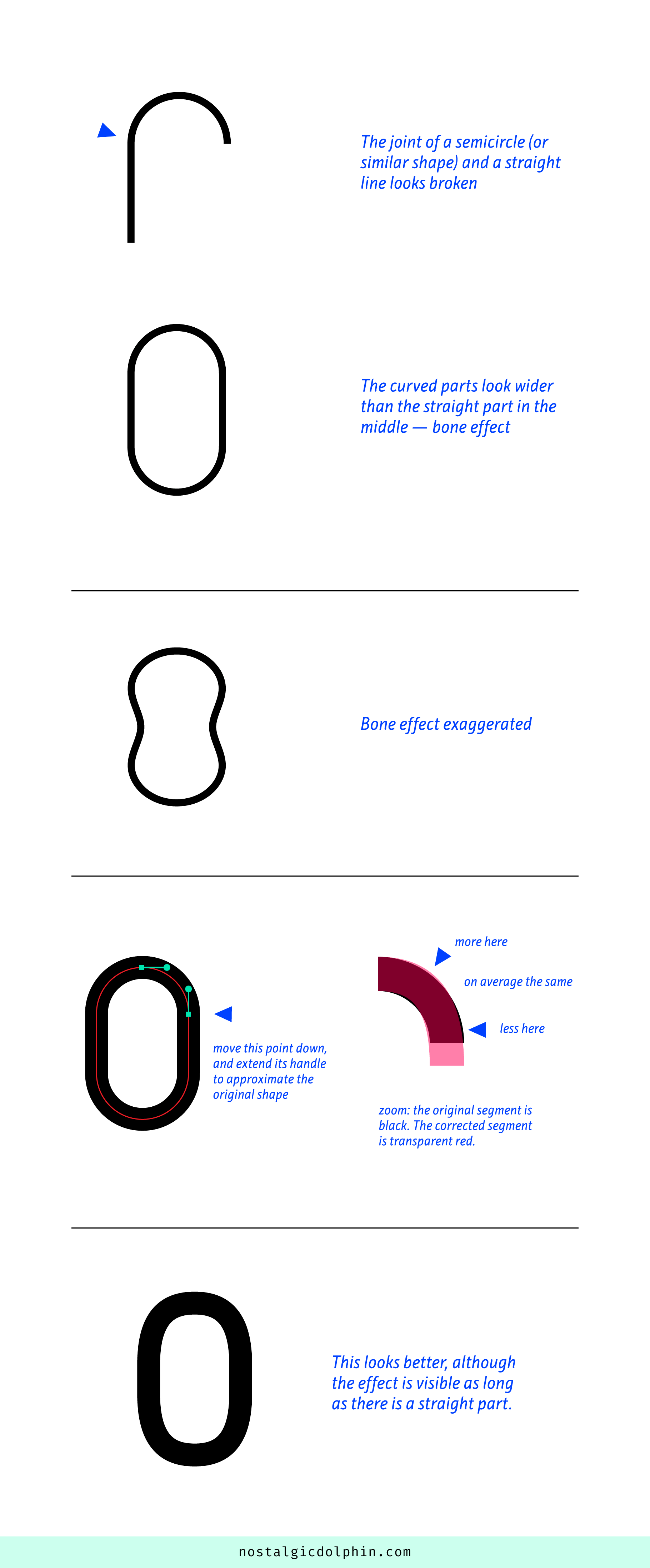
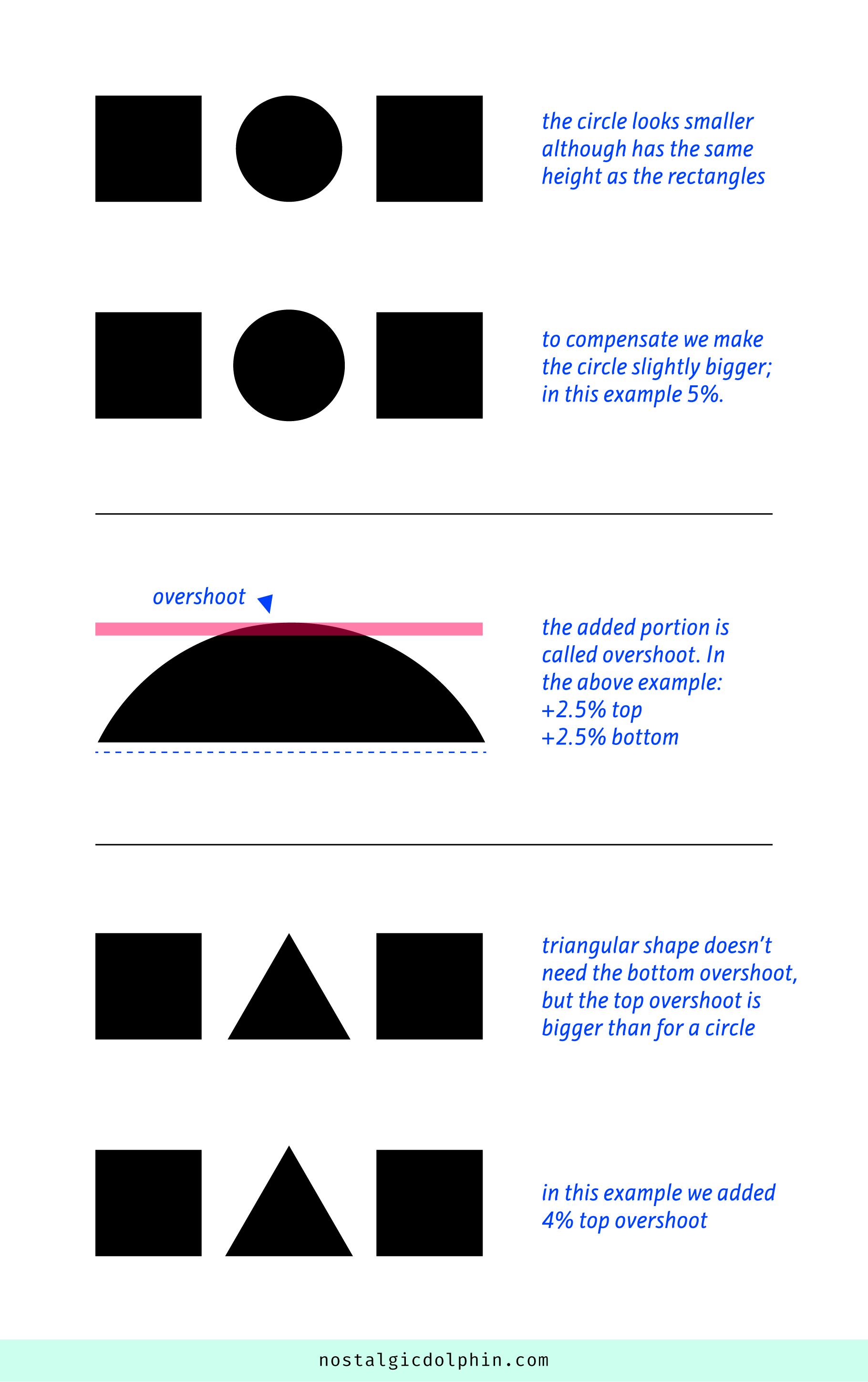
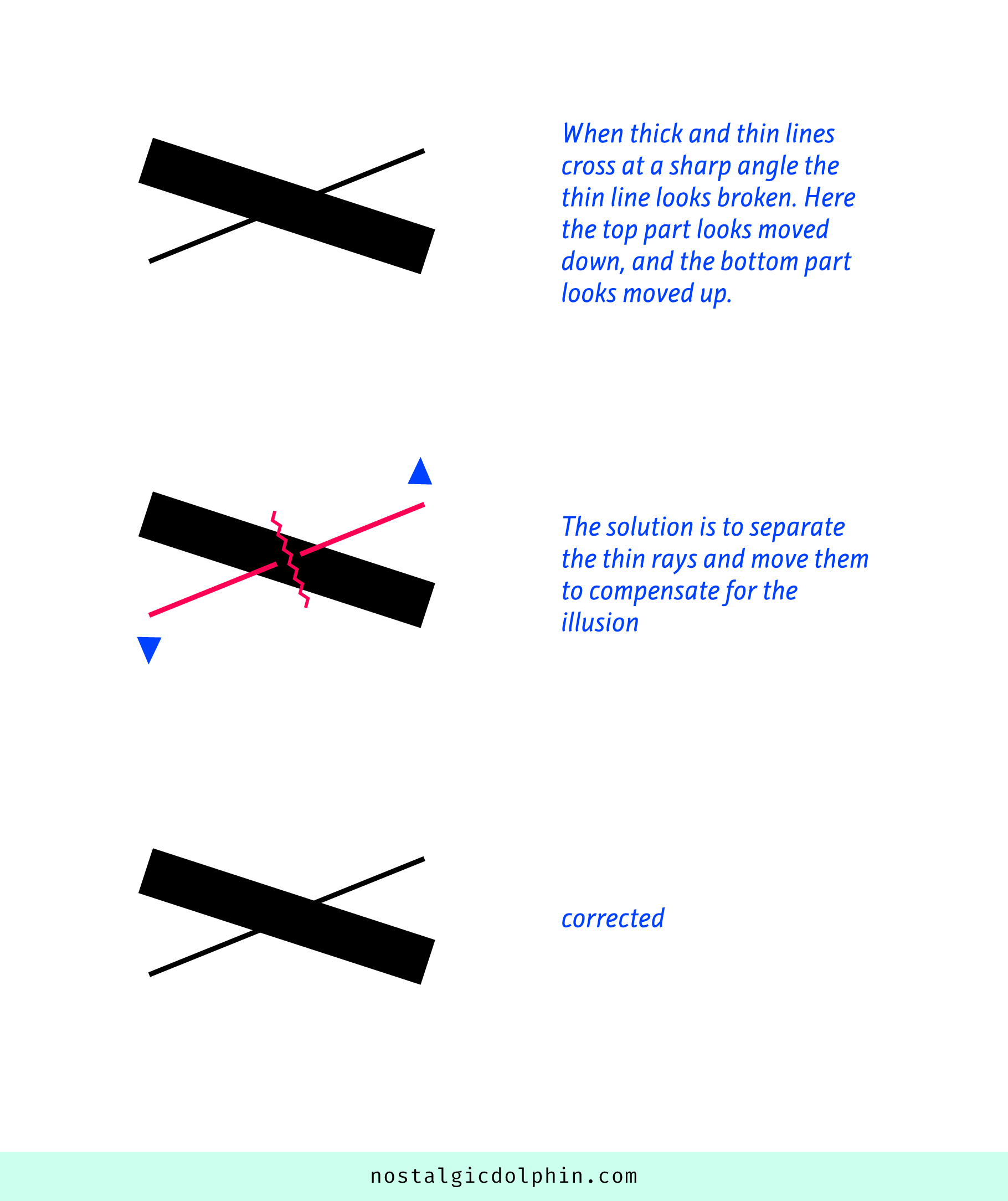
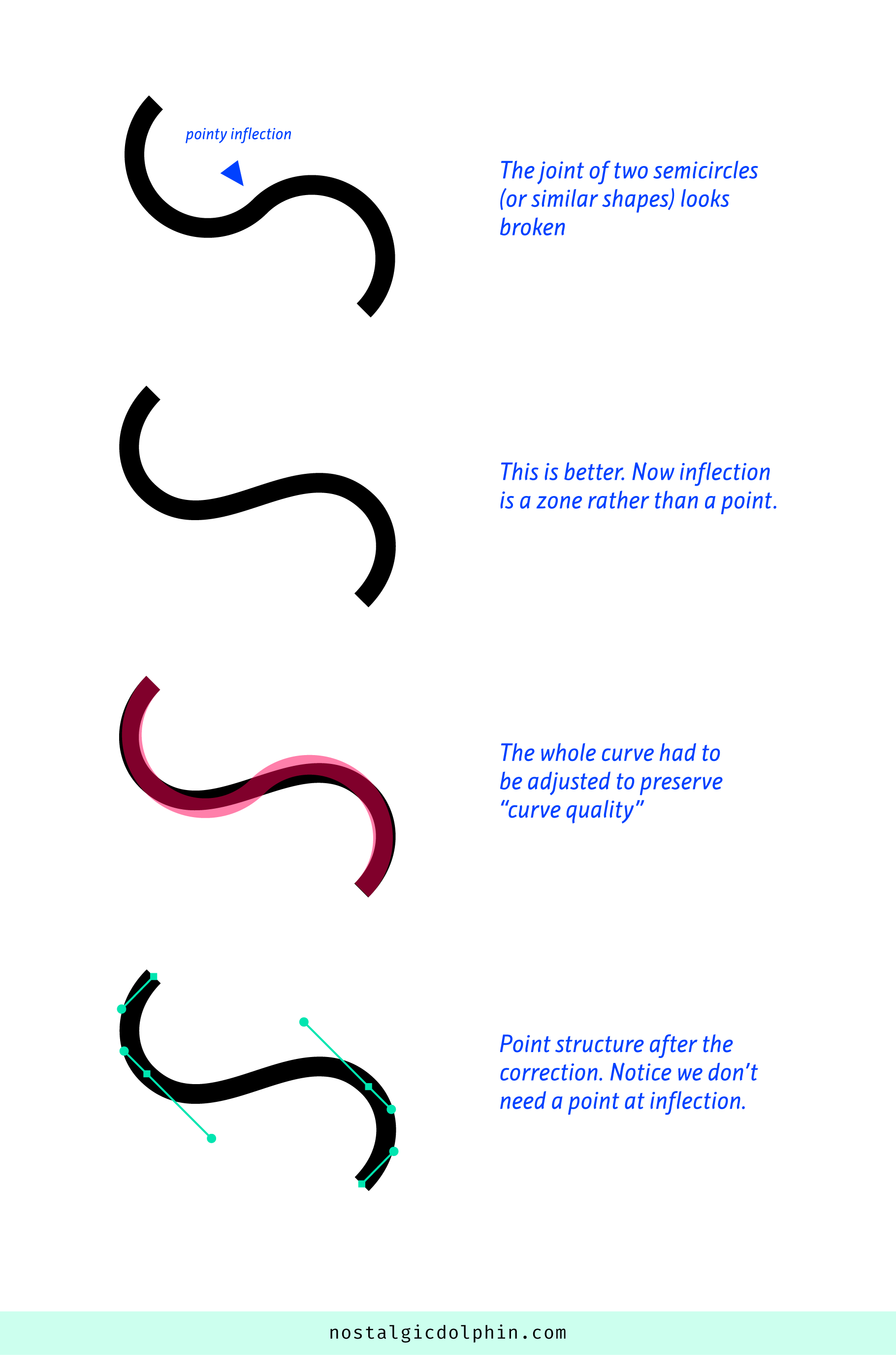COMPOSITION
-
StudioBinder – Roger Deakins on How to Choose a Camera Lens — Cinematography Composition Techniques
Read more: StudioBinder – Roger Deakins on How to Choose a Camera Lens — Cinematography Composition Techniqueshttps://www.studiobinder.com/blog/camera-lens-buying-guide/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/e-books/camera-lenses-explained-volume-1-ebook
-
HuggingFace ai-comic-factory – a FREE AI Comic Book Creator
Read more: HuggingFace ai-comic-factory – a FREE AI Comic Book Creatorhttps://huggingface.co/spaces/jbilcke-hf/ai-comic-factory
this is the epic story of a group of talented digital artists trying to overcame daily technical challenges to achieve incredibly photorealistic projects of monsters and aliens
DESIGN
-
Glenn Marshall – The Crow
Read more: Glenn Marshall – The CrowCreated with AI ‘Style Transfer’ processes to transform video footage into AI video art.
-
Mike Mitchell x Marvel x Mondo – Iconic portraits of Marvel’s huge stable of heroes and villains
Read more: Mike Mitchell x Marvel x Mondo – Iconic portraits of Marvel’s huge stable of heroes and villainshttps://mondoshop.com/blogs/gallery/16910155-mike-mitchell-x-marvel-x-mondo
https://time.com/69659/marvel-comics-mike-mitchell-artist-portraits/
-
Kristina Kashtanova – “This is how GPT-4 sees and hears itself”
Read more: Kristina Kashtanova – “This is how GPT-4 sees and hears itself”“I used GPT-4 to describe itself. Then I used its description to generate an image, a video based on this image and a soundtrack.
Tools I used: GPT-4, Midjourney, Kaiber AI, Mubert, RunwayML
This is the description I used that GPT-4 had of itself as a prompt to text-to-image, image-to-video, and text-to-music. I put the video and sound together in RunwayML.
GPT-4 described itself as: “Imagine a sleek, metallic sphere with a smooth surface, representing the vast knowledge contained within the model. The sphere emits a soft, pulsating glow that shifts between various colors, symbolizing the dynamic nature of the AI as it processes information and generates responses. The sphere appears to float in a digital environment, surrounded by streams of data and code, reflecting the complex algorithms and computing power behind the AI”
-
Disco Diffusion V4.1 Google Colab, Dall-E, Starryai – creating images with AI
Read more: Disco Diffusion V4.1 Google Colab, Dall-E, Starryai – creating images with AIDisco Diffusion (DD) is a Google Colab Notebook which leverages an AI Image generating technique called CLIP-Guided Diffusion to allow you to create compelling and beautiful images from just text inputs. Created by Somnai, augmented by Gandamu, and building on the work of RiversHaveWings, nshepperd, and many others.
Phone app: https://www.starryai.com/
docs.google.com/document/d/1l8s7uS2dGqjztYSjPpzlmXLjl5PM3IGkRWI3IiCuK7g
colab.research.google.com/drive/1sHfRn5Y0YKYKi1k-ifUSBFRNJ8_1sa39
Colab, or “Colaboratory”, allows you to write and execute Python in your browser, with
– Zero configuration required
– Access to GPUs free of charge
– Easy sharinghttps://80.lv/articles/a-beautiful-roman-villa-made-with-disco-diffusion-5-2/
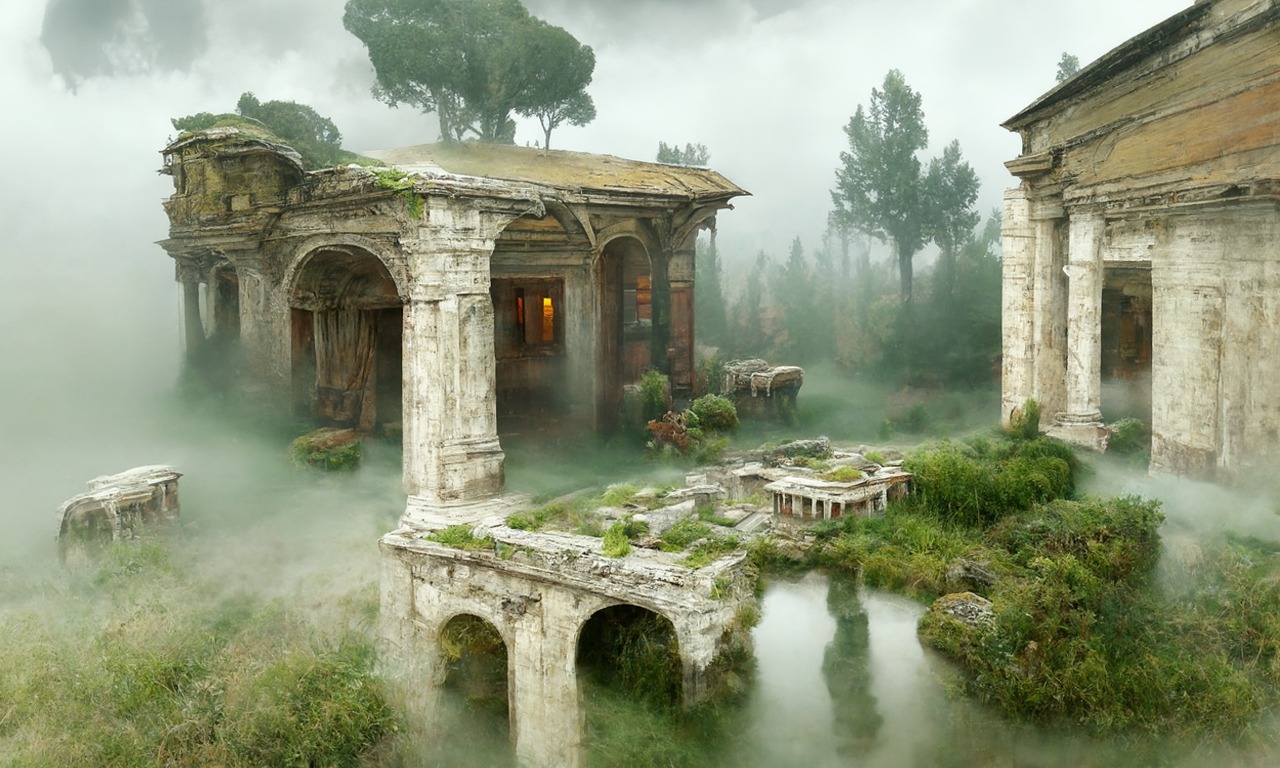
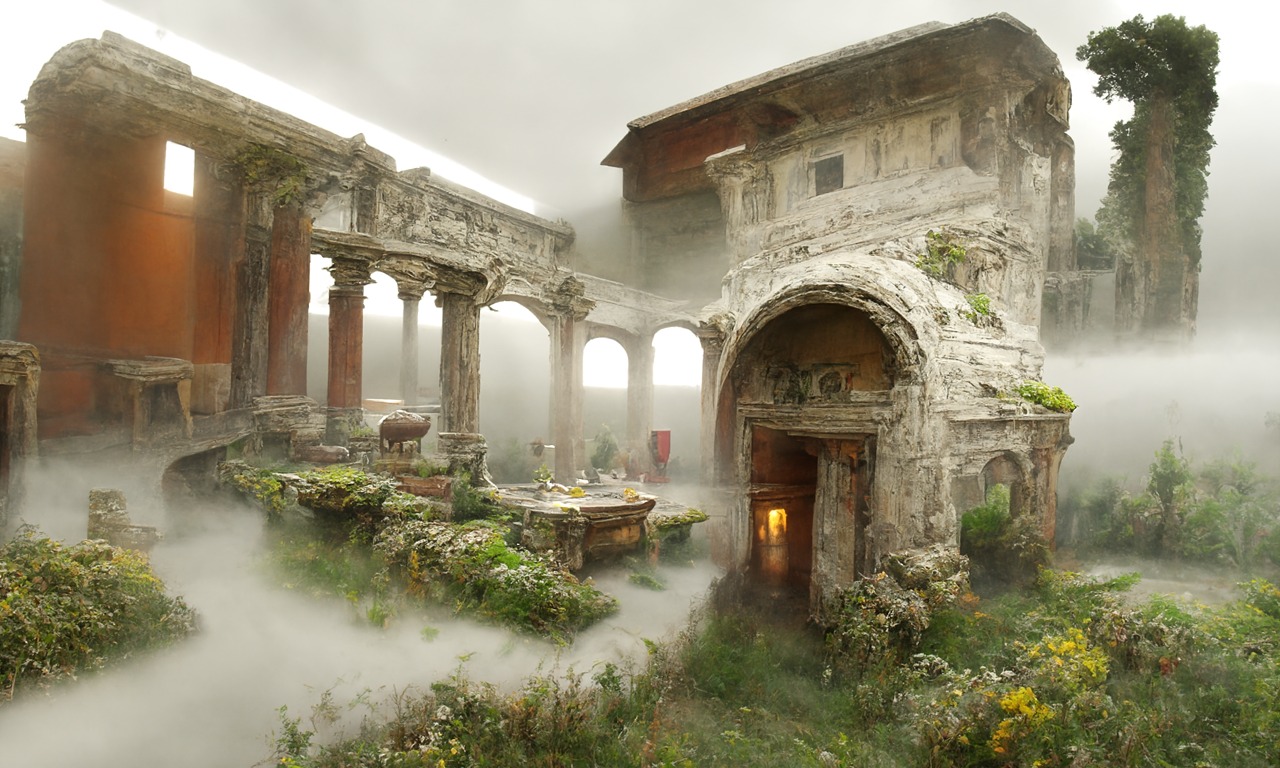
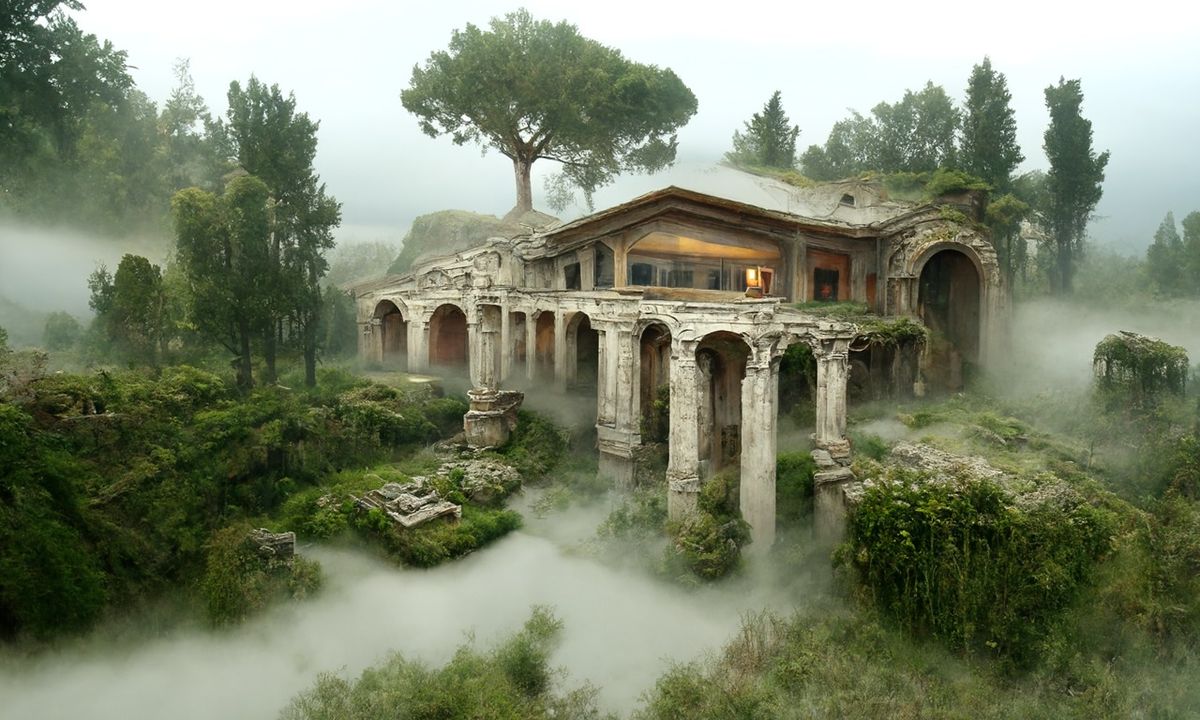



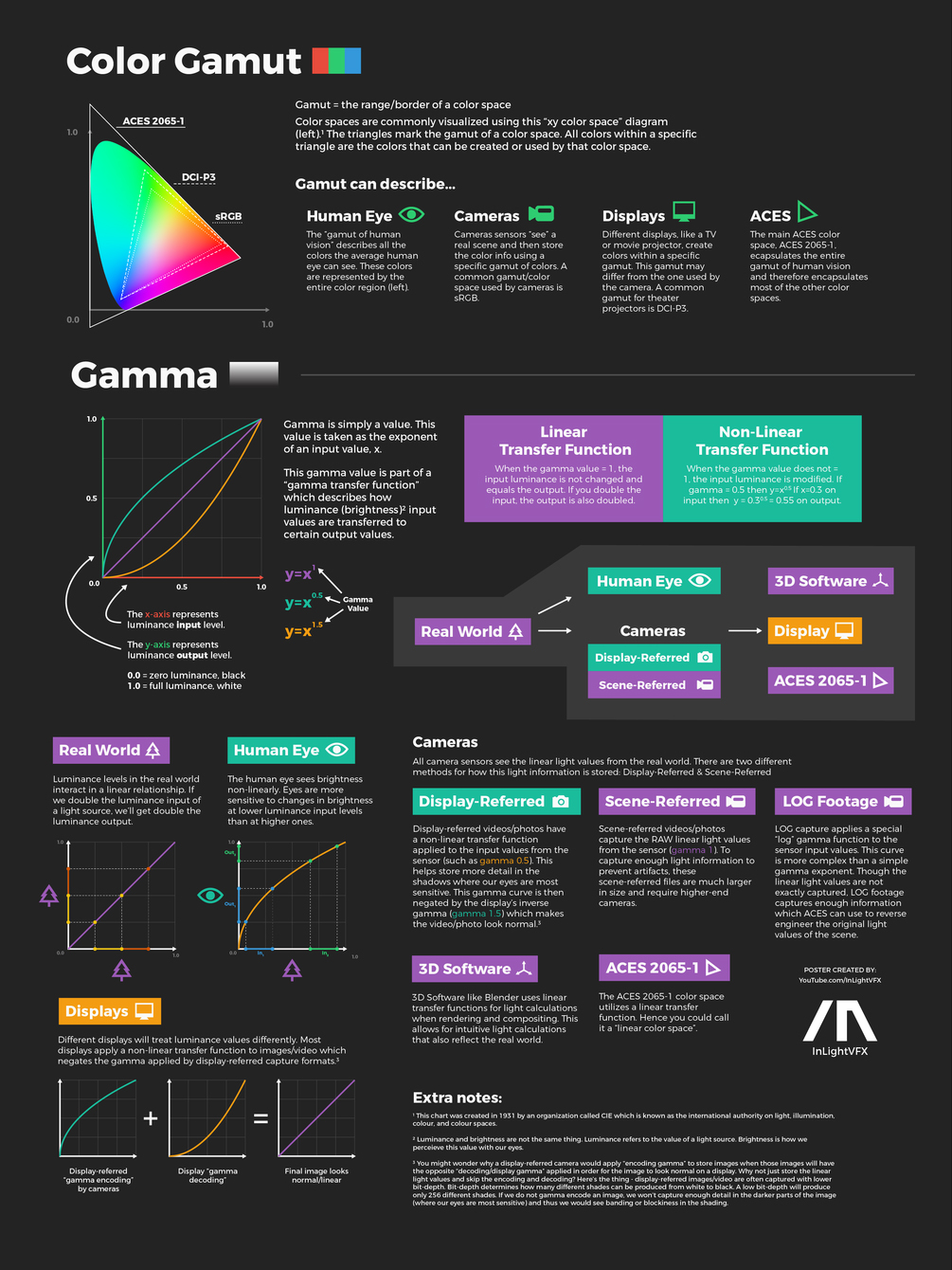
COLOR
-
SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixing
Read more: SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixingInternally, Mixbox treats colors as real-life pigments using the Kubelka & Munk theory to predict realistic color behavior.
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/painter/
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox.pdf
https://github.com/scrtwpns/mixbox
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/docs/
-
What light is best to illuminate gems for resale
Read more: What light is best to illuminate gems for resalewww.palagems.com/gem-lighting2
Artificial light sources, not unlike the diverse phases of natural light, vary considerably in their properties. As a result, some lamps render an object’s color better than others do.
The most important criterion for assessing the color-rendering ability of any lamp is its spectral power distribution curve.
Natural daylight varies too much in strength and spectral composition to be taken seriously as a lighting standard for grading and dealing colored stones. For anything to be a standard, it must be constant in its properties, which natural light is not.
For dealers in particular to make the transition from natural light to an artificial light source, that source must offer:
1- A degree of illuminance at least as strong as the common phases of natural daylight.
2- Spectral properties identical or comparable to a phase of natural daylight.A source combining these two things makes gems appear much the same as when viewed under a given phase of natural light. From the viewpoint of many dealers, this corresponds to a naturalappearance.
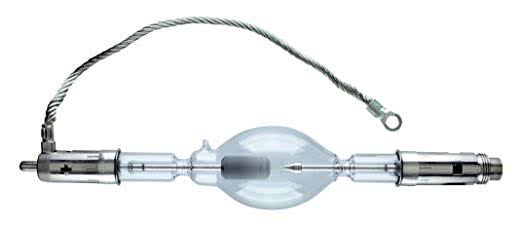
The 6000° Kelvin xenon short-arc lamp appears closest to meeting the criteria for a standard light source. Besides the strong illuminance this lamp affords, its spectrum is very similar to CIE standard illuminants of similar color temperature.

-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction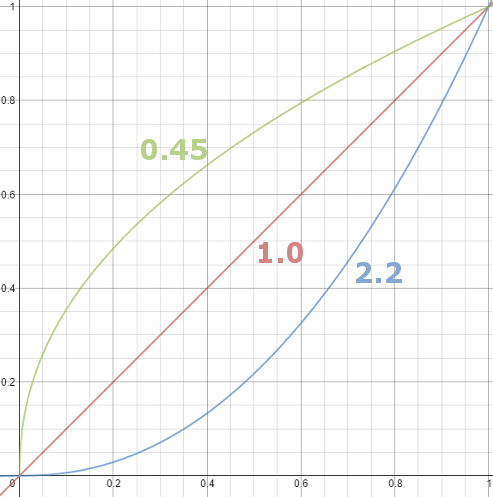
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.Our eyes, different camera or video recorder devices do not correctly capture luminance. (they are not linear)
Different display devices (monitor, phone screen, TV) do not display luminance correctly neither. So, one needs to correct them, therefore the gamma correction function.The human perception of brightness, under common illumination conditions (not pitch black nor blindingly bright), follows an approximate power function (note: no relation to the gamma function), with greater sensitivity to relative differences between darker tones than between lighter ones, consistent with the Stevens’ power law for brightness perception. If images are not gamma-encoded, they allocate too many bits or too much bandwidth to highlights that humans cannot differentiate, and too few bits or too little bandwidth to shadow values that humans are sensitive to and would require more bits/bandwidth to maintain the same visual quality.
https://blog.amerlux.com/4-things-architects-should-know-about-lumens-vs-perceived-brightness/
cones manage color receptivity, rods determine how large our pupils should be. The larger (more dilated) our pupils are, the more light enters our eyes. In dark situations, our rods dilate our pupils so we can see better. This impacts how we perceive brightness.
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
A gamma encoded image has to have “gamma correction” applied when it is viewed — which effectively converts it back into light from the original scene. In other words, the purpose of gamma encoding is for recording the image — not for displaying the image. Fortunately this second step (the “display gamma”) is automatically performed by your monitor and video card. The following diagram illustrates how all of this fits together:
Display gamma
The display gamma can be a little confusing because this term is often used interchangeably with gamma correction, since it corrects for the file gamma. This is the gamma that you are controlling when you perform monitor calibration and adjust your contrast setting. Fortunately, the industry has converged on a standard display gamma of 2.2, so one doesn’t need to worry about the pros/cons of different values.Gamma encoding of images is used to optimize the usage of bits when encoding an image, or bandwidth used to transport an image, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and color. Human response to luminance is also biased. Especially sensible to dark areas.
Thus, the human visual system has a non-linear response to the power of the incoming light, so a fixed increase in power will not have a fixed increase in perceived brightness.
We perceive a value as half bright when it is actually 18% of the original intensity not 50%. As such, our perception is not linear.You probably already know that a pixel can have any ‘value’ of Red, Green, and Blue between 0 and 255, and you would therefore think that a pixel value of 127 would appear as half of the maximum possible brightness, and that a value of 64 would represent one-quarter brightness, and so on. Well, that’s just not the case.
Pixar Color Management
https://renderman.pixar.com/color-management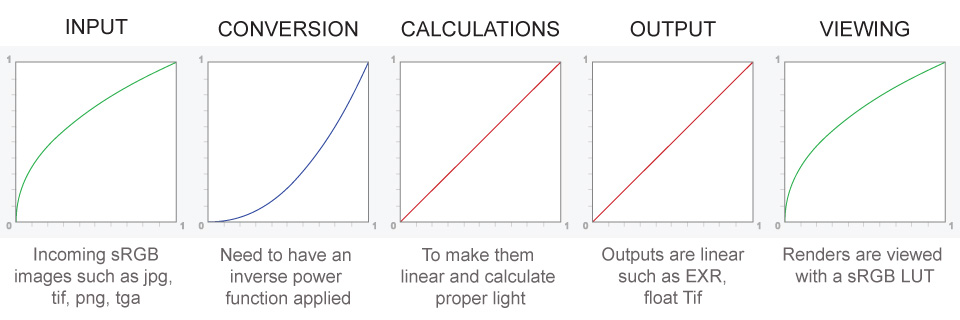
– Why do we need linear gamma?
Because light works linearly and therefore only works properly when it lights linear values.– Why do we need to view in sRGB?
Because the resulting linear image in not suitable for viewing, but contains all the proper data. Pixar’s IT viewer can compensate by showing the rendered image through a sRGB look up table (LUT), which is identical to what will be the final image after the sRGB gamma curve is applied in post.This would be simple enough if every software would play by the same rules, but they don’t. In fact, the default gamma workflow for many 3D software is incorrect. This is where the knowledge of a proper imaging workflow comes in to save the day.
Cathode-ray tubes have a peculiar relationship between the voltage applied to them, and the amount of light emitted. It isn’t linear, and in fact it follows what’s called by mathematicians and other geeks, a ‘power law’ (a number raised to a power). The numerical value of that power is what we call the gamma of the monitor or system.
Thus. Gamma describes the nonlinear relationship between the pixel levels in your computer and the luminance of your monitor (the light energy it emits) or the reflectance of your prints. The equation is,
Luminance = C * value^gamma + black level
– C is set by the monitor Contrast control.
– Value is the pixel level normalized to a maximum of 1. For an 8 bit monitor with pixel levels 0 – 255, value = (pixel level)/255.
– Black level is set by the (misnamed) monitor Brightness control. The relationship is linear if gamma = 1. The chart illustrates the relationship for gamma = 1, 1.5, 1.8 and 2.2 with C = 1 and black level = 0.
Gamma affects middle tones; it has no effect on black or white. If gamma is set too high, middle tones appear too dark. Conversely, if it’s set too low, middle tones appear too light.
The native gamma of monitors– the relationship between grid voltage and luminance– is typically around 2.5, though it can vary considerably. This is well above any of the display standards, so you must be aware of gamma and correct it.
A display gamma of 2.2 is the de facto standard for the Windows operating system and the Internet-standard sRGB color space.
The old standard for Mcintosh and prepress file interchange is 1.8. It is now 2.2 as well.
Video cameras have gammas of approximately 0.45– the inverse of 2.2. The viewing or system gamma is the product of the gammas of all the devices in the system– the image acquisition device (film+scanner or digital camera), color lookup table (LUT), and monitor. System gamma is typically between 1.1 and 1.5. Viewing flare and other factor make images look flat at system gamma = 1.0.
Most laptop LCD screens are poorly suited for critical image editing because gamma is extremely sensitive to viewing angle.
More about screens
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
CRT Monitors. Due to an odd bit of engineering luck, the native gamma of a CRT is 2.5 — almost the inverse of our eyes. Values from a gamma-encoded file could therefore be sent straight to the screen and they would automatically be corrected and appear nearly OK. However, a small gamma correction of ~1/1.1 needs to be applied to achieve an overall display gamma of 2.2. This is usually already set by the manufacturer’s default settings, but can also be set during monitor calibration.
LCD Monitors. LCD monitors weren’t so fortunate; ensuring an overall display gamma of 2.2 often requires substantial corrections, and they are also much less consistent than CRT’s. LCDs therefore require something called a look-up table (LUT) in order to ensure that input values are depicted using the intended display gamma (amongst other things). See the tutorial on monitor calibration: look-up tables for more on this topic.
About black level (brightness). Your monitor’s brightness control (which should actually be called black level) can be adjusted using the mostly black pattern on the right side of the chart. This pattern contains two dark gray vertical bars, A and B, which increase in luminance with increasing gamma. (If you can’t see them, your black level is way low.) The left bar (A) should be just above the threshold of visibility opposite your chosen gamma (2.2 or 1.8)– it should be invisible where gamma is lower by about 0.3. The right bar (B) should be distinctly visible: brighter than (A), but still very dark. This chart is only for monitors; it doesn’t work on printed media.
The 1.8 and 2.2 gray patterns at the bottom of the image represent a test of monitor quality and calibration. If your monitor is functioning properly and calibrated to gamma = 2.2 or 1.8, the corresponding pattern will appear smooth neutral gray when viewed from a distance. Any waviness, irregularity, or color banding indicates incorrect monitor calibration or poor performance.
Another test to see whether one’s computer monitor is properly hardware adjusted and can display shadow detail in sRGB images properly, they should see the left half of the circle in the large black square very faintly but the right half should be clearly visible. If not, one can adjust their monitor’s contrast and/or brightness setting. This alters the monitor’s perceived gamma. The image is best viewed against a black background.
This procedure is not suitable for calibrating or print-proofing a monitor. It can be useful for making a monitor display sRGB images approximately correctly, on systems in which profiles are not used (for example, the Firefox browser prior to version 3.0 and many others) or in systems that assume untagged source images are in the sRGB colorspace.
On some operating systems running the X Window System, one can set the gamma correction factor (applied to the existing gamma value) by issuing the command xgamma -gamma 0.9 for setting gamma correction factor to 0.9, and xgamma for querying current value of that factor (the default is 1.0). In OS X systems, the gamma and other related screen calibrations are made through the System Preference
https://www.kinematicsoup.com/news/2016/6/15/gamma-and-linear-space-what-they-are-how-they-differ
Linear color space means that numerical intensity values correspond proportionally to their perceived intensity. This means that the colors can be added and multiplied correctly. A color space without that property is called ”non-linear”. Below is an example where an intensity value is doubled in a linear and a non-linear color space. While the corresponding numerical values in linear space are correct, in the non-linear space (gamma = 0.45, more on this later) we can’t simply double the value to get the correct intensity.
The need for gamma arises for two main reasons: The first is that screens have been built with a non-linear response to intensity. The other is that the human eye can tell the difference between darker shades better than lighter shades. This means that when images are compressed to save space, we want to have greater accuracy for dark intensities at the expense of lighter intensities. Both of these problems are resolved using gamma correction, which is to say the intensity of every pixel in an image is put through a power function. Specifically, gamma is the name given to the power applied to the image.
CRT screens, simply by how they work, apply a gamma of around 2.2, and modern LCD screens are designed to mimic that behavior. A gamma of 2.2, the reciprocal of 0.45, when applied to the brightened images will darken them, leaving the original image.
-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. …
Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
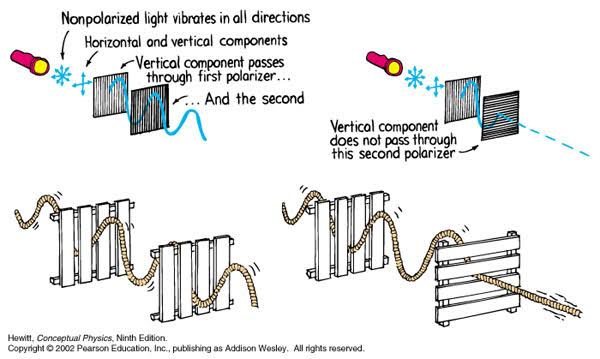
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
The most common use of polarized technology is to reduce lighting complexity on the subject.
Details such as glare and hard edges are not removed, but greatly reduced.This method is usually used in VFX to capture raw images with the least amount of specular diffusion or pollution, thus allowing artists to infer detail back through typical shading and rendering techniques and on demand.
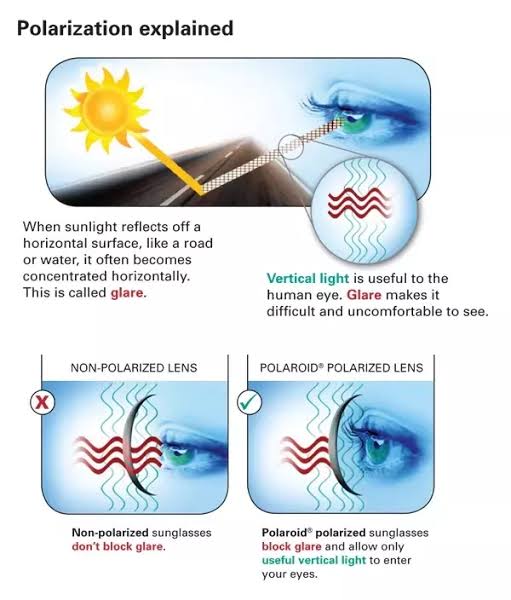
Light reflected from a non-metallic surface becomes polarized; this effect is maximum at Brewster’s angle, about 56° from the vertical for common glass.
A polarizer rotated to pass only light polarized in the direction perpendicular to the reflected light will absorb much of it. This absorption allows glare reflected from, for example, a body of water or a road to be reduced. Reflections from shiny surfaces (e.g. vegetation, sweaty skin, water surfaces, glass) are also reduced. This allows the natural color and detail of what is beneath to come through. Reflections from a window into a dark interior can be much reduced, allowing it to be seen through. (The same effects are available for vision by using polarizing sunglasses.)
www.physicsclassroom.com/class/light/u12l1e.cfm
Some of the light coming from the sky is polarized (bees use this phenomenon for navigation). The electrons in the air molecules cause a scattering of sunlight in all directions. This explains why the sky is not dark during the day. But when looked at from the sides, the light emitted from a specific electron is totally polarized.[3] Hence, a picture taken in a direction at 90 degrees from the sun can take advantage of this polarization.
Use of a polarizing filter, in the correct direction, will filter out the polarized component of skylight, darkening the sky; the landscape below it, and clouds, will be less affected, giving a photograph with a darker and more dramatic sky, and emphasizing the clouds.

There are two types of polarizing filters readily available, linear and “circular”, which have exactly the same effect photographically. But the metering and auto-focus sensors in certain cameras, including virtually all auto-focus SLRs, will not work properly with linear polarizers because the beam splitters used to split off the light for focusing and metering are polarization-dependent.
Polarizing filters reduce the light passed through to the film or sensor by about one to three stops (2–8×) depending on how much of the light is polarized at the filter angle selected. Auto-exposure cameras will adjust for this by widening the aperture, lengthening the time the shutter is open, and/or increasing the ASA/ISO speed of the camera.
www.adorama.com/alc/nd-filter-vs-polarizer-what%25e2%2580%2599s-the-difference
Neutral Density (ND) filters help control image exposure by reducing the light that enters the camera so that you can have more control of your depth of field and shutter speed. Polarizers or polarizing filters work in a similar way, but the difference is that they selectively let light waves of a certain polarization pass through. This effect helps create more vivid colors in an image, as well as manage glare and reflections from water surfaces. Both are regarded as some of the best filters for landscape and travel photography as they reduce the dynamic range in high-contrast images, thus enabling photographers to capture more realistic and dramatic sceneries.
shopfelixgray.com/blog/polarized-vs-non-polarized-sunglasses/
www.eyebuydirect.com/blog/difference-polarized-nonpolarized-sunglasses/
-
What is OLED and what can it do for your TV
Read more: What is OLED and what can it do for your TVhttps://www.cnet.com/news/what-is-oled-and-what-can-it-do-for-your-tv/
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. Each pixel in an OLED display is made of a material that glows when you jab it with electricity. Kind of like the heating elements in a toaster, but with less heat and better resolution. This effect is called electroluminescence, which is one of those delightful words that is big, but actually makes sense: “electro” for electricity, “lumin” for light and “escence” for, well, basically “essence.”
OLED TV marketing often claims “infinite” contrast ratios, and while that might sound like typical hyperbole, it’s one of the extremely rare instances where such claims are actually true. Since OLED can produce a perfect black, emitting no light whatsoever, its contrast ratio (expressed as the brightest white divided by the darkest black) is technically infinite.
OLED is the only technology capable of absolute blacks and extremely bright whites on a per-pixel basis. LCD definitely can’t do that, and even the vaunted, beloved, dearly departed plasma couldn’t do absolute blacks.
-
Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Colorists
Read more: Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Coloristshttps://www.tobiamontanari.com/memory-colors-an-essential-tool-for-colorists/
“Memory colors are colors that are universally associated with specific objects, elements or scenes in our environment. They are the colors that we expect to see in specific situations: these colors are based on our expectation of how certain objects should look based on our past experiences and memories.
For instance, we associate specific hues, saturation and brightness values with human skintones and a slight variation can significantly affect the way we perceive a scene.
Similarly, we expect blue skies to have a particular hue, green trees to be a specific shade and so on.
Memory colors live inside of our brains and we often impose them onto what we see. By considering them during the grading process, the resulting image will be more visually appealing and won’t distract the viewer from the intended message of the story. Even a slight deviation from memory colors in a movie can create a sense of discordance, ultimately detracting from the viewer’s experience.”
LIGHTING
-
Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022
Read more: Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022Comparison to the commercial side

https://www.ecolorled.com/blog/detail/what-is-rgb-rgbw-rgbic-strip-lights
RGBW (RGB + White) LED strip uses a 4-in-1 LED chip made up of red, green, blue, and white.
RGBWW (RGB + White + Warm White) LED strip uses either a 5-in-1 LED chip with red, green, blue, white, and warm white for color mixing. The only difference between RGBW and RGBWW is the intensity of the white color. The term RGBCCT consists of RGB and CCT. CCT (Correlated Color Temperature) means that the color temperature of the led strip light can be adjusted to change between warm white and white. Thus, RGBWW strip light is another name of RGBCCT strip.
RGBCW is the acronym for Red, Green, Blue, Cold, and Warm. These 5-in-1 chips are used in supper bright smart LED lighting products
-
Neural Microfacet Fields for Inverse Rendering
Read more: Neural Microfacet Fields for Inverse Renderinghttps://half-potato.gitlab.io/posts/nmf/
-
What is the Light Field?
Read more: What is the Light Field?http://lightfield-forum.com/what-is-the-lightfield/
The light field consists of the total of all light rays in 3D space, flowing through every point and in every direction.
How to Record a Light Field
- a single, robotically controlled camera
- a rotating arc of cameras
- an array of cameras or camera modules
- a single camera or camera lens fitted with a microlens array
-
Open Source Nvidia Omniverse
Read more: Open Source Nvidia Omniverseblogs.nvidia.com/blog/2019/03/18/omniverse-collaboration-platform/
developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-omniverse
An open, Interactive 3D Design Collaboration Platform for Multi-Tool Workflows to simplify studio workflows for real-time graphics.
It supports Pixar’s Universal Scene Description technology for exchanging information about modeling, shading, animation, lighting, visual effects and rendering across multiple applications.
It also supports NVIDIA’s Material Definition Language, which allows artists to exchange information about surface materials across multiple tools.
With Omniverse, artists can see live updates made by other artists working in different applications. They can also see changes reflected in multiple tools at the same time.
For example an artist using Maya with a portal to Omniverse can collaborate with another artist using UE4 and both will see live updates of each others’ changes in their application.
-
How to Direct and Edit a Fight Scene for Rhythm and Pacing
Read more: How to Direct and Edit a Fight Scene for Rhythm and Pacingwww.premiumbeat.com/blog/directing-fight-scene-cinematography/
1- Frame the action
2- Stage the action
3- Use camera movements
4- Set a rhythm
5- Control the speed of the action
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Mastering The Art Of Photography – PixelSham.com Photography Basics
-
QR code logos
-
Matt Gray – How to generate a profitable business
-
Photography basics: Production Rendering Resolution Charts
-
Advanced Computer Vision with Python OpenCV and Mediapipe
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
-
Kling 1.6 and competitors – advanced tests and comparisons
-
Google – Artificial Intelligence free courses
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.