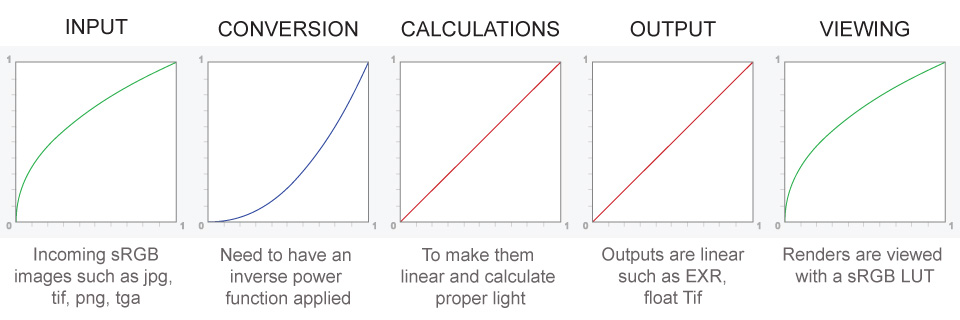
– Why do we need linear gamma?
Because light works linearly and therefore only works properly when it lights linear values.– Why do we need to view in sRGB?
Because the resulting linear image in not suitable for viewing, but contains all the proper data. Pixar’s IT viewer can compensate by showing the rendered image through a sRGB look up table (LUT), which is identical to what will be the final image after the sRGB gamma curve is applied in post.This would be simple enough if every software would play by the same rules, but they don’t. In fact, the default gamma workflow for many 3D software is incorrect. This is where the knowledge of a proper imaging workflow comes in to save the day.
Cathode-ray tubes have a peculiar relationship between the voltage applied to them, and the amount of light emitted. It isn’t linear, and in fact it follows what’s called by mathematicians and other geeks, a ‘power law’ (a number raised to a power). The numerical value of that power is what we call the gamma of the monitor or system.
Thus. Gamma describes the nonlinear relationship between the pixel levels in your computer and the luminance of your monitor (the light energy it emits) or the reflectance of your prints. The equation is,
Luminance = C * value^gamma + black level
– C is set by the monitor Contrast control.
– Value is the pixel level normalized to a maximum of 1. For an 8 bit monitor with pixel levels 0 – 255, value = (pixel level)/255.
– Black level is set by the (misnamed) monitor Brightness control. The relationship is linear if gamma = 1. The chart illustrates the relationship for gamma = 1, 1.5, 1.8 and 2.2 with C = 1 and black level = 0.
Gamma affects middle tones; it has no effect on black or white. If gamma is set too high, middle tones appear too dark. Conversely, if it’s set too low, middle tones appear too light.
The native gamma of monitors – the relationship between grid voltage and luminance – is typically around 2.5, though it can vary considerably. This is well above any of the display standards, so you must be aware of gamma and correct it.
A display gamma of 2.2 is the de facto standard for the Windows operating system and the Internet-standard sRGB color space.
The old standard for Mcintosh and prepress file interchange is 1.8. It is now 2.2 as well.
Video cameras have gammas of approximately 0.45 – the inverse of 2.2. The viewing or system gamma is the product of the gammas of all the devices in the system – the image acquisition device (film+scanner or digital camera), color lookup table (LUT), and monitor. System gamma is typically between 1.1 and 1.5. Viewing flare and other factor make images look flat at system gamma = 1.0.
Most laptop LCD screens are poorly suited for critical image editing because gamma is extremely sensitive to viewing angle.
More about screens
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
CRT Monitors. Due to an odd bit of engineering luck, the native gamma of a CRT is 2.5 — almost the inverse of our eyes. Values from a gamma-encoded file could therefore be sent straight to the screen and they would automatically be corrected and appear nearly OK. However, a small gamma correction of ~1/1.1 needs to be applied to achieve an overall display gamma of 2.2. This is usually already set by the manufacturer’s default settings, but can also be set during monitor calibration.
LCD Monitors. LCD monitors weren’t so fortunate; ensuring an overall display gamma of 2.2 often requires substantial corrections, and they are also much less consistent than CRT’s. LCDs therefore require something called a look-up table (LUT) in order to ensure that input values are depicted using the intended display gamma (amongst other things). See the tutorial on monitor calibration: look-up tables for more on this topic.
About black level (brightness). Your monitor’s brightness control (which should actually be called black level) can be adjusted using the mostly black pattern on the right side of the chart. This pattern contains two dark gray vertical bars, A and B, which increase in luminance with increasing gamma. (If you can’t see them, your black level is way low.) The left bar (A) should be just above the threshold of visibility opposite your chosen gamma (2.2 or 1.8) – it should be invisible where gamma is lower by about 0.3. The right bar (B) should be distinctly visible: brighter than (A), but still very dark. This chart is only for monitors; it doesn’t work on printed media.
The 1.8 and 2.2 gray patterns at the bottom of the image represent a test of monitor quality and calibration. If your monitor is functioning properly and calibrated to gamma = 2.2 or 1.8, the corresponding pattern will appear smooth neutral gray when viewed from a distance. Any waviness, irregularity, or color banding indicates incorrect monitor calibration or poor performance.
Another test to see whether one’s computer monitor is properly hardware adjusted and can display shadow detail in sRGB images properly, they should see the left half of the circle in the large black square very faintly but the right half should be clearly visible. If not, one can adjust their monitor’s contrast and/or brightness setting. This alters the monitor’s perceived gamma. The image is best viewed against a black background.
This procedure is not suitable for calibrating or print-proofing a monitor. It can be useful for making a monitor display sRGB images approximately correctly, on systems in which profiles are not used (for example, the Firefox browser prior to version 3.0 and many others) or in systems that assume untagged source images are in the sRGB colorspace.
On some operating systems running the X Window System, one can set the gamma correction factor (applied to the existing gamma value) by issuing the command xgamma -gamma 0.9 for setting gamma correction factor to 0.9, and xgamma for querying current value of that factor (the default is 1.0). In OS X systems, the gamma and other related screen calibrations are made through the System Preference
https://www.kinematicsoup.com/news/2016/6/15/gamma-and-linear-space-what-they-are-how-they-differ
Linear color space means that numerical intensity values correspond proportionally to their perceived intensity. This means that the colors can be added and multiplied correctly. A color space without that property is called ”non-linear”. Below is an example where an intensity value is doubled in a linear and a non-linear color space. While the corresponding numerical values in linear space are correct, in the non-linear space (gamma = 0.45, more on this later) we can’t simply double the value to get the correct intensity.
The need for gamma arises for two main reasons: The first is that screens have been built with a non-linear response to intensity. The other is that the human eye can tell the difference between darker shades better than lighter shades. This means that when images are compressed to save space, we want to have greater accuracy for dark intensities at the expense of lighter intensities. Both of these problems are resolved using gamma correction, which is to say the intensity of every pixel in an image is put through a power function. Specifically, gamma is the name given to the power applied to the image.
CRT screens, simply by how they work, apply a gamma of around 2.2, and modern LCD screens are designed to mimic that behavior. A gamma of 2.2, the reciprocal of 0.45, when applied to the brightened images will darken them, leaving the original image.
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
LIGHTING
-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. … Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
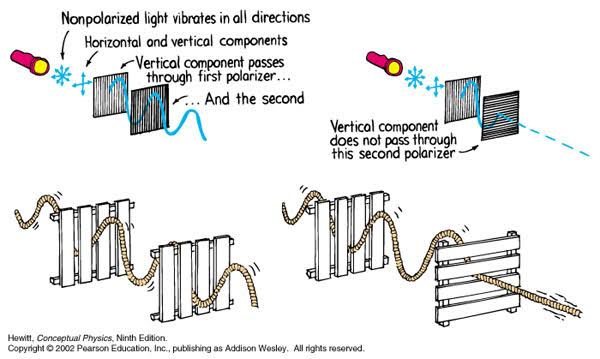
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
Light reflected from a non-metallic surface becomes polarized; this effect is maximum at Brewster’s angle, about 56° from the vertical for common glass.
A polarizer rotated to pass only light polarized in the direction perpendicular to the reflected light will absorb much of it. This absorption allows glare reflected from, for example, a body of water or a road to be reduced. Reflections from shiny surfaces (e.g. vegetation, sweaty skin, water surfaces, glass) are also reduced. This allows the natural color and detail of what is beneath to come through. Reflections from a window into a dark interior can be much reduced, allowing it to be seen through. (The same effects are available for vision by using polarizing sunglasses.)
www.physicsclassroom.com/class/light/u12l1e.cfm
Some of the light coming from the sky is polarized (bees use this phenomenon for navigation). The electrons in the air molecules cause a scattering of sunlight in all directions. This explains why the sky is not dark during the day. But when looked at from the sides, the light emitted from a specific electron is totally polarized.[3] Hence, a picture taken in a direction at 90 degrees from the sun can take advantage of this polarization. Use of a polarizing filter, in the correct direction, will filter out the polarized component of skylight, darkening the sky; the landscape below it, and clouds, will be less affected, giving a photograph with a darker and more dramatic sky, and emphasizing the clouds.

There are two types of polarizing filters readily available, linear and “circular”, which have exactly the same effect photographically. But the metering and auto-focus sensors in certain cameras, including virtually all auto-focus SLRs, will not work properly with linear polarizers because the beam splitters used to split off the light for focusing and metering are polarization-dependent.
Polarizing filters reduce the light passed through to the film or sensor by about one to three stops (2–8×) depending on how much of the light is polarized at the filter angle selected. Auto-exposure cameras will adjust for this by widening the aperture, lengthening the time the shutter is open, and/or increasing the ASA/ISO speed of the camera.
www.adorama.com/alc/nd-filter-vs-polarizer-what%25e2%2580%2599s-the-difference
Neutral Density (ND) filters help control image exposure by reducing the light that enters the camera so that you can have more control of your depth of field and shutter speed. Polarizers or polarizing filters work in a similar way, but the difference is that they selectively let light waves of a certain polarization pass through. This effect helps create more vivid colors in an image, as well as manage glare and reflections from water surfaces. Both are regarded as some of the best filters for landscape and travel photography as they reduce the dynamic range in high-contrast images, thus enabling photographers to capture more realistic and dramatic sceneries.
shopfelixgray.com/blog/polarized-vs-non-polarized-sunglasses/
www.eyebuydirect.com/blog/difference-polarized-nonpolarized-sunglasses/
-
Debayer – A free command line tool to convert camera raw images into scene-linear exr
Read more: Debayer – A free command line tool to convert camera raw images into scene-linear exr
https://github.com/jedypod/debayer
The only required dependency is oiiotool. However other “debayer engines” are also supported.
- OpenImageIO – oiiotool is used for converting debayered tif images to exr.
- Debayer Engines
- RawTherapee – Powerful raw development software used to decode raw images. High quality, good selection of debayer algorithms, and more advanced raw processing like chromatic aberration removal.
- LibRaw – dcraw_emu commandline utility included with LibRaw. Optional alternative for debayer. Simple, fast and effective.
- Darktable – Uses darktable-cli plus an xmp config to process.
- vkdt – uses vkdt-cli to debayer. Pretty experimental still. Uses Vulkan for image processing. Stupidly fast. Pretty limited.
-
HDRI shooting and editing by Xuan Prada and Greg Zaal
Read more: HDRI shooting and editing by Xuan Prada and Greg Zaalwww.xuanprada.com/blog/2014/11/3/hdri-shooting
http://blog.gregzaal.com/2016/03/16/make-your-own-hdri/
http://blog.hdrihaven.com/how-to-create-high-quality-hdri/
Shooting checklist
- Full coverage of the scene (fish-eye shots)
- Backplates for look-development (including ground or floor)
- Macbeth chart for white balance
- Grey ball for lighting calibration
- Chrome ball for lighting orientation
- Basic scene measurements
- Material samples
- Individual HDR artificial lighting sources if required
Methodology
- Plant the tripod where the action happens, stabilise it and level it
- Set manual focus
- Set white balance
- Set ISO
- Set raw+jpg
- Set apperture
- Metering exposure
- Set neutral exposure
- Read histogram and adjust neutral exposure if necessary
- Shot slate (operator name, location, date, time, project code name, etc)
- Set auto bracketing
- Shot 5 to 7 exposures with 3 stops difference covering the whole environment
- Place the aromatic kit where the tripod was placed, and take 3 exposures. Keep half of the grey sphere hit by the sun and half in shade.
- Place the Macbeth chart 1m away from tripod on the floor and take 3 exposures
- Take backplates and ground/floor texture references
- Shoot reference materials
- Write down measurements of the scene, specially if you are shooting interiors.
- If shooting artificial lights take HDR samples of each individual lighting source.
Exposures starting point
- Day light sun visible ISO 100 F22
- Day light sun hidden ISO 100 F16
- Cloudy ISO 320 F16
- Sunrise/Sunset ISO 100 F11
- Interior well lit ISO 320 F16
- Interior ambient bright ISO 320 F10
- Interior bad light ISO 640 F10
- Interior ambient dark ISO 640 F8
- Low light situation ISO 640 F5
NOTE: The goal is to clean the initial individual brackets before or at merging time as much as possible.
This means:- keeping original shooting metadata
- de-fringing
- removing aberration (through camera lens data or automatically)
- at 32 bit
- in ACEScg (or ACES) wherever possible
Here are the tips for using the chromatic ball in VFX projects, written in English:
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/bellrodrigo_here-are-the-tips-for-using-the-chromatic-activity-7200950595438940160-AGBpTips for Using the Chromatic Ball in VFX Projects**
The chromatic ball is an invaluable tool in VFX work, helping to capture lighting and reflection data crucial for integrating CGI elements seamlessly. Here are some tips to maximize its effectiveness:
1. **Positioning**:
– Place the chromatic ball in the same lighting conditions as the main subject. Ensure it is visible in the camera frame but not obstructing the main action.
– Ideally, place the ball where the CGI elements will be integrated to match the lighting and reflections accurately.2. **Recording Reference Footage**:
– Capture reference footage of the chromatic ball at the beginning and end of each scene or lighting setup. This ensures you have consistent lighting data for the entire shoot.3. **Consistent Angles**:
– Use consistent camera angles and heights when recording the chromatic ball. This helps in comparing and matching lighting setups across different shots.4. **Combine with a Gray Ball**:
– Use a gray ball alongside the chromatic ball. The gray ball provides a neutral reference for exposure and color balance, complementing the chromatic ball’s reflection data.5. **Marking Positions**:
– Mark the position of the chromatic ball on the set to ensure consistency when shooting multiple takes or different camera angles.6. **Lighting Analysis**:
– Analyze the chromatic ball footage to understand the light sources, intensity, direction, and color temperature. This information is crucial for creating realistic CGI lighting and shadows.7. **Reflection Analysis**:
– Use the chromatic ball to capture the environment’s reflections. This helps in accurately reflecting the CGI elements within the same scene, making them blend seamlessly.8. **Use HDRI**:
– Capture High Dynamic Range Imagery (HDRI) of the chromatic ball. HDRI provides detailed lighting information and can be used to light CGI scenes with greater realism.9. **Communication with VFX Team**:
– Ensure that the VFX team is aware of the chromatic ball’s data and how it was captured. Clear communication ensures that the data is used effectively in post-production.10. **Post-Production Adjustments**:
– In post-production, use the chromatic ball data to adjust the CGI elements’ lighting and reflections. This ensures that the final output is visually cohesive and realistic. -
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.Our eyes, different camera or video recorder devices do not correctly capture luminance. (they are not linear)
Different display devices (monitor, phone screen, TV) do not display luminance correctly neither. So, one needs to correct them, therefore the gamma correction function.The human perception of brightness, under common illumination conditions (not pitch black nor blindingly bright), follows an approximate power function (note: no relation to the gamma function), with greater sensitivity to relative differences between darker tones than between lighter ones, consistent with the Stevens’ power law for brightness perception. If images are not gamma-encoded, they allocate too many bits or too much bandwidth to highlights that humans cannot differentiate, and too few bits or too little bandwidth to shadow values that humans are sensitive to and would require more bits/bandwidth to maintain the same visual quality.
https://blog.amerlux.com/4-things-architects-should-know-about-lumens-vs-perceived-brightness/
cones manage color receptivity, rods determine how large our pupils should be. The larger (more dilated) our pupils are, the more light enters our eyes. In dark situations, our rods dilate our pupils so we can see better. This impacts how we perceive brightness.
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
A gamma encoded image has to have “gamma correction” applied when it is viewed — which effectively converts it back into light from the original scene. In other words, the purpose of gamma encoding is for recording the image — not for displaying the image. Fortunately this second step (the “display gamma”) is automatically performed by your monitor and video card. The following diagram illustrates how all of this fits together:
Display gamma
The display gamma can be a little confusing because this term is often used interchangeably with gamma correction, since it corrects for the file gamma. This is the gamma that you are controlling when you perform monitor calibration and adjust your contrast setting. Fortunately, the industry has converged on a standard display gamma of 2.2, so one doesn’t need to worry about the pros/cons of different values.Gamma encoding of images is used to optimize the usage of bits when encoding an image, or bandwidth used to transport an image, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and color. Human response to luminance is also biased. Especially sensible to dark areas.
Thus, the human visual system has a non-linear response to the power of the incoming light, so a fixed increase in power will not have a fixed increase in perceived brightness.
We perceive a value as half bright when it is actually 18% of the original intensity not 50%. As such, our perception is not linear.You probably already know that a pixel can have any ‘value’ of Red, Green, and Blue between 0 and 255, and you would therefore think that a pixel value of 127 would appear as half of the maximum possible brightness, and that a value of 64 would represent one-quarter brightness, and so on. Well, that’s just not the case.
Pixar Color Management
https://renderman.pixar.com/color-management
– Why do we need linear gamma?
Because light works linearly and therefore only works properly when it lights linear values.– Why do we need to view in sRGB?
Because the resulting linear image in not suitable for viewing, but contains all the proper data. Pixar’s IT viewer can compensate by showing the rendered image through a sRGB look up table (LUT), which is identical to what will be the final image after the sRGB gamma curve is applied in post.This would be simple enough if every software would play by the same rules, but they don’t. In fact, the default gamma workflow for many 3D software is incorrect. This is where the knowledge of a proper imaging workflow comes in to save the day.
Cathode-ray tubes have a peculiar relationship between the voltage applied to them, and the amount of light emitted. It isn’t linear, and in fact it follows what’s called by mathematicians and other geeks, a ‘power law’ (a number raised to a power). The numerical value of that power is what we call the gamma of the monitor or system.
Thus. Gamma describes the nonlinear relationship between the pixel levels in your computer and the luminance of your monitor (the light energy it emits) or the reflectance of your prints. The equation is,
Luminance = C * value^gamma + black level
– C is set by the monitor Contrast control.
– Value is the pixel level normalized to a maximum of 1. For an 8 bit monitor with pixel levels 0 – 255, value = (pixel level)/255.
– Black level is set by the (misnamed) monitor Brightness control. The relationship is linear if gamma = 1. The chart illustrates the relationship for gamma = 1, 1.5, 1.8 and 2.2 with C = 1 and black level = 0.
Gamma affects middle tones; it has no effect on black or white. If gamma is set too high, middle tones appear too dark. Conversely, if it’s set too low, middle tones appear too light.
The native gamma of monitors – the relationship between grid voltage and luminance – is typically around 2.5, though it can vary considerably. This is well above any of the display standards, so you must be aware of gamma and correct it.
A display gamma of 2.2 is the de facto standard for the Windows operating system and the Internet-standard sRGB color space.
The old standard for Mcintosh and prepress file interchange is 1.8. It is now 2.2 as well.
Video cameras have gammas of approximately 0.45 – the inverse of 2.2. The viewing or system gamma is the product of the gammas of all the devices in the system – the image acquisition device (film+scanner or digital camera), color lookup table (LUT), and monitor. System gamma is typically between 1.1 and 1.5. Viewing flare and other factor make images look flat at system gamma = 1.0.
Most laptop LCD screens are poorly suited for critical image editing because gamma is extremely sensitive to viewing angle.
More about screens
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
CRT Monitors. Due to an odd bit of engineering luck, the native gamma of a CRT is 2.5 — almost the inverse of our eyes. Values from a gamma-encoded file could therefore be sent straight to the screen and they would automatically be corrected and appear nearly OK. However, a small gamma correction of ~1/1.1 needs to be applied to achieve an overall display gamma of 2.2. This is usually already set by the manufacturer’s default settings, but can also be set during monitor calibration.
LCD Monitors. LCD monitors weren’t so fortunate; ensuring an overall display gamma of 2.2 often requires substantial corrections, and they are also much less consistent than CRT’s. LCDs therefore require something called a look-up table (LUT) in order to ensure that input values are depicted using the intended display gamma (amongst other things). See the tutorial on monitor calibration: look-up tables for more on this topic.
About black level (brightness). Your monitor’s brightness control (which should actually be called black level) can be adjusted using the mostly black pattern on the right side of the chart. This pattern contains two dark gray vertical bars, A and B, which increase in luminance with increasing gamma. (If you can’t see them, your black level is way low.) The left bar (A) should be just above the threshold of visibility opposite your chosen gamma (2.2 or 1.8) – it should be invisible where gamma is lower by about 0.3. The right bar (B) should be distinctly visible: brighter than (A), but still very dark. This chart is only for monitors; it doesn’t work on printed media.
The 1.8 and 2.2 gray patterns at the bottom of the image represent a test of monitor quality and calibration. If your monitor is functioning properly and calibrated to gamma = 2.2 or 1.8, the corresponding pattern will appear smooth neutral gray when viewed from a distance. Any waviness, irregularity, or color banding indicates incorrect monitor calibration or poor performance.
Another test to see whether one’s computer monitor is properly hardware adjusted and can display shadow detail in sRGB images properly, they should see the left half of the circle in the large black square very faintly but the right half should be clearly visible. If not, one can adjust their monitor’s contrast and/or brightness setting. This alters the monitor’s perceived gamma. The image is best viewed against a black background.
This procedure is not suitable for calibrating or print-proofing a monitor. It can be useful for making a monitor display sRGB images approximately correctly, on systems in which profiles are not used (for example, the Firefox browser prior to version 3.0 and many others) or in systems that assume untagged source images are in the sRGB colorspace.
On some operating systems running the X Window System, one can set the gamma correction factor (applied to the existing gamma value) by issuing the command xgamma -gamma 0.9 for setting gamma correction factor to 0.9, and xgamma for querying current value of that factor (the default is 1.0). In OS X systems, the gamma and other related screen calibrations are made through the System Preference
https://www.kinematicsoup.com/news/2016/6/15/gamma-and-linear-space-what-they-are-how-they-differ
Linear color space means that numerical intensity values correspond proportionally to their perceived intensity. This means that the colors can be added and multiplied correctly. A color space without that property is called ”non-linear”. Below is an example where an intensity value is doubled in a linear and a non-linear color space. While the corresponding numerical values in linear space are correct, in the non-linear space (gamma = 0.45, more on this later) we can’t simply double the value to get the correct intensity.
The need for gamma arises for two main reasons: The first is that screens have been built with a non-linear response to intensity. The other is that the human eye can tell the difference between darker shades better than lighter shades. This means that when images are compressed to save space, we want to have greater accuracy for dark intensities at the expense of lighter intensities. Both of these problems are resolved using gamma correction, which is to say the intensity of every pixel in an image is put through a power function. Specifically, gamma is the name given to the power applied to the image.
CRT screens, simply by how they work, apply a gamma of around 2.2, and modern LCD screens are designed to mimic that behavior. A gamma of 2.2, the reciprocal of 0.45, when applied to the brightened images will darken them, leaving the original image.
Collections
| Explore posts
| Design And Composition
| Featured AI
Popular Searches
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.