COMPOSITION
-
SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source program
Read more: SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source programhttp://slowmovideo.granjow.net/
slowmoVideo is an OpenSource program that creates slow-motion videos from your footage.
Slow motion cinematography is the result of playing back frames for a longer duration than they were exposed. For example, if you expose 240 frames of film in one second, then play them back at 24 fps, the resulting movie is 10 times longer (slower) than the original filmed event….
Film cameras are relatively simple mechanical devices that allow you to crank up the speed to whatever rate the shutter and pull-down mechanism allow. Some film cameras can operate at 2,500 fps or higher (although film shot in these cameras often needs some readjustment in postproduction). Video, on the other hand, is always captured, recorded, and played back at a fixed rate, with a current limit around 60fps. This makes extreme slow motion effects harder to achieve (and less elegant) on video, because slowing down the video results in each frame held still on the screen for a long time, whereas with high-frame-rate film there are plenty of frames to fill the longer durations of time. On video, the slow motion effect is more like a slide show than smooth, continuous motion.
One obvious solution is to shoot film at high speed, then transfer it to video (a case where film still has a clear advantage, sorry George). Another possibility is to cross dissolve or blur from one frame to the next. This adds a smooth transition from one still frame to the next. The blur reduces the sharpness of the image, and compared to slowing down images shot at a high frame rate, this is somewhat of a cheat. However, there isn’t much you can do about it until video can be recorded at much higher rates. Of course, many film cameras can’t shoot at high frame rates either, so the whole super-slow-motion endeavor is somewhat specialized no matter what medium you are using. (There are some high speed digital cameras available now that allow you to capture lots of digital frames directly to your computer, so technology is starting to catch up with film. However, this feature isn’t going to appear in consumer camcorders any time soon.)
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
-
Photography basics: Depth of Field and composition
Read more: Photography basics: Depth of Field and compositionDepth of field is the range within which focusing is resolved in a photo.
Aperture has a huge affect on to the depth of field.Changing the f-stops (f/#) of a lens will change aperture and as such the DOF.
f-stops are a just certain number which is telling you the size of the aperture. That’s how f-stop is related to aperture (and DOF).
If you increase f-stops, it will increase DOF, the area in focus (and decrease the aperture). On the other hand, decreasing the f-stop it will decrease DOF (and increase the aperture).
The red cone in the figure is an angular representation of the resolution of the system. Versus the dotted lines, which indicate the aperture coverage. Where the lines of the two cones intersect defines the total range of the depth of field.
This image explains why the longer the depth of field, the greater the range of clarity.
DESIGN
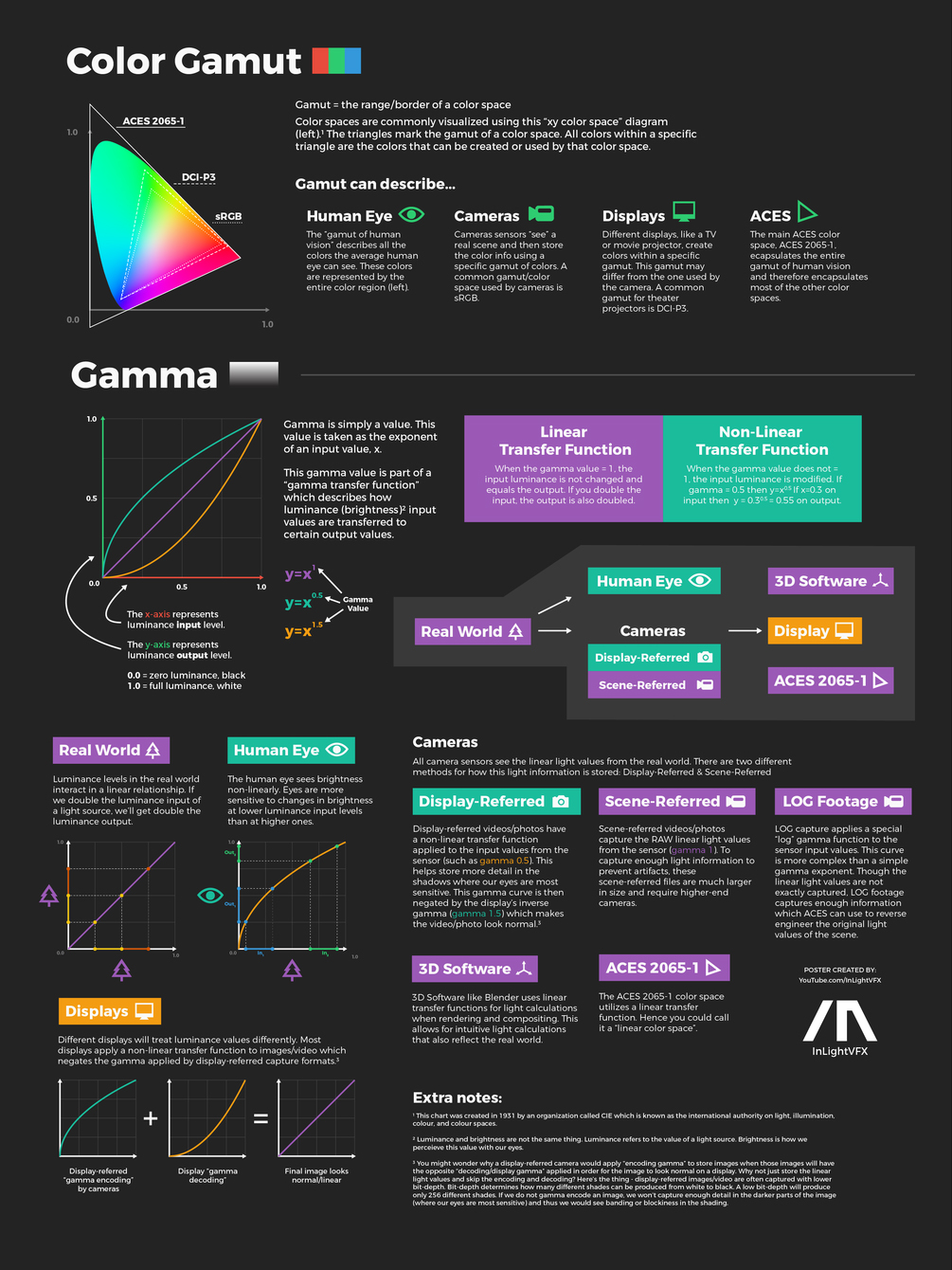
COLOR
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
Read more: Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflowsDisplay Referred it is tied to the target hardware, as such it bakes color requirements into every type of media output request.
Scene Referred uses a common unified wide gamut and targeting audience through CDL and DI libraries instead.
So that color information stays untouched and only “transformed” as/when needed.Sources:
– Victor Perez – Color Management Fundamentals & ACES Workflows in Nuke
– https://z-fx.nl/ColorspACES.pdf
– Wicus
-
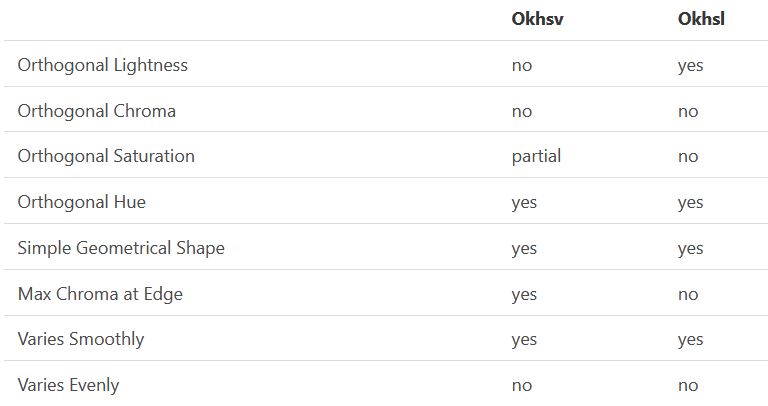
Björn Ottosson – OKHSV and OKHSL – Two new color spaces for color picking
Read more: Björn Ottosson – OKHSV and OKHSL – Two new color spaces for color pickinghttps://bottosson.github.io/misc/colorpicker
https://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorpicker/
https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2024/10/interview-bjorn-ottosson-creator-oklab-color-space/
One problem with sRGB is that in a gradient between blue and white, it becomes a bit purple in the middle of the transition. That’s because sRGB really isn’t created to mimic how the eye sees colors; rather, it is based on how CRT monitors work. That means it works with certain frequencies of red, green, and blue, and also the non-linear coding called gamma. It’s a miracle it works as well as it does, but it’s not connected to color perception. When using those tools, you sometimes get surprising results, like purple in the gradient.
There were also attempts to create simple models matching human perception based on XYZ, but as it turned out, it’s not possible to model all color vision that way. Perception of color is incredibly complex and depends, among other things, on whether it is dark or light in the room and the background color it is against. When you look at a photograph, it also depends on what you think the color of the light source is. The dress is a typical example of color vision being very context-dependent. It is almost impossible to model this perfectly.
I based Oklab on two other color spaces, CIECAM16 and IPT. I used the lightness and saturation prediction from CIECAM16, which is a color appearance model, as a target. I actually wanted to use the datasets used to create CIECAM16, but I couldn’t find them.
IPT was designed to have better hue uniformity. In experiments, they asked people to match light and dark colors, saturated and unsaturated colors, which resulted in a dataset for which colors, subjectively, have the same hue. IPT has a few other issues but is the basis for hue in Oklab.
In the Munsell color system, colors are described with three parameters, designed to match the perceived appearance of colors: Hue, Chroma and Value. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. Modern color spaces and models, such as CIELAB, Cam16 and Björn Ottosson own Oklab, are very similar in their construction.
By far the most used color spaces today for color picking are HSL and HSV, two representations introduced in the classic 1978 paper “Color Spaces for Computer Graphics”. HSL and HSV designed to roughly correlate with perceptual color properties while being very simple and cheap to compute.
Today HSL and HSV are most commonly used together with the sRGB color space.

One of the main advantages of HSL and HSV over the different Lab color spaces is that they map the sRGB gamut to a cylinder. This makes them easy to use since all parameters can be changed independently, without the risk of creating colors outside of the target gamut.
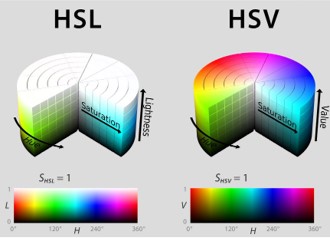
The main drawback on the other hand is that their properties don’t match human perception particularly well.
Reconciling these conflicting goals perfectly isn’t possible, but given that HSV and HSL don’t use anything derived from experiments relating to human perception, creating something that makes a better tradeoff does not seem unreasonable.
With this new lightness estimate, we are ready to look into the construction of Okhsv and Okhsl.
-
What Is The Resolution and view coverage Of The human Eye. And what distance is TV at best?
Read more: What Is The Resolution and view coverage Of The human Eye. And what distance is TV at best?https://www.discovery.com/science/mexapixels-in-human-eye
About 576 megapixels for the entire field of view.
Consider a view in front of you that is 90 degrees by 90 degrees, like looking through an open window at a scene. The number of pixels would be:
90 degrees * 60 arc-minutes/degree * 1/0.3 * 90 * 60 * 1/0.3 = 324,000,000 pixels (324 megapixels).At any one moment, you actually do not perceive that many pixels, but your eye moves around the scene to see all the detail you want. But the human eye really sees a larger field of view, close to 180 degrees. Let’s be conservative and use 120 degrees for the field of view. Then we would see:
120 * 120 * 60 * 60 / (0.3 * 0.3) = 576 megapixels.
Or.
7 megapixels for the 2 degree focus arc… + 1 megapixel for the rest.
https://clarkvision.com/articles/eye-resolution.html
Details in the post
-
Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Colorists
Read more: Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Coloristshttps://www.tobiamontanari.com/memory-colors-an-essential-tool-for-colorists/
“Memory colors are colors that are universally associated with specific objects, elements or scenes in our environment. They are the colors that we expect to see in specific situations: these colors are based on our expectation of how certain objects should look based on our past experiences and memories.
For instance, we associate specific hues, saturation and brightness values with human skintones and a slight variation can significantly affect the way we perceive a scene.
Similarly, we expect blue skies to have a particular hue, green trees to be a specific shade and so on.
Memory colors live inside of our brains and we often impose them onto what we see. By considering them during the grading process, the resulting image will be more visually appealing and won’t distract the viewer from the intended message of the story. Even a slight deviation from memory colors in a movie can create a sense of discordance, ultimately detracting from the viewer’s experience.”
-
Virtual Production volumes study
Read more: Virtual Production volumes studyColor Fidelity in LED Volumes
https://theasc.com/articles/color-fidelity-in-led-volumesVirtual Production Glossary
https://vpglossary.com/What is Virtual Production – In depth analysis
https://www.leadingledtech.com/what-is-a-led-virtual-production-studio-in-depth-technical-analysis/A comparison of LED panels for use in Virtual Production:
Findings and recommendations
https://eprints.bournemouth.ac.uk/36826/1/LED_Comparison_White_Paper%281%29.pdf -
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction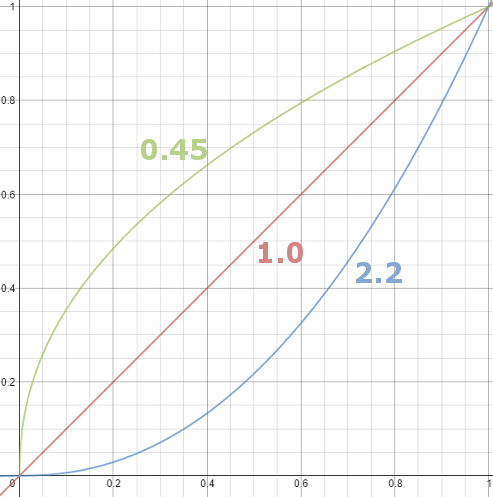
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.Our eyes, different camera or video recorder devices do not correctly capture luminance. (they are not linear)
Different display devices (monitor, phone screen, TV) do not display luminance correctly neither. So, one needs to correct them, therefore the gamma correction function.The human perception of brightness, under common illumination conditions (not pitch black nor blindingly bright), follows an approximate power function (note: no relation to the gamma function), with greater sensitivity to relative differences between darker tones than between lighter ones, consistent with the Stevens’ power law for brightness perception. If images are not gamma-encoded, they allocate too many bits or too much bandwidth to highlights that humans cannot differentiate, and too few bits or too little bandwidth to shadow values that humans are sensitive to and would require more bits/bandwidth to maintain the same visual quality.
https://blog.amerlux.com/4-things-architects-should-know-about-lumens-vs-perceived-brightness/
cones manage color receptivity, rods determine how large our pupils should be. The larger (more dilated) our pupils are, the more light enters our eyes. In dark situations, our rods dilate our pupils so we can see better. This impacts how we perceive brightness.
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
A gamma encoded image has to have “gamma correction” applied when it is viewed — which effectively converts it back into light from the original scene. In other words, the purpose of gamma encoding is for recording the image — not for displaying the image. Fortunately this second step (the “display gamma”) is automatically performed by your monitor and video card. The following diagram illustrates how all of this fits together:
Display gamma
The display gamma can be a little confusing because this term is often used interchangeably with gamma correction, since it corrects for the file gamma. This is the gamma that you are controlling when you perform monitor calibration and adjust your contrast setting. Fortunately, the industry has converged on a standard display gamma of 2.2, so one doesn’t need to worry about the pros/cons of different values.Gamma encoding of images is used to optimize the usage of bits when encoding an image, or bandwidth used to transport an image, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and color. Human response to luminance is also biased. Especially sensible to dark areas.
Thus, the human visual system has a non-linear response to the power of the incoming light, so a fixed increase in power will not have a fixed increase in perceived brightness.
We perceive a value as half bright when it is actually 18% of the original intensity not 50%. As such, our perception is not linear.You probably already know that a pixel can have any ‘value’ of Red, Green, and Blue between 0 and 255, and you would therefore think that a pixel value of 127 would appear as half of the maximum possible brightness, and that a value of 64 would represent one-quarter brightness, and so on. Well, that’s just not the case.
Pixar Color Management
https://renderman.pixar.com/color-management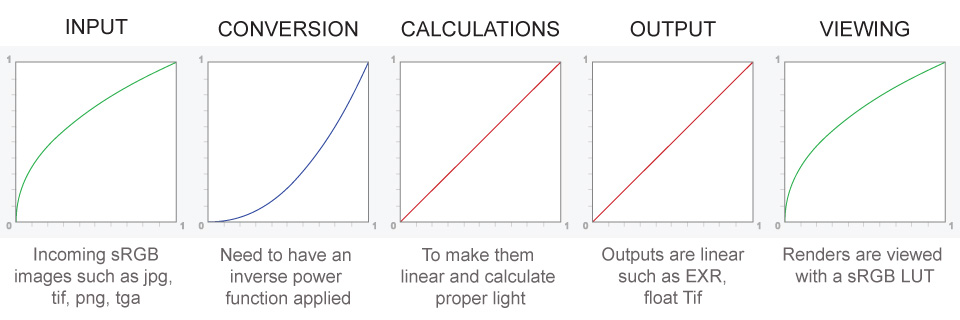
– Why do we need linear gamma?
Because light works linearly and therefore only works properly when it lights linear values.– Why do we need to view in sRGB?
Because the resulting linear image in not suitable for viewing, but contains all the proper data. Pixar’s IT viewer can compensate by showing the rendered image through a sRGB look up table (LUT), which is identical to what will be the final image after the sRGB gamma curve is applied in post.This would be simple enough if every software would play by the same rules, but they don’t. In fact, the default gamma workflow for many 3D software is incorrect. This is where the knowledge of a proper imaging workflow comes in to save the day.
Cathode-ray tubes have a peculiar relationship between the voltage applied to them, and the amount of light emitted. It isn’t linear, and in fact it follows what’s called by mathematicians and other geeks, a ‘power law’ (a number raised to a power). The numerical value of that power is what we call the gamma of the monitor or system.
Thus. Gamma describes the nonlinear relationship between the pixel levels in your computer and the luminance of your monitor (the light energy it emits) or the reflectance of your prints. The equation is,
Luminance = C * value^gamma + black level
– C is set by the monitor Contrast control.
– Value is the pixel level normalized to a maximum of 1. For an 8 bit monitor with pixel levels 0 – 255, value = (pixel level)/255.
– Black level is set by the (misnamed) monitor Brightness control. The relationship is linear if gamma = 1. The chart illustrates the relationship for gamma = 1, 1.5, 1.8 and 2.2 with C = 1 and black level = 0.
Gamma affects middle tones; it has no effect on black or white. If gamma is set too high, middle tones appear too dark. Conversely, if it’s set too low, middle tones appear too light.
The native gamma of monitors– the relationship between grid voltage and luminance– is typically around 2.5, though it can vary considerably. This is well above any of the display standards, so you must be aware of gamma and correct it.
A display gamma of 2.2 is the de facto standard for the Windows operating system and the Internet-standard sRGB color space.
The old standard for Mcintosh and prepress file interchange is 1.8. It is now 2.2 as well.
Video cameras have gammas of approximately 0.45– the inverse of 2.2. The viewing or system gamma is the product of the gammas of all the devices in the system– the image acquisition device (film+scanner or digital camera), color lookup table (LUT), and monitor. System gamma is typically between 1.1 and 1.5. Viewing flare and other factor make images look flat at system gamma = 1.0.
Most laptop LCD screens are poorly suited for critical image editing because gamma is extremely sensitive to viewing angle.
More about screens
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
CRT Monitors. Due to an odd bit of engineering luck, the native gamma of a CRT is 2.5 — almost the inverse of our eyes. Values from a gamma-encoded file could therefore be sent straight to the screen and they would automatically be corrected and appear nearly OK. However, a small gamma correction of ~1/1.1 needs to be applied to achieve an overall display gamma of 2.2. This is usually already set by the manufacturer’s default settings, but can also be set during monitor calibration.
LCD Monitors. LCD monitors weren’t so fortunate; ensuring an overall display gamma of 2.2 often requires substantial corrections, and they are also much less consistent than CRT’s. LCDs therefore require something called a look-up table (LUT) in order to ensure that input values are depicted using the intended display gamma (amongst other things). See the tutorial on monitor calibration: look-up tables for more on this topic.
About black level (brightness). Your monitor’s brightness control (which should actually be called black level) can be adjusted using the mostly black pattern on the right side of the chart. This pattern contains two dark gray vertical bars, A and B, which increase in luminance with increasing gamma. (If you can’t see them, your black level is way low.) The left bar (A) should be just above the threshold of visibility opposite your chosen gamma (2.2 or 1.8)– it should be invisible where gamma is lower by about 0.3. The right bar (B) should be distinctly visible: brighter than (A), but still very dark. This chart is only for monitors; it doesn’t work on printed media.
The 1.8 and 2.2 gray patterns at the bottom of the image represent a test of monitor quality and calibration. If your monitor is functioning properly and calibrated to gamma = 2.2 or 1.8, the corresponding pattern will appear smooth neutral gray when viewed from a distance. Any waviness, irregularity, or color banding indicates incorrect monitor calibration or poor performance.
Another test to see whether one’s computer monitor is properly hardware adjusted and can display shadow detail in sRGB images properly, they should see the left half of the circle in the large black square very faintly but the right half should be clearly visible. If not, one can adjust their monitor’s contrast and/or brightness setting. This alters the monitor’s perceived gamma. The image is best viewed against a black background.
This procedure is not suitable for calibrating or print-proofing a monitor. It can be useful for making a monitor display sRGB images approximately correctly, on systems in which profiles are not used (for example, the Firefox browser prior to version 3.0 and many others) or in systems that assume untagged source images are in the sRGB colorspace.
On some operating systems running the X Window System, one can set the gamma correction factor (applied to the existing gamma value) by issuing the command xgamma -gamma 0.9 for setting gamma correction factor to 0.9, and xgamma for querying current value of that factor (the default is 1.0). In OS X systems, the gamma and other related screen calibrations are made through the System Preference
https://www.kinematicsoup.com/news/2016/6/15/gamma-and-linear-space-what-they-are-how-they-differ
Linear color space means that numerical intensity values correspond proportionally to their perceived intensity. This means that the colors can be added and multiplied correctly. A color space without that property is called ”non-linear”. Below is an example where an intensity value is doubled in a linear and a non-linear color space. While the corresponding numerical values in linear space are correct, in the non-linear space (gamma = 0.45, more on this later) we can’t simply double the value to get the correct intensity.
The need for gamma arises for two main reasons: The first is that screens have been built with a non-linear response to intensity. The other is that the human eye can tell the difference between darker shades better than lighter shades. This means that when images are compressed to save space, we want to have greater accuracy for dark intensities at the expense of lighter intensities. Both of these problems are resolved using gamma correction, which is to say the intensity of every pixel in an image is put through a power function. Specifically, gamma is the name given to the power applied to the image.
CRT screens, simply by how they work, apply a gamma of around 2.2, and modern LCD screens are designed to mimic that behavior. A gamma of 2.2, the reciprocal of 0.45, when applied to the brightened images will darken them, leaving the original image.
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
The exposure meter in the camera does not know whether the subject itself is bright or not. It simply measures the amount of light that comes in, and makes a guess based on that. The camera will aim for 18% gray independently, meaning if you take a photo of an entirely white surface, and an entirely black surface you should get two identical images which both are gray (at least in theory). Thus enters the Macbeth chart.
<!–more–>
Note that Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
http://www.rags-int-inc.com/PhotoTechStuff/MacbethTarget/
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b4/CIE1931xy_ColorChecker_SMIL.svg
RGB coordinates of the Macbeth ColorChecker
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/0e03/251ad1e6d3c3fb9cb0b1f9754351a959e065.pdf
-
Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space
Read more: Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space8bit sRGB encoded
2000K 255 139 22
2700K 255 172 89
3000K 255 184 109
3200K 255 190 122
4000K 255 211 165
4300K 255 219 178
D50 255 235 205
D55 255 243 224
D5600 255 244 227
D6000 255 249 240
D65 255 255 255
D10000 202 221 255
D20000 166 196 2558bit Rec709 Gamma 2.4
2000K 255 145 34
2700K 255 177 97
3000K 255 187 117
3200K 255 193 129
4000K 255 214 170
4300K 255 221 182
D50 255 236 208
D55 255 243 226
D5600 255 245 229
D6000 255 250 241
D65 255 255 255
D10000 204 222 255
D20000 170 199 2558bit Display P3 encoded
2000K 255 154 63
2700K 255 185 109
3000K 255 195 127
3200K 255 201 138
4000K 255 219 176
4300K 255 225 187
D50 255 239 212
D55 255 245 228
D5600 255 246 231
D6000 255 251 242
D65 255 255 255
D10000 208 223 255
D20000 175 199 25510bit Rec2020 PQ (100 nits)
2000K 520 435 273
2700K 520 466 358
3000K 520 475 384
3200K 520 480 399
4000K 520 495 446
4300K 520 500 458
D50 520 510 482
D55 520 514 497
D5600 520 514 500
D6000 520 517 509
D65 520 520 520
D10000 479 489 520
D20000 448 464 520
LIGHTING
-
Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesis
Read more: Lighting Every Darkness with 3DGS: Fast Training and Real-Time Rendering and Denoising for HDR View Synthesishttps://srameo.github.io/projects/le3d/
LE3D is a method for real-time HDR view synthesis from RAW images. It is particularly effective for nighttime scenes.
https://github.com/Srameo/LE3D
-
Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution function
Read more: Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution functionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bidirectional_reflectance_distribution_function
The bidirectional reflectance distribution function is a four-dimensional function that defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface
http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~zhu/tutorial/An_Introduction_to_BRDF-Based_Lighting.pdf
In general, when light interacts with matter, a complicated light-matter dynamic occurs. This interaction depends on the physical characteristics of the light as well as the physical composition and characteristics of the matter.
That is, some of the incident light is reflected, some of the light is transmitted, and another portion of the light is absorbed by the medium itself.
A BRDF describes how much light is reflected when light makes contact with a certain material. Similarly, a BTDF (Bi-directional Transmission Distribution Function) describes how much light is transmitted when light makes contact with a certain material
http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~smr/cs348c-97/surveypaper.html
It is difficult to establish exactly how far one should go in elaborating the surface model. A truly complete representation of the reflective behavior of a surface might take into account such phenomena as polarization, scattering, fluorescence, and phosphorescence, all of which might vary with position on the surface. Therefore, the variables in this complete function would be:
incoming and outgoing angle incoming and outgoing wavelength incoming and outgoing polarization (both linear and circular) incoming and outgoing position (which might differ due to subsurface scattering) time delay between the incoming and outgoing light ray
-
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
Read more: Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
Wide color gamut, or WCG, is often lumped in with HDR. While they’re often found together, they’re not intrinsically linked. Where HDR is an increase in the dynamic range of the picture (with contrast and brighter highlights in particular), a TV’s wide color gamut coverage refers to how much of the new, larger color gamuts a TV can display.
Wide color gamuts only really matter for HDR video sources like UHD Blu-rays and some streaming video, as only HDR sources are meant to take advantage of the ability to display more colors.
www.cnet.com/how-to/what-is-wide-color-gamut-wcg/
Color depth is only one aspect of color representation, expressing the precision with which the amount of each primary can be expressed through a pixel; the other aspect is how broad a range of colors can be expressed (the gamut)
Image rendering bit depth
Wide color gamuts include a greater number of colors than what most current TVs can display, so the greater a TV’s coverage of a wide color gamut, the more colors a TV will be able to reproduce.
When we talk about a color space or color gamut we refer to the range of color values stored in an image. The perception of these color also requires a display that has been tuned with to resolve these color profiles at best. This is often referred to as a ‘viewer lut’.
So this comes also usually paired with an increase in bit depth, going from the old 8 bit system (256 shades per color, with the potential of over 16.7 million colors: 256 green x 256 blue x 256 red) to 10 (1024+ shades per color, with access to over a billion colors) or higher bits, like 12 bit (4096 shades per RGB for 68 billion colors).
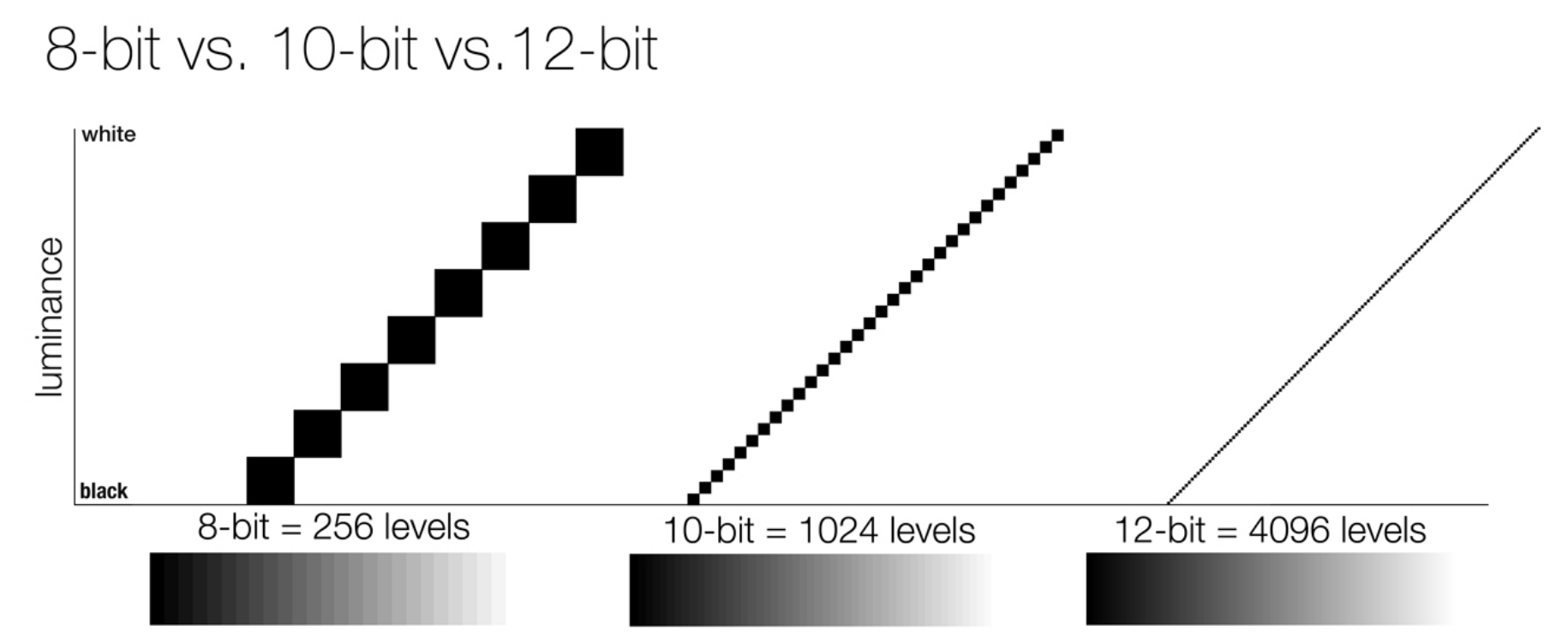
The advantage of higher bit depth is in the ability to bias color with the minimum loss.
For an extreme example, raising the brightness from a completely dark image allows for better reproduction, independently on the reproduction medium, due to the amount of data available at editing time:
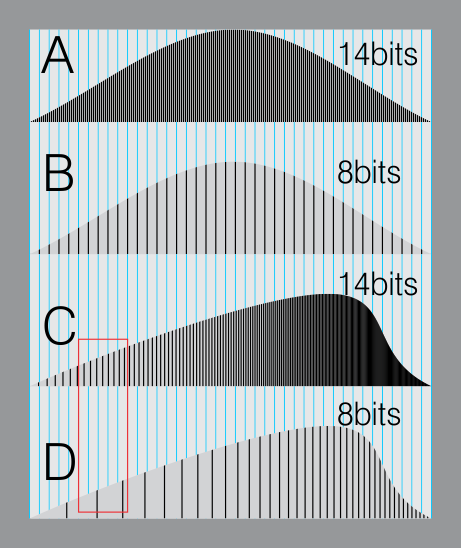
For reference, 8-bit images (i.e. 24 bits per pixel for a color image) are considered Low Dynamic Range.
They can store around 5 stops of light and each pixel carry a value from 0 (black) to 255 (white).
As a comparison, DSLR cameras can capture ~12-15 stops of light and they use RAW files to store the information.
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/dynamic-range.htm
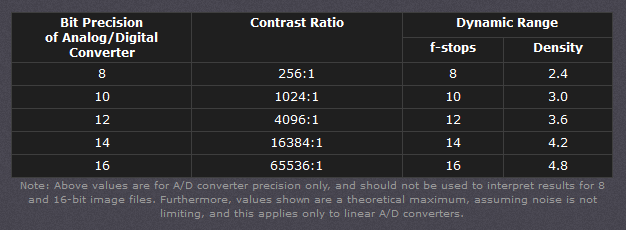
https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
Note that the number of bits itself may be a misleading indication of the real dynamic range that the image reproduces — converting a Low Dynamic Range image to a higher bit depth does not change its dynamic range, of course.
- 8-bit images (i.e. 24 bits per pixel for a color image) are considered Low Dynamic Range.
- 16-bit images (i.e. 48 bits per pixel for a color image) resulting from RAW conversion are still considered Low Dynamic Range, even though the range of values they can encode is significantly higher than for 8-bit images (65536 versus 256). Note that converting a RAW file involves applying a tonal curve that compresses the dynamic range of the RAW data so that the converted image shows correctly on low dynamic range monitors. The need to adapt the output image file to the dynamic range of the display is the factor that dictates how much the dynamic range is compressed, not the output bit-depth. By using 16 instead of 8 bits, you will gain precision but you will not gain dynamic range.
- 32-bit images (i.e. 96 bits per pixel for a color image) are considered High Dynamic Range.Unlike 8- and 16-bit images which can take a finite number of values, 32-bit images are coded using floating point numbers, which means the values they can take is unlimited.It is important to note, though, that storing an image in a 32-bit HDR format is a necessary condition for an HDR image but not a sufficient one. When an image comes from a single capture with a standard camera, it will remain a Low Dynamic Range image,
Also note that bit depth and dynamic range are often confused as one, but are indeed separate concepts and there is no direct one to one relationship between them. Bit depth is about capacity, dynamic range is about the actual ratio of data stored.
The bit depth of a capturing or displaying device gives you an indication of its dynamic range capacity. That is, the highest dynamic range that the device would be capable of reproducing if all other constraints are eliminated.https://rawpedia.rawtherapee.com/Bit_Depth
Finally, note that there are two ways to “count” bits for an image — either the number of bits per color channel (BPC) or the number of bits per pixel (BPP). A bit (0,1) is the smallest unit of data stored in a computer.
For a grayscale image, 8-bit means that each pixel can be one of 256 levels of gray (256 is 2 to the power 8).
For an RGB color image, 8-bit means that each one of the three color channels can be one of 256 levels of color.
Since each pixel is represented by 3 colors in this case, 8-bit per color channel actually means 24-bit per pixel.Similarly, 16-bit for an RGB image means 65,536 levels per color channel and 48-bit per pixel.
To complicate matters, when an image is classified as 16-bit, it just means that it can store a maximum 65,535 values. It does not necessarily mean that it actually spans that range. If the camera sensors can not capture more than 12 bits of tonal values, the actual bit depth of the image will be at best 12-bit and probably less because of noise.
The following table attempts to summarize the above for the case of an RGB color image.
Type of digital support Bit depth per color channel Bit depth per pixel FStops Theoretical maximum Dynamic Range Reality 8-bit 8 24 8 256:1 most consumer images 12-bit CCD 12 36 12 4,096:1 real maximum limited by noise 14-bit CCD 14 42 14 16,384:1 real maximum limited by noise 16-bit TIFF (integer) 16 48 16 65,536:1 bit-depth in this case is not directly related to the dynamic range captured 16-bit float EXR 16 48 30 65,536:1 values are distributed more closely in the (lower) darker tones than in the (higher) lighter ones, thus allowing for a more accurate description of the tones more significant to humans. The range of normalized 16-bit floats can represent thirty stops of information with 1024 steps per stop. We have eighteen and a half stops over middle gray, and eleven and a half below. The denormalized numbers provide an additional ten stops with decreasing precision per stop.
http://download.nvidia.com/developer/GPU_Gems/CD_Image/Image_Processing/OpenEXR/OpenEXR-1.0.6/doc/#recsHDR image (e.g. Radiance format) 32 96 “infinite” 4.3 billion:1 real maximum limited by the captured dynamic range 32-bit floats are often called “single-precision” floats, and 64-bit floats are often called “double-precision” floats. 16-bit floats therefore are called “half-precision” floats, or just “half floats”.
https://petapixel.com/2018/09/19/8-12-14-vs-16-bit-depth-what-do-you-really-need
On a separate note, even Photoshop does not handle 16bit per channel. Photoshop does actually use 16-bits per channel. However, it treats the 16th digit differently – it is simply added to the value created from the first 15-digits. This is sometimes called 15+1 bits. This means that instead of 216 possible values (which would be 65,536 possible values) there are only 215+1 possible values (which is 32,768 +1 = 32,769 possible values).
Rec-601 (for the older SDTV format, very similar to rec-709) and Rec-709 (the HDTV’s recommended set of color standards, at times also referred to sRGB, although not exactly the same) are currently the most spread color formats and hardware configurations in the world.
Following those you can find the larger P3 gamut, more commonly used in theaters and in digital production houses (with small variations and improvements to color coverage), as well as most of best 4K/WCG TVs.
And a new standard is now promoted against P3, referred to Rec-2020 and UHDTV.
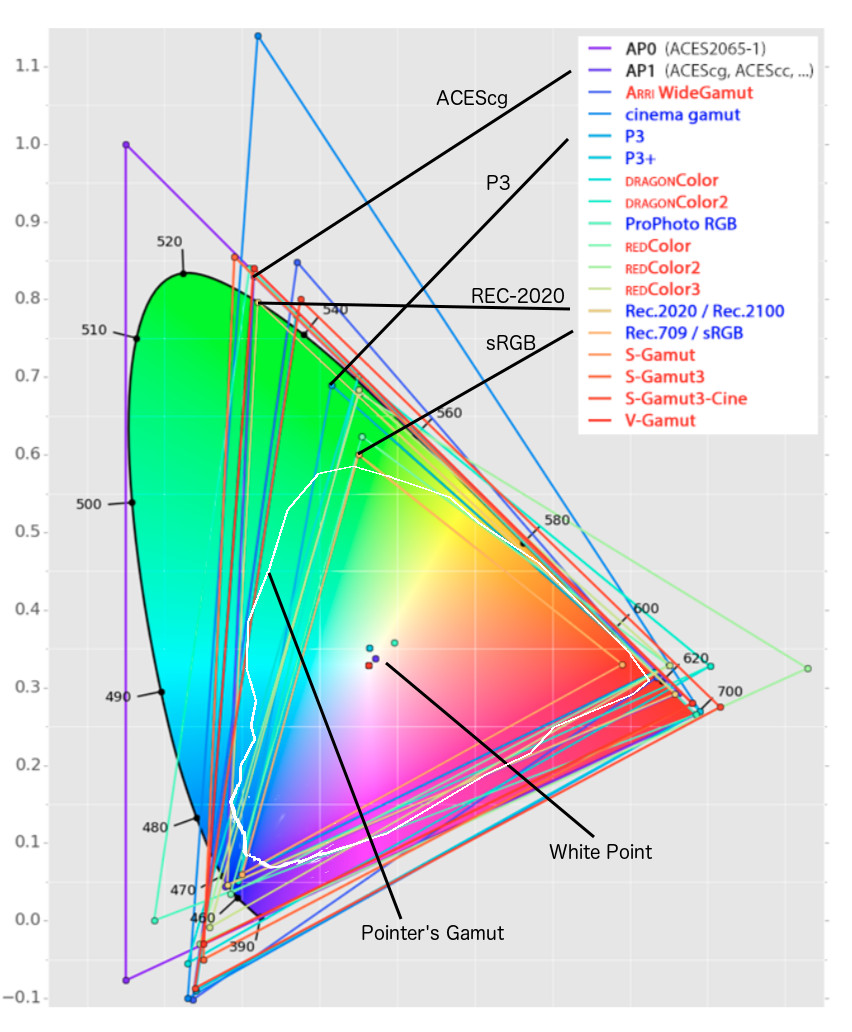
It is still debatable if this is going to be adopted at consumer level beyond the P3, mainly due to lack of hardware supporting it. But initial tests do prove that it would be a future proof investment.
www.colour-science.org/anders-langlands/
Rec. 2020 is ultimately designed for television, and not cinema. Therefore, it is to be expected that its properties must behave according to current signal processing standards. In this respect, its foundation is based on current HD and SD video signal characteristics.
As far as color bit depth is concerned, it allows for a maximum of 12 bits, which is more than enough for humans.
Comparing standards, REC-709 covers 35.9% of the human visible spectrum. P3 45.5%. And REC-2020 75.8%.
https://www.avsforum.com/forum/166-lcd-flat-panel-displays/2812161-what-color-volume.htmlComparing coverage to hardware devices
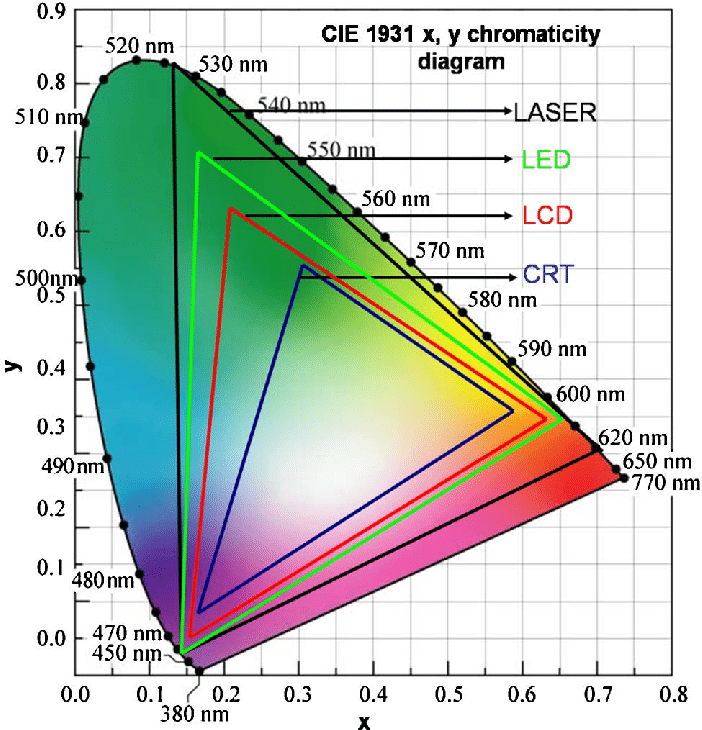
To note that all the new standards generally score very high on the Pointer’s Gamut chart. But with REC-2020 scoring 99.9% vs P3 at 88.2%.
www.tftcentral.co.uk/articles/pointers_gamut.htmhttps://www.slideshare.net/hpduiker/acescg-a-common-color-encoding-for-visual-effects-applications
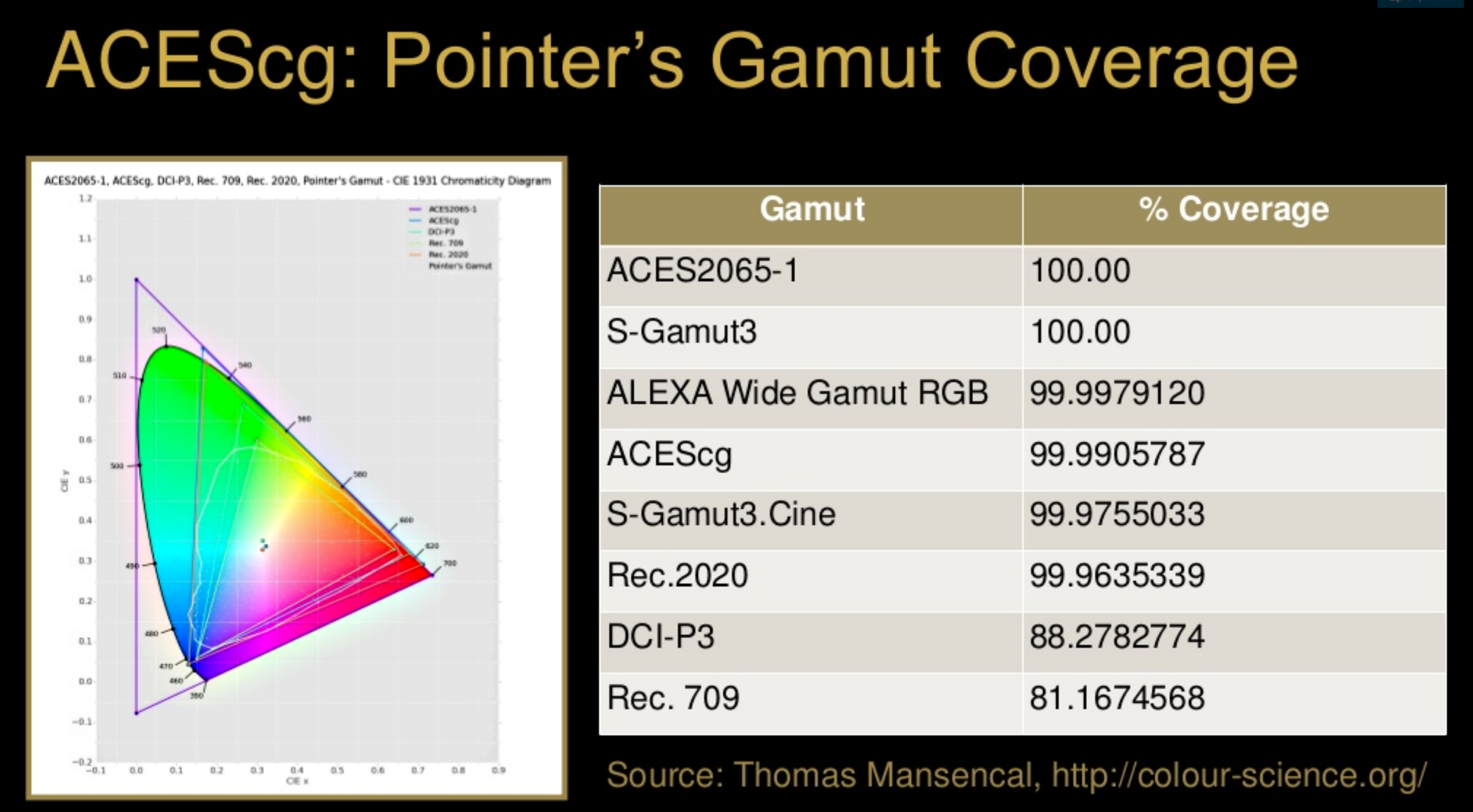
The Pointer’s gamut is (an approximation of) the gamut of real surface colors as can be seen by the human eye, based on the research by Michael R. Pointer (1980). What this means is that every color that can be reflected by the surface of an object of any material is inside the Pointer’s gamut. Basically establishing a widely respected target for color reproduction. Visually, Pointers Gamut represents the colors we see about us in the natural world. Colors outside Pointers Gamut include those that do not occur naturally, such as neon lights and computer-generated colors possible in animation. Which would partially be accounted for with the new gamuts.
cinepedia.com/picture/color-gamut/
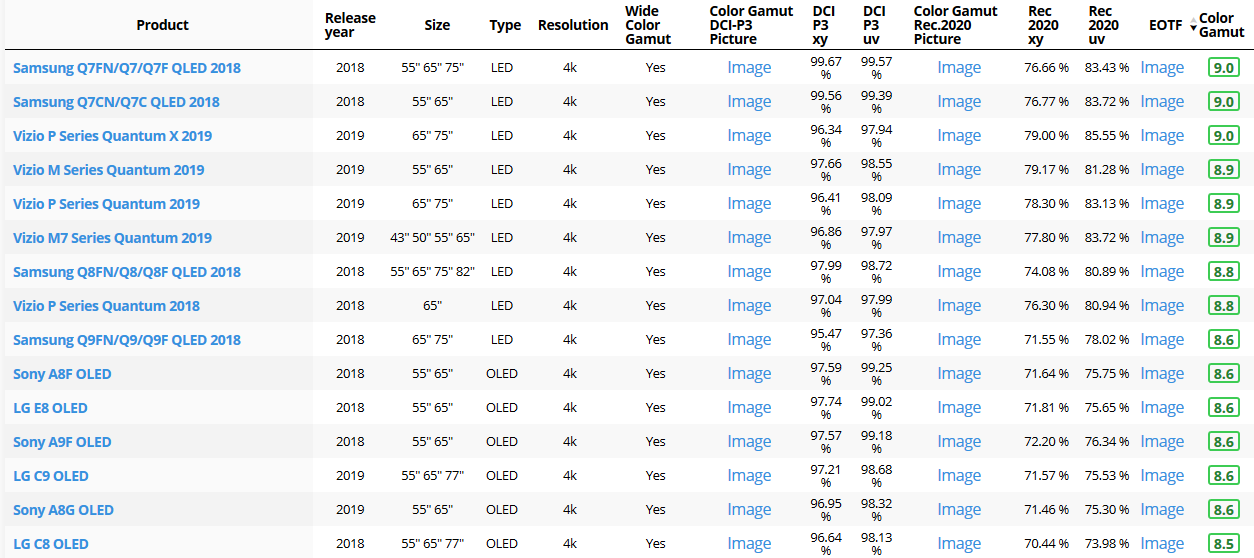
Not all current TVs can support the full spread of the new gamuts. Here is a list of modern TVs’ color coverage in percentage:
www.rtings.com/tv/tests/picture-quality/wide-color-gamut-rec-709-dci-p3-rec-2020There are no TVs that can come close to displaying all the colors within Rec.2020, and there likely won’t be for at least a few years. However, to help future-proof the technology, Rec.2020 support is already baked into the HDR spec. That means that the same genuine HDR media that fills the DCI P3 space on a compatible TV now, will in a few years also fill Rec.2020 on a TV supporting that larger space.
Rec.2020’s main gains are in the number of new tones of green that it will display, though it also offers improvements to the number of blue and red colors as well. Altogether, Rec.2020 will cover about 75% of the visual spectrum, which is a sizeable increase in coverage even over DCI P3.
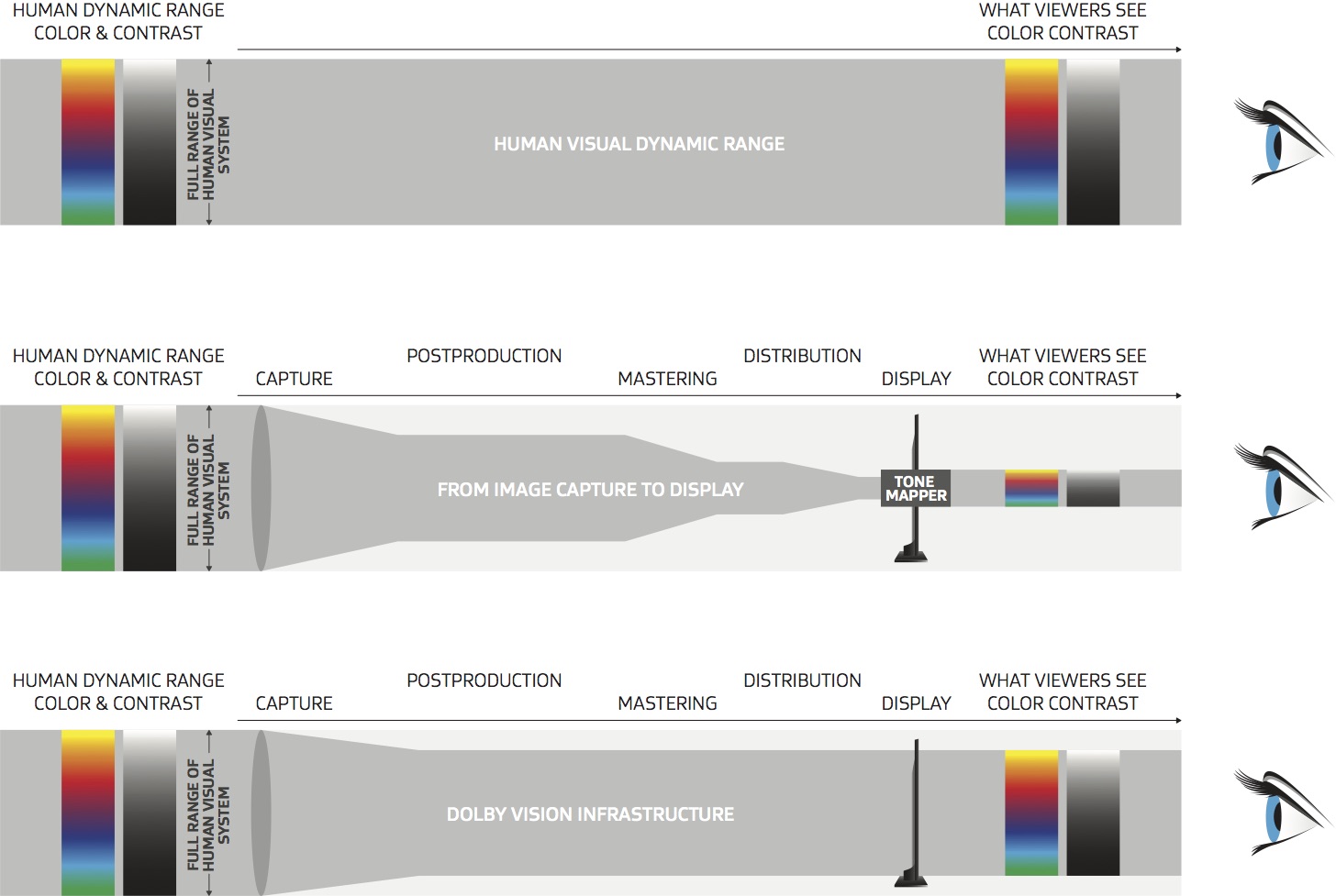
Dolby Vision
https://www.highdefdigest.com/news/show/what-is-dolby-vision/39049
https://www.techhive.com/article/3237232/dolby-vision-vs-hdr10-which-is-best.html
Dolby Vision is a proprietary end-to-end High Dynamic Range (HDR) format that covers content creation and playback through select cinemas, Ultra HD displays, and 4K titles. Like other HDR standards, the process uses expanded brightness to improve contrast between dark and light aspects of an image, bringing out deeper black levels and more realistic details in specular highlights — like the sun reflecting off of an ocean — in specially graded Dolby Vision material.
The iPhone 12 Pro gets the ability to record 4K 10-bit HDR video. According to Apple, it is the very first smartphone that is capable of capturing Dolby Vision HDR.
The iPhone 12 Pro takes two separate exposures and runs them through Apple’s custom image signal processor to create a histogram, which is a graph of the tonal values in each frame. The Dolby Vision metadata is then generated based on that histogram. In Laymen’s terms, it is essentially doing real-time grading while you are shooting. This is only possible due to the A14 Bionic chip.
Dolby Vision also allows for 12-bit color, as opposed to HDR10’s and HDR10+’s 10-bit color. While no retail TV we’re aware of supports 12-bit color, Dolby claims it can be down-sampled in such a way as to render 10-bit color more accurately.

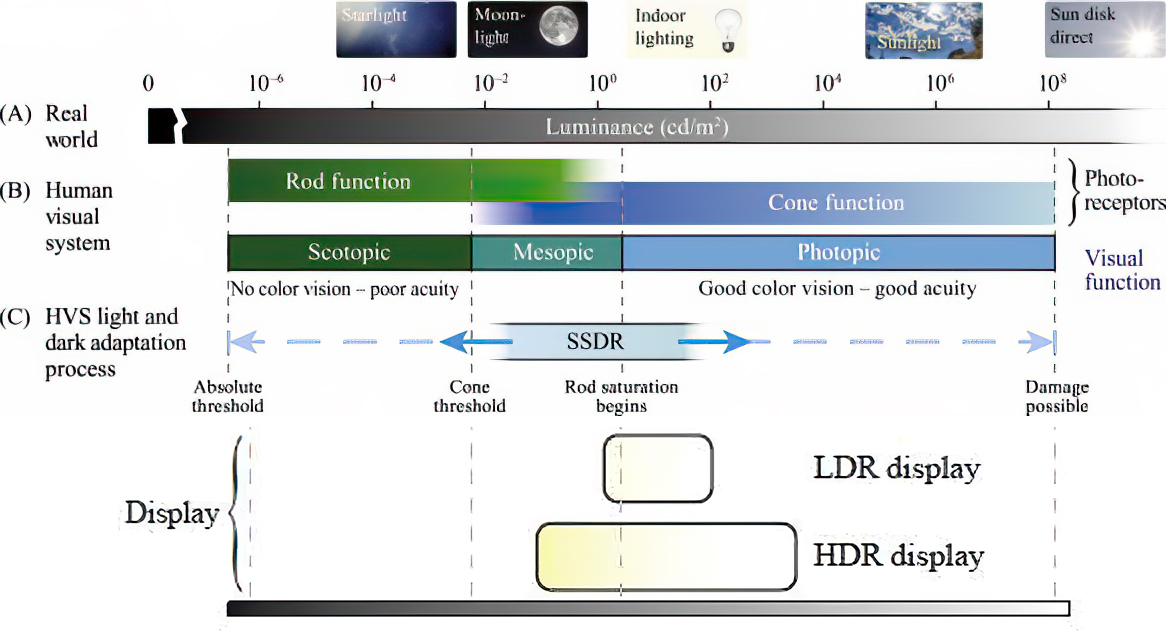
Resources for more reading:
https://www.avsforum.com/forum/166-lcd-flat-panel-displays/2812161-what-color-volume.html
wolfcrow.com/say-hello-to-rec-2020-the-color-space-of-the-future/
www.cnet.com/news/ultra-hd-tv-color-part-ii-the-future/
-
LUX vs LUMEN vs NITS vs CANDELA – What is the difference
Read more: LUX vs LUMEN vs NITS vs CANDELA – What is the differenceMore details here: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
https://www.inhouseav.com.au/blog/beginners-guide-nits-lumens-brightness/

Candela
Candela is the basic unit of measure of the entire volume of light intensity from any point in a single direction from a light source. Note the detail: it measures the total volume of light within a certain beam angle and direction.
While the luminance of starlight is around 0.001 cd/m2, that of a sunlit scene is around 100,000 cd/m2, which is a hundred millions times higher. The luminance of the sun itself is approximately 1,000,000,000 cd/m2.NIT
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Candela_per_square_metre
The candela per square metre (symbol: cd/m2) is the unit of luminance in the International System of Units (SI). The unit is based on the candela, the SI unit of luminous intensity, and the square metre, the SI unit of area. The nit (symbol: nt) is a non-SI name also used for this unit (1 nt = 1 cd/m2).[1] The term nit is believed to come from the Latin word nitēre, “to shine”. As a measure of light emitted per unit area, this unit is frequently used to specify the brightness of a display device.
NIT and cd/m2 (candela power) represent the same thing and can be used interchangeably. One nit is equivalent to one candela per square meter, where the candela is the amount of light which has been emitted by a common tallow candle, but NIT is not part of the International System of Units (abbreviated SI, from Systeme International, in French).
It’s easiest to think of a TV as emitting light directly, in much the same way as the Sun does. Nits are simply the measurement of the level of light (luminance) in a given area which the emitting source sends to your eyes or a camera sensor.
The Nit can be considered a unit of visible-light intensity which is often used to specify the brightness level of an LCD.
1 Nit is approximately equal to 3.426 Lumens. To work out a comparable number of Nits to Lumens, you need to multiply the number of Nits by 3.426. If you know the number of Lumens, and wish to know the Nits, simply divide the number of Lumens by 3.426.
Most consumer desktop LCDs have Nits of 200 to 300, the average TV most likely has an output capability of between 100 and 200 Nits, and an HDR TV ranges from 400 to 1,500 Nits.
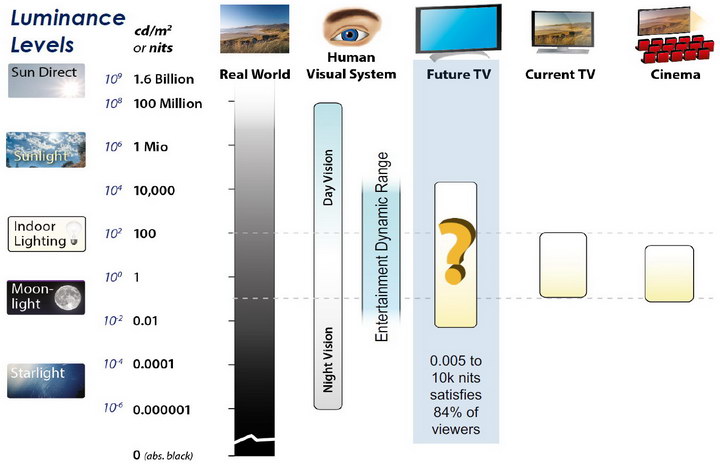
Virtual Production sets currently sport around 6000 NIT ceiling and 1000 NIT wall panels.The ambient brightness of a sunny day with clear blue skies is between 7000-10,000 nits (between 3000-7000 nits for overcast skies and indirect sunlight).
A bright sunny day can have specular highlights that reach over 100,000 nits. Direct sunlight is around 1,600,000,000 nits.
10,000 nits is also the typical brightness of a fluorescent tube – bright, but not painful to look at.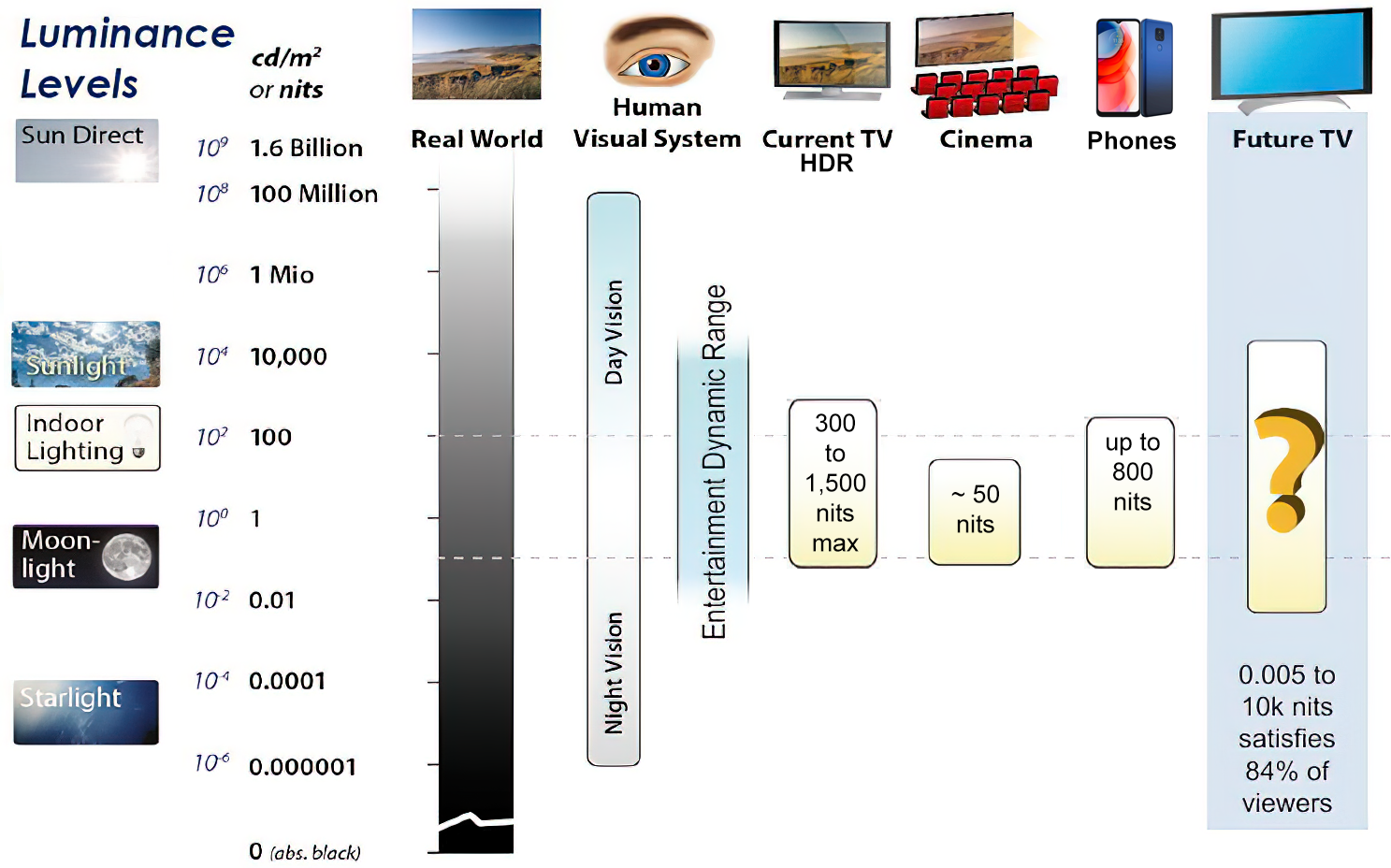
https://www.displaydaily.com/article/display-daily/dolby-vision-vs-hdr10-clarified
Tests showed that a “black level” of 0.005 nits (cd/m²) satisfied the vast majority of viewers. While 0.005 nits is very close to true black, Griffis says Dolby can go down to a black of 0.0001 nits, even though there is no need or ability for displays to get that dark today.
How bright is white? Dolby says the range of 0.005 nits – 10,000 nits satisfied 84% of the viewers in their viewing tests.
The brightest consumer HDR displays today are about 1,500 nits. Professional displays where HDR content is color-graded can achieve up to 4,000 nits peak brightness.High brightness that would be in danger of damaging the eye would be in the neighborhood of 250,000 nits.
Lumens
Lumen is a measure of how much light is emitted (luminance, luminous flux) by an object. It indicates the total potential amount of light from a light source that is visible to the human eye.
Lumen is commonly used in the context of light bulbs or video-projectors as a metric for their brightness power.Lumen is used to describe light output, and about video projectors, it is commonly referred to as ANSI Lumens. Simply put, lumens is how to find out how bright a LED display is. The higher the lumens, the brighter to display!
Technically speaking, a Lumen is the SI unit of luminous flux, which is equal to the amount of light which is emitted per second in a unit solid angle of one steradian from a uniform source of one-candela intensity radiating in all directions.
LUX
Lux (lx) or often Illuminance, is a photometric unit along a given area, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts. It is the measure of light at a specific distance within a specific area at that distance. Often used to measure the incidental sun’s intensity.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
59 AI Filmmaking Tools For Your Workflow
-
Google – Artificial Intelligence free courses
-
Photography basics: Solid Angle measures
-
Animation/VFX/Game Industry JOB POSTINGS by Chris Mayne
-
Methods for creating motion blur in Stop motion
-
Image rendering bit depth
-
Jesse Zumstein – Jobs in games
-
PixelSham – Introduction to Python 2022
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.