COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camera
Read more: Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camerahttps://color-lab-eilat.github.io/Spectral-sensitivity-estimation-web/
A number of problems in computer vision and related fields would be mitigated if camera spectral sensitivities were known. As consumer cameras are not designed for high-precision visual tasks, manufacturers do not disclose spectral sensitivities. Their estimation requires a costly optical setup, which triggered researchers to come up with numerous indirect methods that aim to lower cost and complexity by using color targets. However, the use of color targets gives rise to new complications that make the estimation more difficult, and consequently, there currently exists no simple, low-cost, robust go-to method for spectral sensitivity estimation that non-specialized research labs can adopt. Furthermore, even if not limited by hardware or cost, researchers frequently work with imagery from multiple cameras that they do not have in their possession.
To provide a practical solution to this problem, we propose a framework for spectral sensitivity estimation that not only does not require any hardware (including a color target), but also does not require physical access to the camera itself. Similar to other work, we formulate an optimization problem that minimizes a two-term objective function: a camera-specific term from a system of equations, and a universal term that bounds the solution space.
Different than other work, we utilize publicly available high-quality calibration data to construct both terms. We use the colorimetric mapping matrices provided by the Adobe DNG Converter to formulate the camera-specific system of equations, and constrain the solutions using an autoencoder trained on a database of ground-truth curves. On average, we achieve reconstruction errors as low as those that can arise due to manufacturing imperfections between two copies of the same camera. We provide predicted sensitivities for more than 1,000 cameras that the Adobe DNG Converter currently supports, and discuss which tasks can become trivial when camera responses are available.
-
Akiyoshi Kitaoka – Surround biased illumination perception
Read more: Akiyoshi Kitaoka – Surround biased illumination perceptionhttps://x.com/AkiyoshiKitaoka/status/1798705648001327209
The left face appears whitish and the right one blackish, but they are made up of the same luminance.
https://community.wolfram.com/groups/-/m/t/3191015
Illusory staircase Gelb effect
https://www.psy.ritsumei.ac.jp/akitaoka/illgelbe.html
LIGHTING
-
StudioBinder.com – Photography basics: What is Dynamic Range in Photography
Read more: StudioBinder.com – Photography basics: What is Dynamic Range in Photographyhttps://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-dynamic-range-photography/
https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction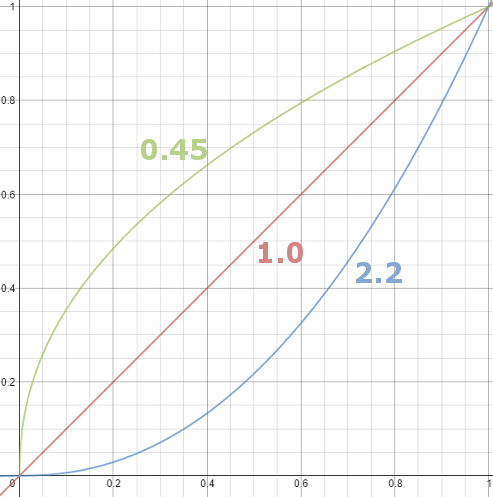
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.Our eyes, different camera or video recorder devices do not correctly capture luminance. (they are not linear)
Different display devices (monitor, phone screen, TV) do not display luminance correctly neither. So, one needs to correct them, therefore the gamma correction function.The human perception of brightness, under common illumination conditions (not pitch black nor blindingly bright), follows an approximate power function (note: no relation to the gamma function), with greater sensitivity to relative differences between darker tones than between lighter ones, consistent with the Stevens’ power law for brightness perception. If images are not gamma-encoded, they allocate too many bits or too much bandwidth to highlights that humans cannot differentiate, and too few bits or too little bandwidth to shadow values that humans are sensitive to and would require more bits/bandwidth to maintain the same visual quality.
https://blog.amerlux.com/4-things-architects-should-know-about-lumens-vs-perceived-brightness/
cones manage color receptivity, rods determine how large our pupils should be. The larger (more dilated) our pupils are, the more light enters our eyes. In dark situations, our rods dilate our pupils so we can see better. This impacts how we perceive brightness.
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
A gamma encoded image has to have “gamma correction” applied when it is viewed — which effectively converts it back into light from the original scene. In other words, the purpose of gamma encoding is for recording the image — not for displaying the image. Fortunately this second step (the “display gamma”) is automatically performed by your monitor and video card. The following diagram illustrates how all of this fits together:
Display gamma
The display gamma can be a little confusing because this term is often used interchangeably with gamma correction, since it corrects for the file gamma. This is the gamma that you are controlling when you perform monitor calibration and adjust your contrast setting. Fortunately, the industry has converged on a standard display gamma of 2.2, so one doesn’t need to worry about the pros/cons of different values.Gamma encoding of images is used to optimize the usage of bits when encoding an image, or bandwidth used to transport an image, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and color. Human response to luminance is also biased. Especially sensible to dark areas.
Thus, the human visual system has a non-linear response to the power of the incoming light, so a fixed increase in power will not have a fixed increase in perceived brightness.
We perceive a value as half bright when it is actually 18% of the original intensity not 50%. As such, our perception is not linear.You probably already know that a pixel can have any ‘value’ of Red, Green, and Blue between 0 and 255, and you would therefore think that a pixel value of 127 would appear as half of the maximum possible brightness, and that a value of 64 would represent one-quarter brightness, and so on. Well, that’s just not the case.
Pixar Color Management
https://renderman.pixar.com/color-management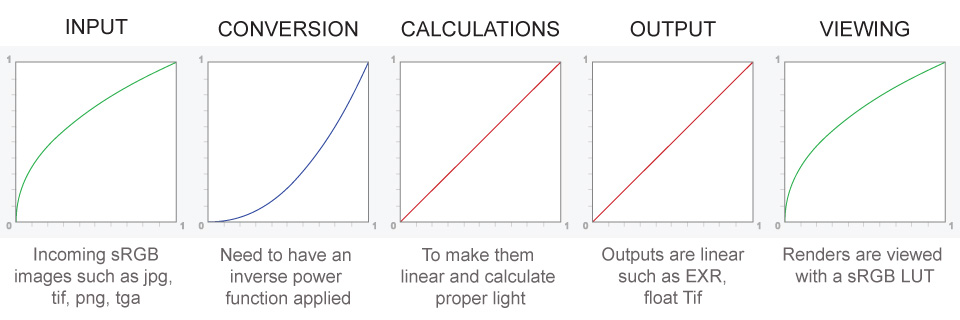
– Why do we need linear gamma?
Because light works linearly and therefore only works properly when it lights linear values.– Why do we need to view in sRGB?
Because the resulting linear image in not suitable for viewing, but contains all the proper data. Pixar’s IT viewer can compensate by showing the rendered image through a sRGB look up table (LUT), which is identical to what will be the final image after the sRGB gamma curve is applied in post.This would be simple enough if every software would play by the same rules, but they don’t. In fact, the default gamma workflow for many 3D software is incorrect. This is where the knowledge of a proper imaging workflow comes in to save the day.
Cathode-ray tubes have a peculiar relationship between the voltage applied to them, and the amount of light emitted. It isn’t linear, and in fact it follows what’s called by mathematicians and other geeks, a ‘power law’ (a number raised to a power). The numerical value of that power is what we call the gamma of the monitor or system.
Thus. Gamma describes the nonlinear relationship between the pixel levels in your computer and the luminance of your monitor (the light energy it emits) or the reflectance of your prints. The equation is,
Luminance = C * value^gamma + black level
– C is set by the monitor Contrast control.
– Value is the pixel level normalized to a maximum of 1. For an 8 bit monitor with pixel levels 0 – 255, value = (pixel level)/255.
– Black level is set by the (misnamed) monitor Brightness control. The relationship is linear if gamma = 1. The chart illustrates the relationship for gamma = 1, 1.5, 1.8 and 2.2 with C = 1 and black level = 0.
Gamma affects middle tones; it has no effect on black or white. If gamma is set too high, middle tones appear too dark. Conversely, if it’s set too low, middle tones appear too light.
The native gamma of monitors– the relationship between grid voltage and luminance– is typically around 2.5, though it can vary considerably. This is well above any of the display standards, so you must be aware of gamma and correct it.
A display gamma of 2.2 is the de facto standard for the Windows operating system and the Internet-standard sRGB color space.
The old standard for Mcintosh and prepress file interchange is 1.8. It is now 2.2 as well.
Video cameras have gammas of approximately 0.45– the inverse of 2.2. The viewing or system gamma is the product of the gammas of all the devices in the system– the image acquisition device (film+scanner or digital camera), color lookup table (LUT), and monitor. System gamma is typically between 1.1 and 1.5. Viewing flare and other factor make images look flat at system gamma = 1.0.
Most laptop LCD screens are poorly suited for critical image editing because gamma is extremely sensitive to viewing angle.
More about screens
https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/gamma-correction.htm
CRT Monitors. Due to an odd bit of engineering luck, the native gamma of a CRT is 2.5 — almost the inverse of our eyes. Values from a gamma-encoded file could therefore be sent straight to the screen and they would automatically be corrected and appear nearly OK. However, a small gamma correction of ~1/1.1 needs to be applied to achieve an overall display gamma of 2.2. This is usually already set by the manufacturer’s default settings, but can also be set during monitor calibration.
LCD Monitors. LCD monitors weren’t so fortunate; ensuring an overall display gamma of 2.2 often requires substantial corrections, and they are also much less consistent than CRT’s. LCDs therefore require something called a look-up table (LUT) in order to ensure that input values are depicted using the intended display gamma (amongst other things). See the tutorial on monitor calibration: look-up tables for more on this topic.
About black level (brightness). Your monitor’s brightness control (which should actually be called black level) can be adjusted using the mostly black pattern on the right side of the chart. This pattern contains two dark gray vertical bars, A and B, which increase in luminance with increasing gamma. (If you can’t see them, your black level is way low.) The left bar (A) should be just above the threshold of visibility opposite your chosen gamma (2.2 or 1.8)– it should be invisible where gamma is lower by about 0.3. The right bar (B) should be distinctly visible: brighter than (A), but still very dark. This chart is only for monitors; it doesn’t work on printed media.
The 1.8 and 2.2 gray patterns at the bottom of the image represent a test of monitor quality and calibration. If your monitor is functioning properly and calibrated to gamma = 2.2 or 1.8, the corresponding pattern will appear smooth neutral gray when viewed from a distance. Any waviness, irregularity, or color banding indicates incorrect monitor calibration or poor performance.
Another test to see whether one’s computer monitor is properly hardware adjusted and can display shadow detail in sRGB images properly, they should see the left half of the circle in the large black square very faintly but the right half should be clearly visible. If not, one can adjust their monitor’s contrast and/or brightness setting. This alters the monitor’s perceived gamma. The image is best viewed against a black background.
This procedure is not suitable for calibrating or print-proofing a monitor. It can be useful for making a monitor display sRGB images approximately correctly, on systems in which profiles are not used (for example, the Firefox browser prior to version 3.0 and many others) or in systems that assume untagged source images are in the sRGB colorspace.
On some operating systems running the X Window System, one can set the gamma correction factor (applied to the existing gamma value) by issuing the command xgamma -gamma 0.9 for setting gamma correction factor to 0.9, and xgamma for querying current value of that factor (the default is 1.0). In OS X systems, the gamma and other related screen calibrations are made through the System Preference
https://www.kinematicsoup.com/news/2016/6/15/gamma-and-linear-space-what-they-are-how-they-differ
Linear color space means that numerical intensity values correspond proportionally to their perceived intensity. This means that the colors can be added and multiplied correctly. A color space without that property is called ”non-linear”. Below is an example where an intensity value is doubled in a linear and a non-linear color space. While the corresponding numerical values in linear space are correct, in the non-linear space (gamma = 0.45, more on this later) we can’t simply double the value to get the correct intensity.
The need for gamma arises for two main reasons: The first is that screens have been built with a non-linear response to intensity. The other is that the human eye can tell the difference between darker shades better than lighter shades. This means that when images are compressed to save space, we want to have greater accuracy for dark intensities at the expense of lighter intensities. Both of these problems are resolved using gamma correction, which is to say the intensity of every pixel in an image is put through a power function. Specifically, gamma is the name given to the power applied to the image.
CRT screens, simply by how they work, apply a gamma of around 2.2, and modern LCD screens are designed to mimic that behavior. A gamma of 2.2, the reciprocal of 0.45, when applied to the brightened images will darken them, leaving the original image.
-
Bella – Fast Spectral Rendering
Read more: Bella – Fast Spectral RenderingBella works in spectral space, allowing effects such as BSDF wavelength dependency, diffraction, or atmosphere to be modeled far more accurately than in color space.
https://superrendersfarm.com/blog/uncategorized/bella-a-new-spectral-physically-based-renderer/
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
Read more: HDRI Median Cut pluginwww.hdrlabs.com/picturenaut/plugins.html
Note. The Median Cut algorithm is typically used for color quantization, which involves reducing the number of colors in an image while preserving its visual quality. It doesn’t directly provide a way to identify the brightest areas in an image. However, if you’re interested in identifying the brightest areas, you might want to look into other methods like thresholding, histogram analysis, or edge detection, through openCV for example.
Here is an openCV example:
# bottom left coordinates = 0,0 import numpy as np import cv2 # Load the HDR or EXR image image = cv2.imread('your_image_path.exr', cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED) # Load as-is without modification # Calculate the luminance from the HDR channels (assuming RGB format) luminance = np.dot(image[..., :3], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114]) # Set a threshold value based on estimated EV threshold_value = 2.4 # Estimated threshold value based on 4.8 EV # Apply the threshold to identify bright areas # Theluminancearray contains the calculated luminance values for each pixel in the image. # Thethreshold_valueis a user-defined value that represents a cutoff point, separating "bright" and "dark" areas in terms of perceived luminance.thresholded = (luminance > threshold_value) * 255 # Convert the thresholded image to uint8 for contour detection thresholded = thresholded.astype(np.uint8) # Find contours of the bright areas contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresholded, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # Create a list to store the bounding boxes of bright areas bright_areas = [] # Iterate through contours and extract bounding boxes for contour in contours: x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour) # Adjust y-coordinate based on bottom-left origin y_bottom_left_origin = image.shape[0] - (y + h) bright_areas.append((x, y_bottom_left_origin, x + w, y_bottom_left_origin + h)) # Store as (x1, y1, x2, y2) # Print the identified bright areas print("Bright Areas (x1, y1, x2, y2):") for area in bright_areas: print(area)More details
Luminance and Exposure in an EXR Image:
- An EXR (Extended Dynamic Range) image format is often used to store high dynamic range (HDR) images that contain a wide range of luminance values, capturing both dark and bright areas.
- Luminance refers to the perceived brightness of a pixel in an image. In an RGB image, luminance is often calculated using a weighted sum of the red, green, and blue channels, where different weights are assigned to each channel to account for human perception.
- In an EXR image, the pixel values can represent radiometrically accurate scene values, including actual radiance or irradiance levels. These values are directly related to the amount of light emitted or reflected by objects in the scene.
The luminance line is calculating the luminance of each pixel in the image using a weighted sum of the red, green, and blue channels. The three float values [0.299, 0.587, 0.114] are the weights used to perform this calculation.
These weights are based on the concept of luminosity, which aims to approximate the perceived brightness of a color by taking into account the human eye’s sensitivity to different colors. The values are often derived from the NTSC (National Television System Committee) standard, which is used in various color image processing operations.
Here’s the breakdown of the float values:
- 0.299: Weight for the red channel.
- 0.587: Weight for the green channel.
- 0.114: Weight for the blue channel.
The weighted sum of these channels helps create a grayscale image where the pixel values represent the perceived brightness. This technique is often used when converting a color image to grayscale or when calculating luminance for certain operations, as it takes into account the human eye’s sensitivity to different colors.
For the threshold, remember that the exact relationship between EV values and pixel values can depend on the tone-mapping or normalization applied to the HDR image, as well as the dynamic range of the image itself.
To establish a relationship between exposure and the threshold value, you can consider the relationship between linear and logarithmic scales:
- Linear and Logarithmic Scales:
- Exposure values in an EXR image are often represented in logarithmic scales, such as EV (exposure value). Each increment in EV represents a doubling or halving of the amount of light captured.
- Threshold values for luminance thresholding are usually linear, representing an actual luminance level.
- Conversion Between Scales:
- To establish a mathematical relationship, you need to convert between the logarithmic exposure scale and the linear threshold scale.
- One common method is to use a power function. For instance, you can use a power function to convert EV to a linear intensity value.
threshold_value = base_value * (2 ** EV)Here,
EVis the exposure value,base_valueis a scaling factor that determines the relationship between EV and threshold_value, and2 ** EVis used to convert the logarithmic EV to a linear intensity value. - Choosing the Base Value:
- The
base_valuefactor should be determined based on the dynamic range of your EXR image and the specific luminance values you are dealing with. - You may need to experiment with different values of
base_valueto achieve the desired separation of bright areas from the rest of the image.
- The
Let’s say you have an EXR image with a dynamic range of 12 EV, which is a common range for many high dynamic range images. In this case, you want to set a threshold value that corresponds to a certain number of EV above the middle gray level (which is often considered to be around 0.18).
Here’s an example of how you might determine a
base_valueto achieve this:# Define the dynamic range of the image in EV dynamic_range = 12 # Choose the desired number of EV above middle gray for thresholding desired_ev_above_middle_gray = 2 # Calculate the threshold value based on the desired EV above middle gray threshold_value = 0.18 * (2 ** (desired_ev_above_middle_gray / dynamic_range)) print("Threshold Value:", threshold_value) -
HDRI Resources
Read more: HDRI ResourcesText2Light
- https://www.cgtrader.com/free-3d-models/exterior/other/10-free-hdr-panoramas-created-with-text2light-zero-shot
- https://frozenburning.github.io/projects/text2light/
- https://github.com/FrozenBurning/Text2Light
Royalty free links
- https://locationtextures.com/panoramas/
- http://www.noahwitchell.com/freebies
- https://polyhaven.com/hdris
- https://hdrmaps.com/
- https://www.ihdri.com/
- https://hdrihaven.com/
- https://www.domeble.com/
- http://www.hdrlabs.com/sibl/archive.html
- https://www.hdri-hub.com/hdrishop/hdri
- http://noemotionhdrs.net/hdrevening.html
- https://www.openfootage.net/hdri-panorama/
- https://www.zwischendrin.com/en/browse/hdri
Nvidia GauGAN360
-
Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a scene
Read more: Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a sceneIt’s a new Magnific spell that allows you to change the entire lighting of a scene and, optionally, the background with just:
1/ A prompt OR
2/ A reference image OR
3/ A light map (drawing your own lights)https://x.com/javilopen/status/1805274155065176489
-
Ethan Roffler interviews CG Supervisor Daniele Tosti
Read more: Ethan Roffler interviews CG Supervisor Daniele TostiEthan Roffler
I recently had the honor of interviewing this VFX genius and gained great insight into what it takes to work in the entertainment industry. Keep in mind, these questions are coming from an artist’s perspective but can be applied to any creative individual looking for some wisdom from a professional. So grab a drink, sit back, and enjoy this fun and insightful conversation.
Ethan
To start, I just wanted to say thank you so much for taking the time for this interview!Daniele
My pleasure.
When I started my career I struggled to find help. Even people in the industry at the time were not that helpful. Because of that, I decided very early on that I was going to do exactly the opposite. I spend most of my weekends talking or helping students. ;)Ethan
That’s awesome! I have also come across the same struggle! Just a heads up, this will probably be the most informal interview you’ll ever have haha! Okay, so let’s start with a small introduction!Daniele
Short introduction: I worked very hard and got lucky enough to work on great shows with great people. ;) Slightly longer version: I started working for a TV channel, very early, while I was learning about CG. Slowly made my way across the world, working along very great people and amazing shows. I learned that to be successful in this business, you have to really love what you do as much as respecting the people around you. What you do will improve to the final product; the way you work with people will make a difference in your life.
Ethan
How long have you been an artist?Daniele
Loaded question. I believe I am still trying and craving to be one. After each production I finish I realize how much I still do not know. And how many things I would like to try. I guess in my CG Sup and generalist world, being an artist is about learning as much about the latest technologies and production cycles as I can, then putting that in practice. Having said that, I do consider myself a cinematographer first, as I have been doing that for about 25 years now.Ethan
Words of true wisdom, the more I know the less I know:) How did you get your start in the industry?
How did you break into such a competitive field?Daniele
There were not many schools when I started. It was all about a few magazines, some books, and pushing software around trying to learn how to make pretty images. Opportunities opened because of that knowledge! The true break was learning to work hard to achieve a Suspension of Disbelief in my work that people would recognize as such. It’s not something everyone can do, but I was fortunate to not be scared of working hard, being a quick learner and having very good supervisors and colleagues to learn from.Ethan
Which do you think is better, having a solid art degree or a strong portfolio?Daniele
Very good question. A strong portfolio will get you a job now. A solid strong degree will likely get you a job for a longer period. Let me digress here; Working as an artist is not about being an artist, it’s about making money as an artist. Most people fail to make that difference and have either a poor career or lack the understanding to make a stable one. One should never mix art with working as an artist. You can do both only if you understand business and are fair to yourself.
Ethan
That’s probably the most helpful answer to that question I have ever heard.
What’s some advice you can offer to someone just starting out who wants to break into the industry?Daniele
Breaking in the industry is not just about knowing your art. It’s about knowing good business practices. Prepare a good demo reel based on the skill you are applying for; research all the places where you want to apply and why; send as many reels around; follow up each reel with a phone call. Business is all about right time, right place.Ethan
A follow-up question to that is: Would you consider it a bad practice to send your demo reels out in mass quantity rather than focusing on a handful of companies to research and apply for?Daniele
Depends how desperate you are… I would say research is a must. To improve your options, you need to know which company is working on what and what skills they are after. If you were selling vacuum cleaners you probably would not want to waste energy contacting shoemakers or cattle farmers.Ethan
What do you think the biggest killer of creativity and productivity is for you?Daniele
Money…If you were thinking as an artist. ;) If you were thinking about making money as an artist… then I would say “thinking that you work alone”.Ethan
Best. Answer. Ever.
What are ways you fight complacency and maintain fresh ideas, outlooks, and perspectivesDaniele
Two things: Challenge yourself to go outside your comfort zone. And think outside of the box.Ethan
What are the ways/habits you have that challenge yourself to get out of your comfort zone and think outside the box?Daniele
If you think you are a good character painter, pick up a camera and go take pictures of amazing landscapes. If you think you are good only at painting or sketching, learn how to code in python. If you cannot solve a problem, that being a project or a person, learn to ask for help or learn about looking at the problem from various perspectives. If you are introvert, learn to be extrovert. And vice versa. And so on…
Ethan
How do you avoid burnout?Daniele
Oh… I wish I learned about this earlier. I think anyone that has a passion in something is at risk of burning out. Artists, more than many, because we see the world differently and our passion goes deep. You avoid burnouts by thinking that you are in a long term plan and that you have an obligation to pay or repay your talent by supporting and cherishing yourself and your family, not your paycheck. You do this by treating your art as a business and using business skills when dealing with your career and using artistic skills only when you are dealing with a project itself.Ethan
Looking back, what was a big defining moment for you?Daniele
Recognizing that people around you, those being colleagues, friends or family, come first.
It changed my career overnight.Ethan
Who are some of your personal heroes?Daniele
Too many to list. Most recently… James Cameron; Joe Letteri; Lawrence Krauss; Richard Dawkins. Because they all mix science, art, and poetry in their own way.Ethan
Last question:
What’s your dream job? ;)Daniele
Teaching artists to be better at being business people… as it will help us all improve our lives and the careers we took…
Being a VFX artist is fundamentally based on mistrust.
This because schedules, pipelines, technology, creative calls… all have a native and naive instability to them that causes everyone to grow a genuine but beneficial lack of trust in the status quo. This is a fine balance act to build into your character. The VFX motto: “Love everyone but trust no one” is born on that.
-
Photography basics: Solid Angle measures
Read more: Photography basics: Solid Angle measureshttp://www.calculator.org/property.aspx?name=solid+angle
A measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point. Thus. A measure for objects in the sky. Useful to retuen the size of the sun and moon… and in perspective, how much of their contribution to lighting. Solid angle can be represented in ‘angular diameter’ as well.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle
http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/steradian.html
A solid angle is expressed in a dimensionless unit called a steradian (symbol: sr). By default in terms of the total celestial sphere and before atmospheric’s scattering, the Sun and the Moon subtend fractional areas of 0.000546% (Sun) and 0.000531% (Moon).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle#Sun_and_Moon
On earth the sun is likely closer to 0.00011 solid angle after athmospheric scattering. The sun as perceived from earth has a diameter of 0.53 degrees. This is about 0.000064 solid angle.
http://www.numericana.com/answer/angles.htm
The mean angular diameter of the full moon is 2q = 0.52° (it varies with time around that average, by about 0.009°). This translates into a solid angle of 0.0000647 sr, which means that the whole night sky covers a solid angle roughly one hundred thousand times greater than the full moon.
More info
http://lcogt.net/spacebook/using-angles-describe-positions-and-apparent-sizes-objects
http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/glossary/def.php.s=topic_astronomy
Angular Size
The apparent size of an object as seen by an observer; expressed in units of degrees (of arc), arc minutes, or arc seconds. The moon, as viewed from the Earth, has an angular diameter of one-half a degree.
The angle covered by the diameter of the full moon is about 31 arcmin or 1/2°, so astronomers would say the Moon’s angular diameter is 31 arcmin, or the Moon subtends an angle of 31 arcmin.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
AI Data Laundering: How Academic and Nonprofit Researchers Shield Tech Companies from Accountability
-
Guide to Prompt Engineering
-
Most common ways to smooth 3D prints
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
-
How do LLMs like ChatGPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) work? Explained by Deep-Fake Ryan Gosling
-
Film Production walk-through – pipeline – I want to make a … movie
-
Sensitivity of human eye
-
Game Development tips
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.