COMPOSITION
-
Photography basics: Camera Aspect Ratio, Sensor Size and Depth of Field – resolutions
Read more: Photography basics: Camera Aspect Ratio, Sensor Size and Depth of Field – resolutionshttp://www.shutterangle.com/2012/cinematic-look-aspect-ratio-sensor-size-depth-of-field/
http://www.shutterangle.com/2012/film-video-aspect-ratio-artistic-choice/
-
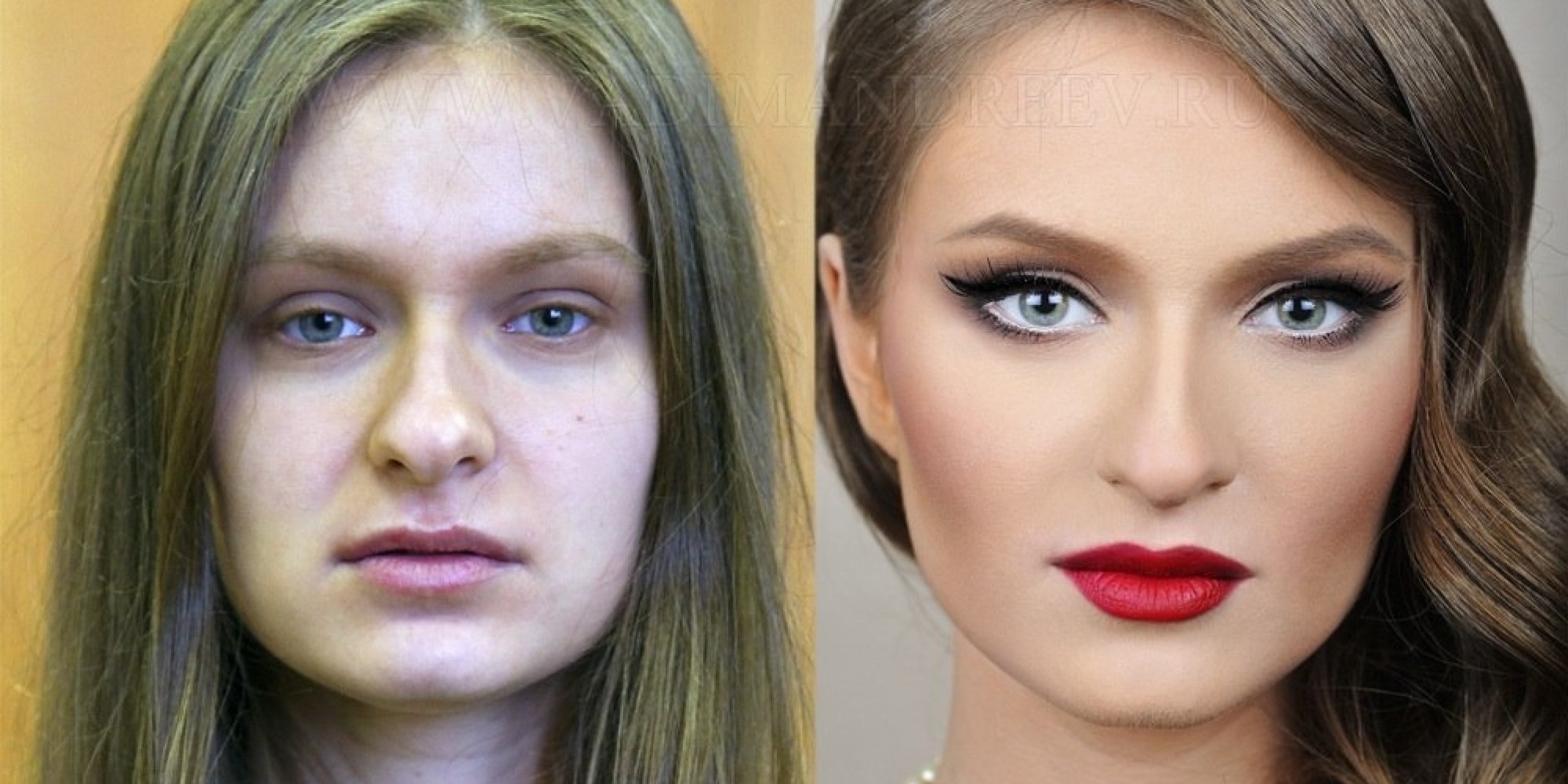
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
-
7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition
Read more: 7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition1. Watch every frame of raw footage twice. On the second time, take notes. If you don’t do this and try to start developing a scene premature, then it’s a big disservice to yourself and to the director, actors and production crew.
2. Nurture the relationships with the director. You are the secondary person in the relationship. Be calm and continually offer solutions. Get the main intention of the film as soon as possible from the director.
3. Organize your media so that you can find any shot instantly.
4. Factor in extra time for renders, exports, errors and crashes.
5. Attempt edits and ideas that shouldn’t work. It just might work. Until you do it and watch it, you won’t know. Don’t rule out ideas just because they don’t make sense in your mind.
6. Spend more time on your audio. It’s the glue of your edit. AUDIO SAVES EVERYTHING. Create fluid and seamless audio under your video.
7. Make cuts for the scene, but always in context for the whole film. Have a macro and a micro view at all times.
DESIGN
-
Arminas Valunas – “Coca-Cola: Wherever you are.”
Read more: Arminas Valunas – “Coca-Cola: Wherever you are.”Arminas created this using Juggernaut Xl model and QR Code Monster SDXL ControlNet.
His pipeline:
Static Images – Forge UI.
Upscaled with Leonardo AI universal upscaler.
Animated with Runway ML and Minimax.
Video upscale – Topaz Video AI.
Composited in Adobe Premiere.
Juggernaut Xl download here:
https://civitai.com/models/133005/juggernaut-xl
QR Code Monster SDXL:
https://civitai.com/models/197247?modelVersionId=221829
COLOR
-
OpenColorIO standard
Read more: OpenColorIO standardhttps://www.provideocoalition.com/color-management-part-11-introducing-opencolorio/
OpenColorIO (OCIO) is a new open source project from Sony Imageworks.
Based on development started in 2003, OCIO enables color transforms and image display to be handled in a consistent manner across multiple graphics applications. Unlike other color management solutions, OCIO is geared towards motion-picture post production, with an emphasis on visual effects and animation color pipelines.
LIGHTING
-
Neural Microfacet Fields for Inverse Rendering
Read more: Neural Microfacet Fields for Inverse Renderinghttps://half-potato.gitlab.io/posts/nmf/
-
Sun cone angle (angular diameter) as perceived by earth viewers
Read more: Sun cone angle (angular diameter) as perceived by earth viewersAlso see:
https://www.pixelsham.com/2020/08/01/solid-angle-measures/
The cone angle of the sun refers to the angular diameter of the sun as observed from Earth, which is related to the apparent size of the sun in the sky.
The angular diameter of the sun, or the cone angle of the sunlight as perceived from Earth, is approximately 0.53 degrees on average. This value can vary slightly due to the elliptical nature of Earth’s orbit around the sun, but it generally stays within a narrow range.
Here’s a more precise breakdown:
-
- Average Angular Diameter: About 0.53 degrees (31 arcminutes)
- Minimum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.52 degrees (when Earth is at aphelion, the farthest point from the sun)
- Maximum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.54 degrees (when Earth is at perihelion, the closest point to the sun)
This angular diameter remains relatively constant throughout the day because the sun’s distance from Earth does not change significantly over a single day.
To summarize, the cone angle of the sun’s light, or its angular diameter, is typically around 0.53 degrees, regardless of the time of day.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angular_diameter
-
-
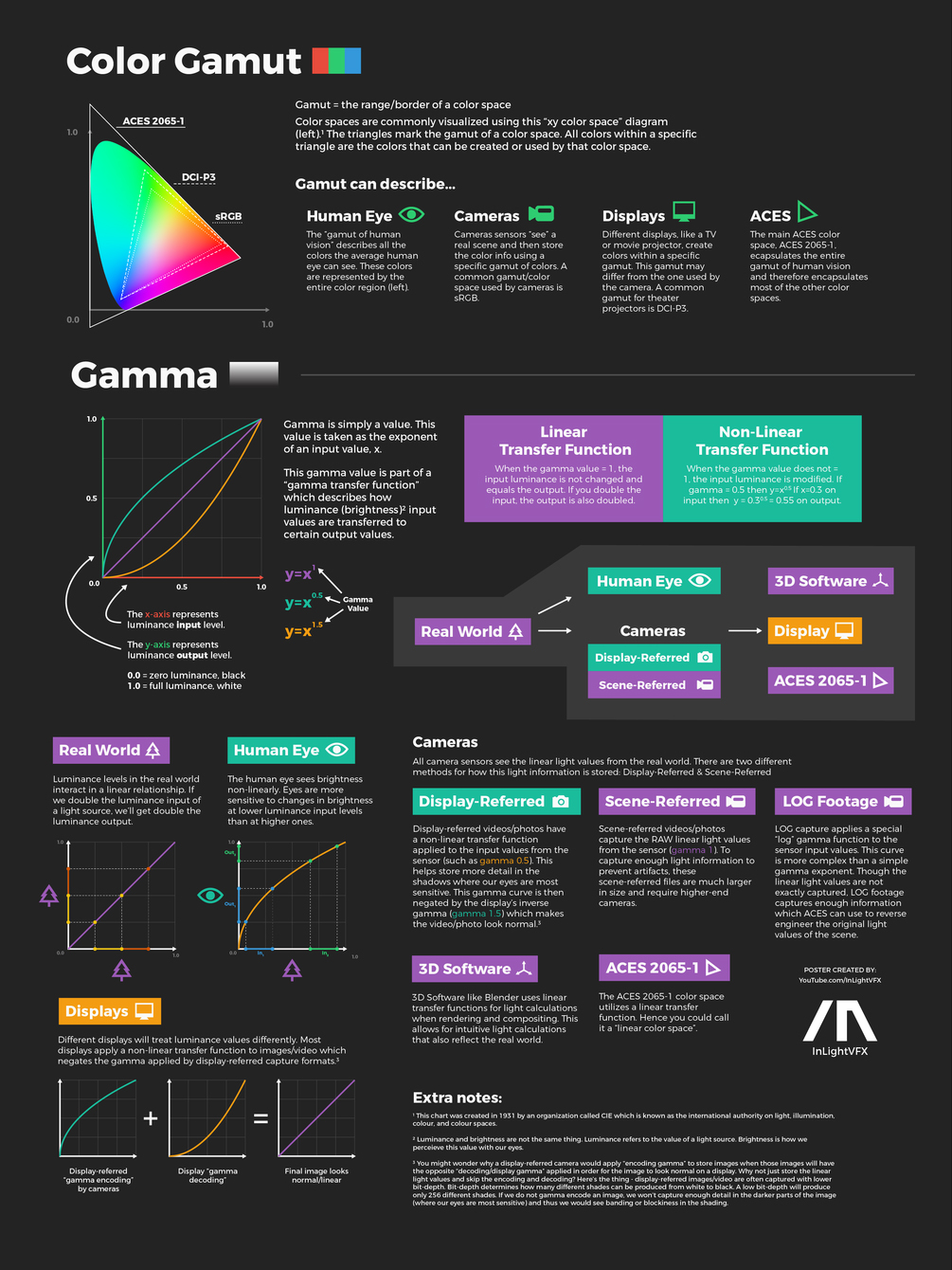
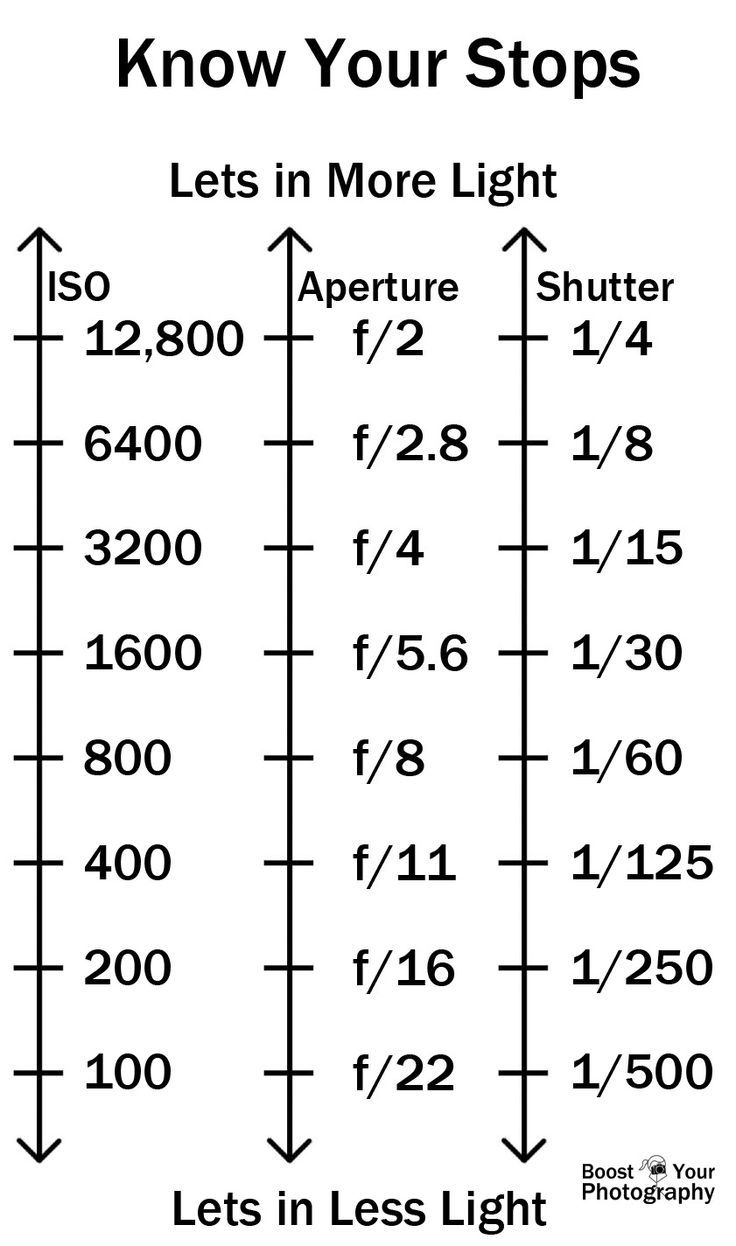
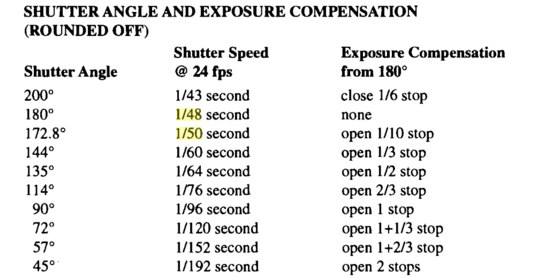
Photography basics: How Exposure Stops (Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO) Affect Your Photos – cheat sheet cards
Read more: Photography basics: How Exposure Stops (Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO) Affect Your Photos – cheat sheet cardsAlso see:
https://www.pixelsham.com/2018/11/22/exposure-value-measurements/
https://www.pixelsham.com/2016/03/03/f-stop-vs-t-stop/
An exposure stop is a unit measurement of Exposure as such it provides a universal linear scale to measure the increase and decrease in light, exposed to the image sensor, due to changes in shutter speed, iso and f-stop.
+-1 stop is a doubling or halving of the amount of light let in when taking a photo
1 EV (exposure value) is just another way to say one stop of exposure change.
https://www.photographymad.com/pages/view/what-is-a-stop-of-exposure-in-photography
Same applies to shutter speed, iso and aperture.
Doubling or halving your shutter speed produces an increase or decrease of 1 stop of exposure.
Doubling or halving your iso speed produces an increase or decrease of 1 stop of exposure.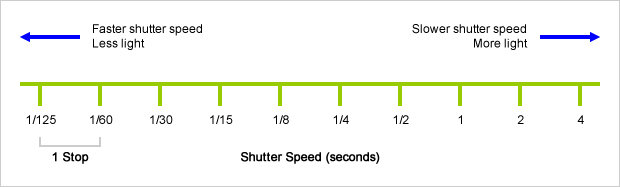
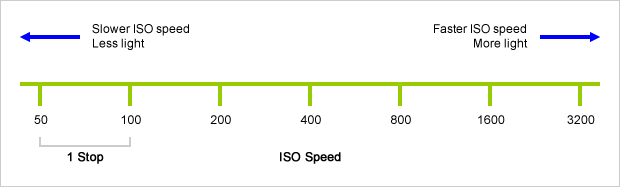

Because of the way f-stop numbers are calculated (ratio of focal length/lens diameter, where focal length is the distance between the lens and the sensor), an f-stop doesn’t relate to a doubling or halving of the value, but to the doubling/halving of the area coverage of a lens in relation to its focal length. And as such, to a multiplying or dividing by 1.41 (the square root of 2). For example, going from f/2.8 to f/4 is a decrease of 1 stop because 4 = 2.8 * 1.41. Changing from f/16 to f/11 is an increase of 1 stop because 11 = 16 / 1.41.
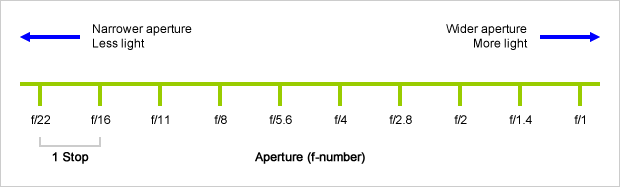
A wider aperture means that light proceeding from the foreground, subject, and background is entering at more oblique angles than the light entering less obliquely.
Consider that absolutely everything is bathed in light, therefore light bouncing off of anything is effectively omnidirectional. Your camera happens to be picking up a tiny portion of the light that’s bouncing off into infinity.
Now consider that the wider your iris/aperture, the more of that omnidirectional light you’re picking up:
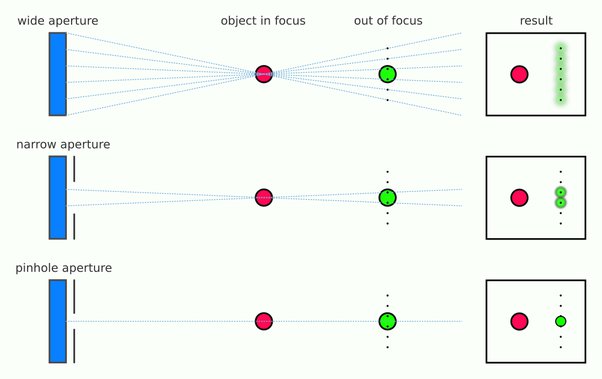
When you have a very narrow iris you are eliminating a lot of oblique light. Whatever light enters, from whatever distance, enters moderately parallel as a whole. When you have a wide aperture, much more light is entering at a multitude of angles. Your lens can only focus the light from one depth – the foreground/background appear blurred because it cannot be focused on.
https://frankwhitephotography.com/index.php?id=28:what-is-a-stop-in-photography
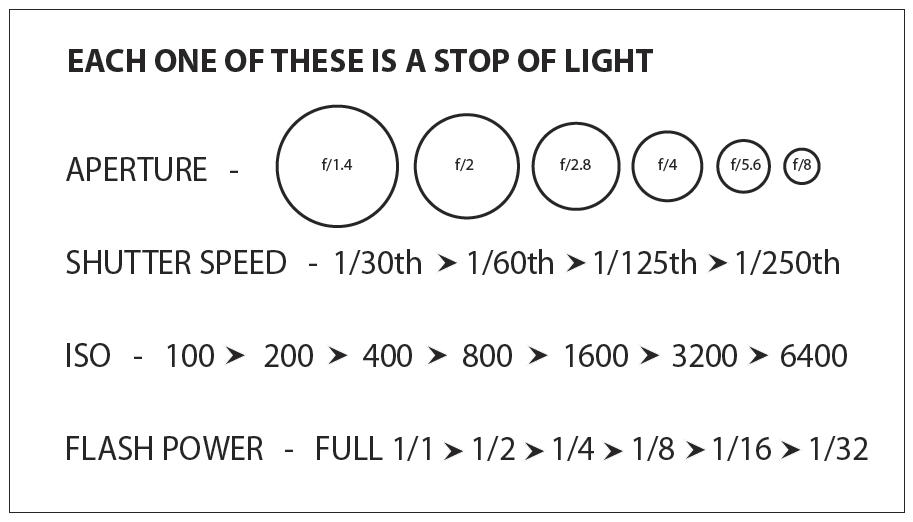
The great thing about stops is that they give us a way to directly compare shutter speed, aperture diameter, and ISO speed. This means that we can easily swap these three components about while keeping the overall exposure the same.
http://lifehacker.com/how-aperture-shutter-speed-and-iso-affect-pictures-sh-1699204484
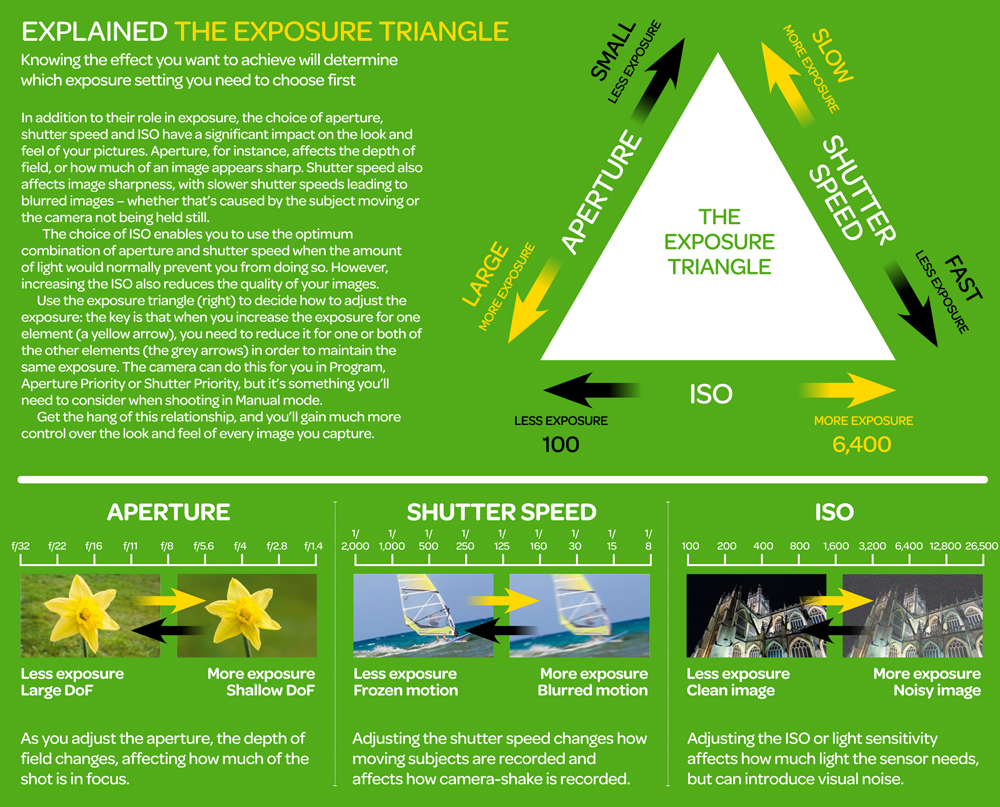
https://www.techradar.com/how-to/the-exposure-triangle
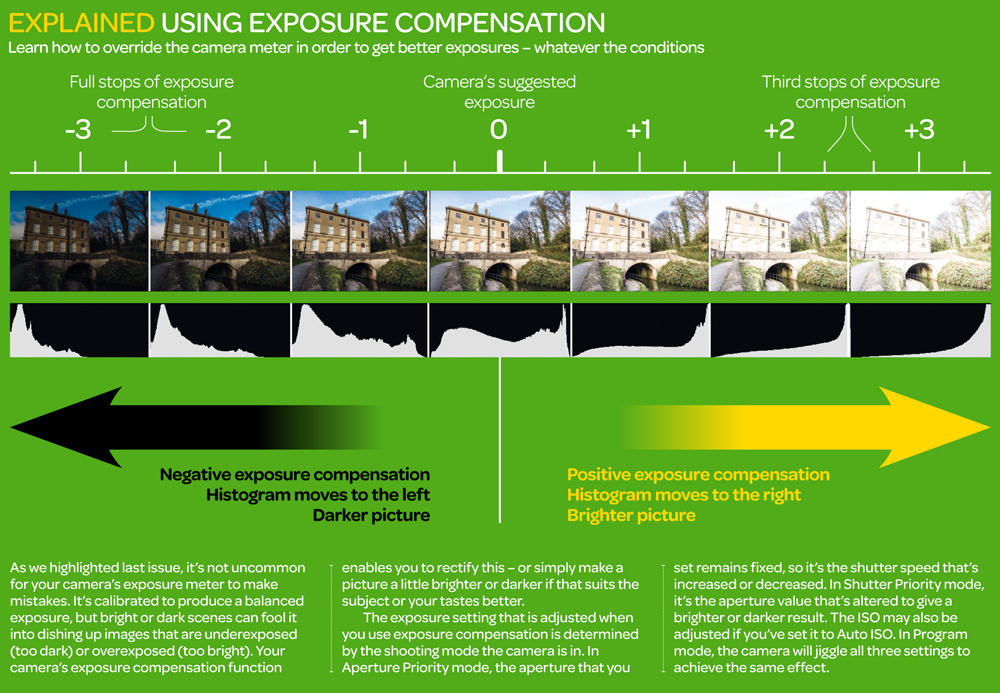
https://www.videoschoolonline.com/what-is-an-exposure-stop
Note. All three of these measurements (aperture, shutter, iso) have full stops, half stops and third stops, but if you look at the numbers they aren’t always consistent. For example, a one third stop between ISO100 and ISO 200 would be ISO133, yet most cameras are marked at ISO125.
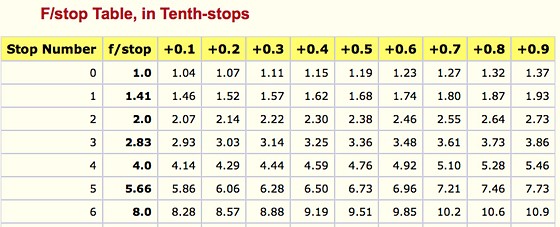
Third-stops are especially important as they’re the increment that most cameras use for their settings. These are just imaginary divisions in each stop.
From a practical standpoint manufacturers only standardize the full stops, meaning that while they try and stay somewhat consistent there is some rounding up going on between the smaller numbers.
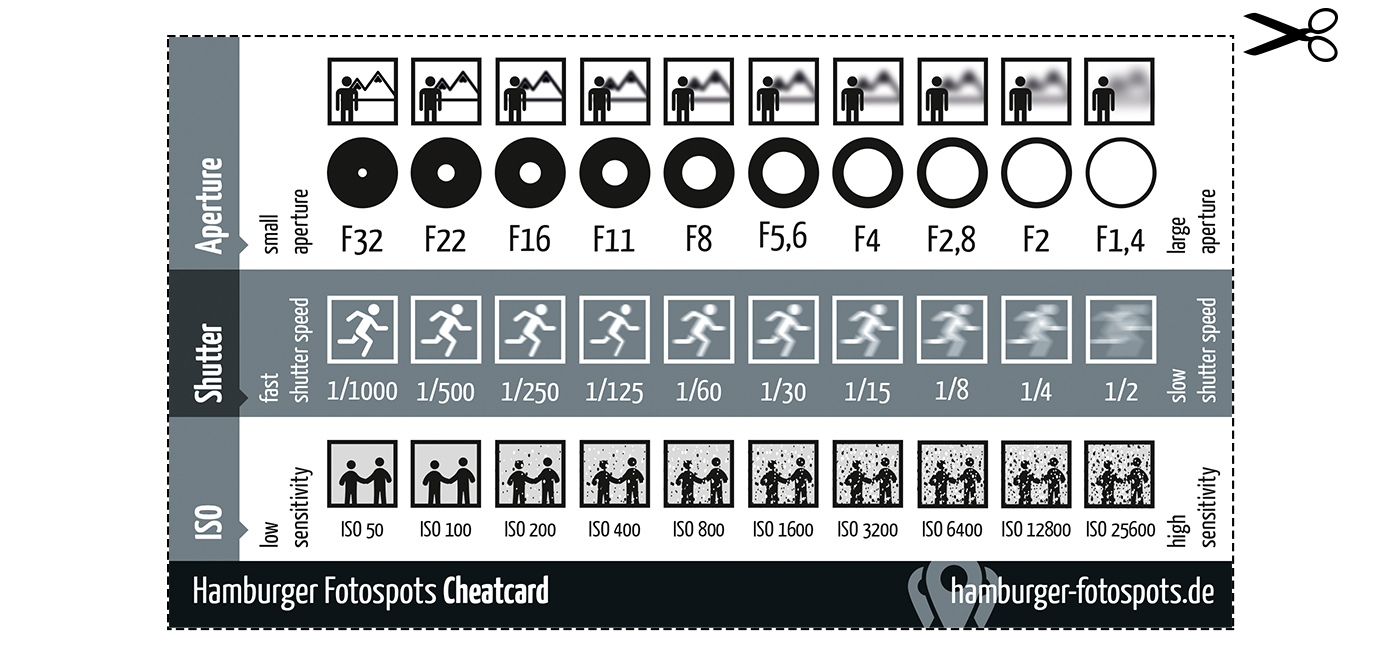
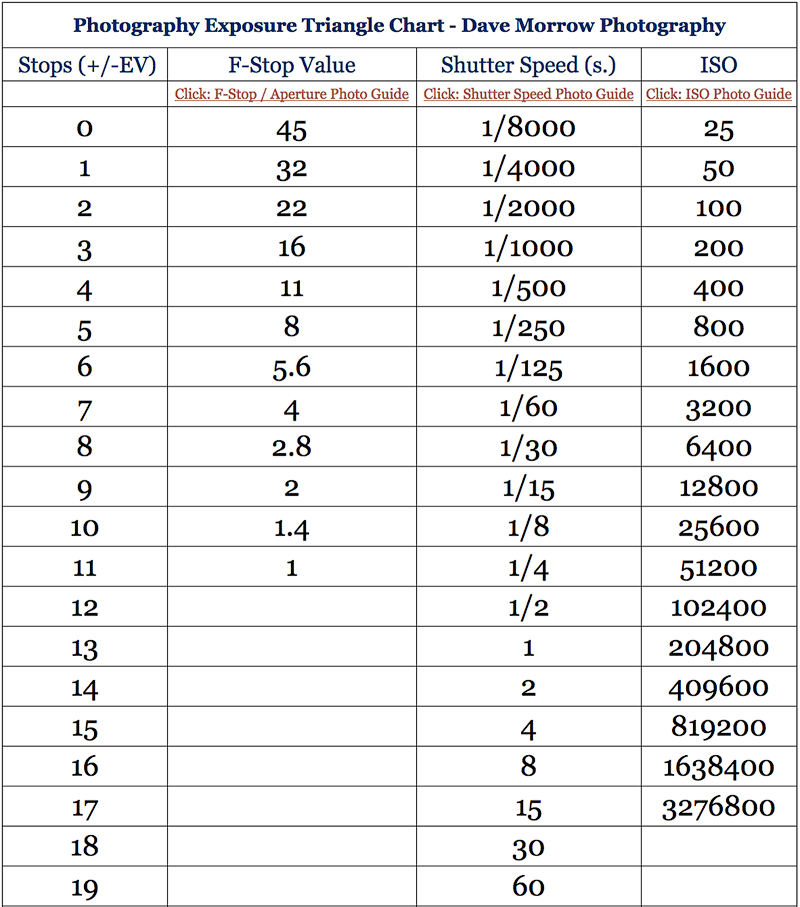
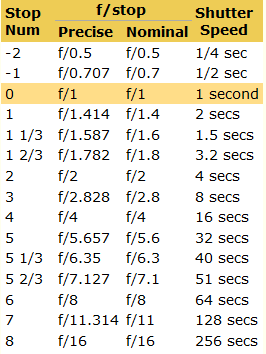
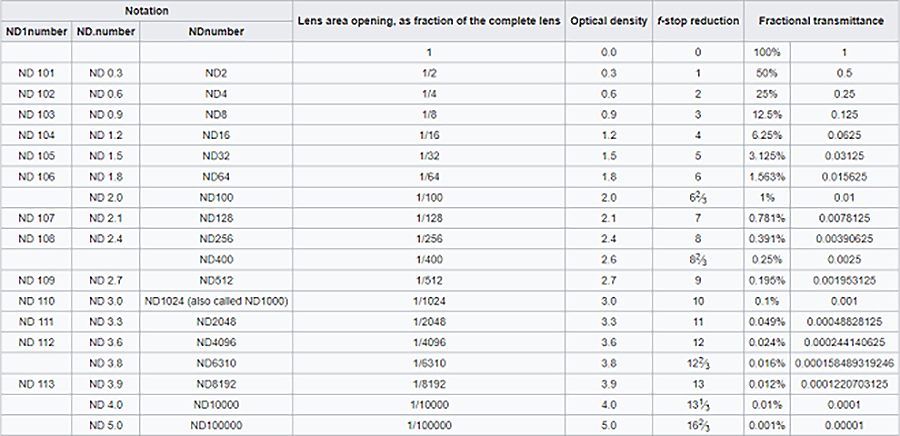
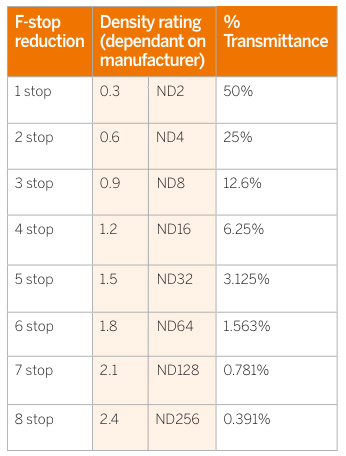
Note that ND Filters directly modify the exposure triangle.

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Yann Lecun: Meta AI, Open Source, Limits of LLMs, AGI & the Future of AI | Lex Fridman Podcast #416
-
Google – Artificial Intelligence free courses
-
Photography basics: Solid Angle measures
-
UV maps
-
RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program
-
Web vs Printing or digital RGB vs CMYK
-
Godot Cheat Sheets
-
Film Production walk-through – pipeline – I want to make a … movie
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.