COMPOSITION
-
Key/Fill ratios and scene composition using false colors
Read more: Key/Fill ratios and scene composition using false colorsTo measure the contrast ratio you will need a light meter. The process starts with you measuring the main source of light, or the key light.
Get a reading from the brightest area on the face of your subject. Then, measure the area lit by the secondary light, or fill light. To make sense of what you have just measured you have to understand that the information you have just gathered is in F-stops, a measure of light. With each additional F-stop, for example going one stop from f/1.4 to f/2.0, you create a doubling of light. The reverse is also true; moving one stop from f/8.0 to f/5.6 results in a halving of the light.
Let’s say you grabbed a measurement from your key light of f/8.0. Then, when you measured your fill light area, you get a reading of f/4.0. This will lead you to a contrast ratio of 4:1 because there are two stops between f/4.0 and f/8.0 and each stop doubles the amount of light. In other words, two stops x twice the light per stop = four times as much light at f/8.0 than at f/4.0.
theslantedlens.com/2017/lighting-ratios-photo-video/
Examples in the post
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space
Read more: Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space8bit sRGB encoded
2000K 255 139 22
2700K 255 172 89
3000K 255 184 109
3200K 255 190 122
4000K 255 211 165
4300K 255 219 178
D50 255 235 205
D55 255 243 224
D5600 255 244 227
D6000 255 249 240
D65 255 255 255
D10000 202 221 255
D20000 166 196 2558bit Rec709 Gamma 2.4
2000K 255 145 34
2700K 255 177 97
3000K 255 187 117
3200K 255 193 129
4000K 255 214 170
4300K 255 221 182
D50 255 236 208
D55 255 243 226
D5600 255 245 229
D6000 255 250 241
D65 255 255 255
D10000 204 222 255
D20000 170 199 2558bit Display P3 encoded
2000K 255 154 63
2700K 255 185 109
3000K 255 195 127
3200K 255 201 138
4000K 255 219 176
4300K 255 225 187
D50 255 239 212
D55 255 245 228
D5600 255 246 231
D6000 255 251 242
D65 255 255 255
D10000 208 223 255
D20000 175 199 25510bit Rec2020 PQ (100 nits)
2000K 520 435 273
2700K 520 466 358
3000K 520 475 384
3200K 520 480 399
4000K 520 495 446
4300K 520 500 458
D50 520 510 482
D55 520 514 497
D5600 520 514 500
D6000 520 517 509
D65 520 520 520
D10000 479 489 520
D20000 448 464 520 -
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
As such, the color temperature of a light source is a numerical measurement of its color appearance. It is based on the principle that any object will emit light if it is heated to a high enough temperature, and that the color of that light will shift in a predictable manner as the temperature is increased. The system is based on the color changes of a theoretical “blackbody radiator” as it is heated from a cold black to a white hot state.
So, why do we measure the hue of the light as a “temperature”? This was started in the late 1800s, when the British physicist William Kelvin heated a block of carbon. It glowed in the heat, producing a range of different colors at different temperatures. The black cube first produced a dim red light, increasing to a brighter yellow as the temperature went up, and eventually produced a bright blue-white glow at the highest temperatures. In his honor, Color Temperatures are measured in degrees Kelvin, which are a variation on Centigrade degrees. Instead of starting at the temperature water freezes, the Kelvin scale starts at “absolute zero,” which is -273 Centigrade.
More about black bodies here: https://www.pixelsham.com/2013/03/14/black-body-color
Details in the post
-
Sensitivity of human eye
Read more: Sensitivity of human eyehttp://www.wikilectures.eu/index.php/Spectral_sensitivity_of_the_human_eye
http://www.normankoren.com/Human_spectral_sensitivity_small.jpg
Spectral sensitivity of eye is influenced by light intensity. And the light intensity determines the level of activity of cones cell and rod cell. This is the main characteristic of human vision. Sensitivity to individual colors, in other words, wavelengths of the light spectrum, is explained by the RGB (red-green-blue) theory. This theory assumed that there are three kinds of cones. It’s selectively sensitive to red (700-630 nm), green (560-500 nm), and blue (490-450 nm) light. And their mutual interaction allow to perceive all colors of the spectrum.
http://weeklysciencequiz.blogspot.com/2013/01/violet-skies-are-for-birds.html

Sensitivity of human eye Sensitivity of human eyes to light increase with the decrease in light intensity. In day-light condition, the cones cell is responding to this condition. And the eye is most sensitive at 555 nm. In darkness condition, the rod cell is responding to this condition. And the eye is most sensitive at 507 nm.
As light intensity decreases, cone function changes more effective way. And when decrease the light intensity, it prompt to accumulation of rhodopsin. Furthermore, in activates rods, it allow to respond to stimuli of light in much lower intensity.
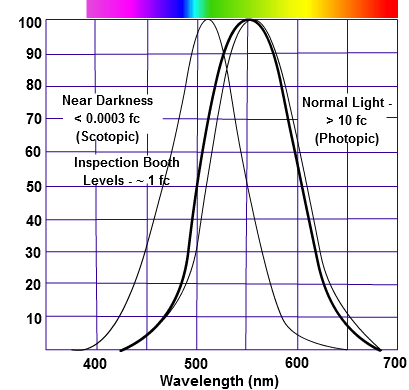
The three curves in the figure above shows the normalized response of an average human eye to various amounts of ambient light. The shift in sensitivity occurs because two types of photoreceptors called cones and rods are responsible for the eye’s response to light. The curve on the right shows the eye’s response under normal lighting conditions and this is called the photopic response. The cones respond to light under these conditions.
As mentioned previously, cones are composed of three different photo pigments that enable color perception. This curve peaks at 555 nanometers, which means that under normal lighting conditions, the eye is most sensitive to a yellowish-green color. When the light levels drop to near total darkness, the response of the eye changes significantly as shown by the scotopic response curve on the left. At this level of light, the rods are most active and the human eye is more sensitive to the light present, and less sensitive to the range of color. Rods are highly sensitive to light but are comprised of a single photo pigment, which accounts for the loss in ability to discriminate color. At this very low light level, sensitivity to blue, violet, and ultraviolet is increased, but sensitivity to yellow and red is reduced. The heavier curve in the middle represents the eye’s response at the ambient light level found in a typical inspection booth. This curve peaks at 550 nanometers, which means the eye is most sensitive to yellowish-green color at this light level. Fluorescent penetrant inspection materials are designed to fluoresce at around 550 nanometers to produce optimal sensitivity under dim lighting conditions.
-
The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t See
Read more: The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t Seewww.livescience.com/17948-red-green-blue-yellow-stunning-colors.html
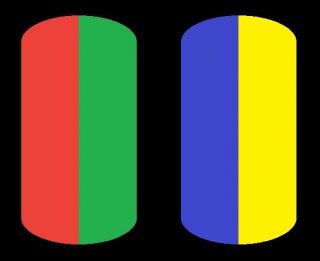
While the human eye has red, green, and blue-sensing cones, those cones are cross-wired in the retina to produce a luminance channel plus a red-green and a blue-yellow channel, and it’s data in that color space (known technically as “LAB”) that goes to the brain. That’s why we can’t perceive a reddish-green or a yellowish-blue, whereas such colors can be represented in the RGB color space used by digital cameras.
https://en.rockcontent.com/blog/the-use-of-yellow-in-data-design
The back of the retina is covered in light-sensitive neurons known as cone cells and rod cells. There are three types of cone cells, each sensitive to different ranges of light. These ranges overlap, but for convenience the cones are referred to as blue (short-wavelength), green (medium-wavelength), and red (long-wavelength). The rod cells are primarily used in low-light situations, so we’ll ignore those for now.
When light enters the eye and hits the cone cells, the cones get excited and send signals to the brain through the visual cortex. Different wavelengths of light excite different combinations of cones to varying levels, which generates our perception of color. You can see that the red cones are most sensitive to light, and the blue cones are least sensitive. The sensitivity of green and red cones overlaps for most of the visible spectrum.
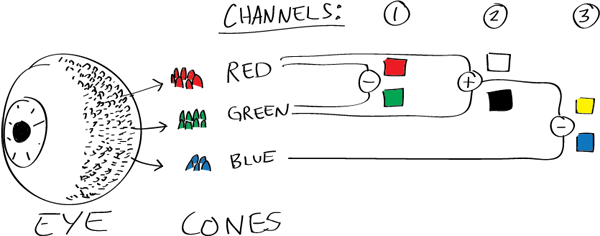
Here’s how your brain takes the signals of light intensity from the cones and turns it into color information. To see red or green, your brain finds the difference between the levels of excitement in your red and green cones. This is the red-green channel.
To get “brightness,” your brain combines the excitement of your red and green cones. This creates the luminance, or black-white, channel. To see yellow or blue, your brain then finds the difference between this luminance signal and the excitement of your blue cones. This is the yellow-blue channel.
From the calculations made in the brain along those three channels, we get four basic colors: blue, green, yellow, and red. Seeing blue is what you experience when low-wavelength light excites the blue cones more than the green and red.
Seeing green happens when light excites the green cones more than the red cones. Seeing red happens when only the red cones are excited by high-wavelength light.
Here’s where it gets interesting. Seeing yellow is what happens when BOTH the green AND red cones are highly excited near their peak sensitivity. This is the biggest collective excitement that your cones ever have, aside from seeing pure white.
Notice that yellow occurs at peak intensity in the graph to the right. Further, the lens and cornea of the eye happen to block shorter wavelengths, reducing sensitivity to blue and violet light.
LIGHTING
-
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
Read more: Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacynofilmschool.com/types-of-film-lights
“Not every light performs the same way. Lights and lighting are tricky to handle. You have to plan for every circumstance. But the good news is, lighting can be adjusted. Let’s look at different factors that affect lighting in every scene you shoot. ”
Use CRI, Luminous Efficacy and color temperature controls to match your needs.
Color Temperature
Color temperature describes the “color” of white light by a light source radiated by a perfect black body at a given temperature measured in degrees Kelvinhttps://www.pixelsham.com/2019/10/18/color-temperature/
CRI
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. ”https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_rendering_index
Light source CCT (K) CRI Low-pressure sodium (LPS/SOX) 1800 −44 Clear mercury-vapor 6410 17 High-pressure sodium (HPS/SON) 2100 24 Coated mercury-vapor 3600 49 Halophosphate warm-white fluorescent 2940 51 Halophosphate cool-white fluorescent 4230 64 Tri-phosphor warm-white fluorescent 2940 73 Halophosphate cool-daylight fluorescent 6430 76 “White” SON 2700 82 Standard LED Lamp 2700–5000 83 Quartz metal halide 4200 85 Tri-phosphor cool-white fluorescent 4080 89 High-CRI LED lamp (blue LED) 2700–5000 95 Ceramic discharge metal-halide lamp 5400 96 Ultra-high-CRI LED lamp (violet LED) 2700–5000 99 Incandescent/halogen bulb 3200 100 Luminous Efficacy
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light, watts out versus watts in, measured in lumens per watt. In other words it is a measurement that indicates the ability of a light source to emit visible light using a given amount of power. It is a ratio of the visible energy to the power that goes into the bulb.FILM LIGHT TYPES
Consumer light types
Tungsten Lights
Light interiors and match domestic places or office locations. Daylight.Advantages of Tungsten Lights
Almost perfect color rendition
Low cost
Does not use mercury like CFLs (fluorescent) or mercury vapor lights
Better color temperature than standard tungsten
Longer life than a conventional incandescent
Instant on to full brightness, no warm-up time, and it is dimmableDisadvantages of Tungsten Lights
Extremely hot
High power requirement
The lamp is sensitive to oils and cannot be touched
The bulb is capable of blowing and sending hot glass shards outward. A screen or layer of glass on the outside of the lamp can protect users.Hydrargyrum medium-arc iodide lights
HMI’s are used when high output is required. They are also used to recreate sun shining through windows or to fake additional sun while shooting exteriors. HMIs can light huge areas at once.Advantages of HMI lights
High light output
Higher efficiency
High color temperatureDisadvantages of HMI lights:
High cost
High power requirement
Dims only to about 50%
the color temperature increases with dimming
HMI bulbs will explode is dropped and release toxic chemicalsFluorescent
Fluorescent film lighting is achieved by laying multiple tubes next to each other, combining as many as you want for the desired brightness. The good news is you can choose your bulbs to either be warm or cool depending on the scenario you’re shooting. You want to get these bulbs close to the subject because they’re not great at opening up spaces. Fluorescent lighting is used to light interiors and is more compact and cooler than tungsten or HMI lighting.Advantages of Fluorescent lights
High efficiency
Low power requirement
Low cost
Long lamp life
Cool
Capable of soft even lighting over a large area
LightweightDisadvantages of Fluorescent lights
Flicker
High CRI
Domestic tubes have low CRI & poor color rendition.LED
LED’s are more and more common on film sets. You can use batteries to power them. That makes them portable and sleek – no messy cabled needed. You can rig your own panels of LED lights to fit any space necessary as well. LED’s can also power Fresnel style lamp heads such as the Arri L-series.Advantages of LED light
Soft, even lighting
Pure light without UV-artifacts
High efficiency
Low power consumption, can be battery powered
Excellent dimming by means of pulse width modulation control
Long lifespan
Environmentally friendly
Insensitive to shock
No risk of explosionDisadvantages of LED light
High cost.
LED’s are currently still expensive for their total light output -
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
As such, the color temperature of a light source is a numerical measurement of its color appearance. It is based on the principle that any object will emit light if it is heated to a high enough temperature, and that the color of that light will shift in a predictable manner as the temperature is increased. The system is based on the color changes of a theoretical “blackbody radiator” as it is heated from a cold black to a white hot state.
So, why do we measure the hue of the light as a “temperature”? This was started in the late 1800s, when the British physicist William Kelvin heated a block of carbon. It glowed in the heat, producing a range of different colors at different temperatures. The black cube first produced a dim red light, increasing to a brighter yellow as the temperature went up, and eventually produced a bright blue-white glow at the highest temperatures. In his honor, Color Temperatures are measured in degrees Kelvin, which are a variation on Centigrade degrees. Instead of starting at the temperature water freezes, the Kelvin scale starts at “absolute zero,” which is -273 Centigrade.
More about black bodies here: https://www.pixelsham.com/2013/03/14/black-body-color
Details in the post
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
Read more: HDRI Median Cut pluginwww.hdrlabs.com/picturenaut/plugins.html
Note. The Median Cut algorithm is typically used for color quantization, which involves reducing the number of colors in an image while preserving its visual quality. It doesn’t directly provide a way to identify the brightest areas in an image. However, if you’re interested in identifying the brightest areas, you might want to look into other methods like thresholding, histogram analysis, or edge detection, through openCV for example.
Here is an openCV example:
# bottom left coordinates = 0,0 import numpy as np import cv2 # Load the HDR or EXR image image = cv2.imread('your_image_path.exr', cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED) # Load as-is without modification # Calculate the luminance from the HDR channels (assuming RGB format) luminance = np.dot(image[..., :3], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114]) # Set a threshold value based on estimated EV threshold_value = 2.4 # Estimated threshold value based on 4.8 EV # Apply the threshold to identify bright areas # Theluminancearray contains the calculated luminance values for each pixel in the image. # Thethreshold_valueis a user-defined value that represents a cutoff point, separating "bright" and "dark" areas in terms of perceived luminance.thresholded = (luminance > threshold_value) * 255 # Convert the thresholded image to uint8 for contour detection thresholded = thresholded.astype(np.uint8) # Find contours of the bright areas contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresholded, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # Create a list to store the bounding boxes of bright areas bright_areas = [] # Iterate through contours and extract bounding boxes for contour in contours: x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour) # Adjust y-coordinate based on bottom-left origin y_bottom_left_origin = image.shape[0] - (y + h) bright_areas.append((x, y_bottom_left_origin, x + w, y_bottom_left_origin + h)) # Store as (x1, y1, x2, y2) # Print the identified bright areas print("Bright Areas (x1, y1, x2, y2):") for area in bright_areas: print(area)More details
Luminance and Exposure in an EXR Image:
- An EXR (Extended Dynamic Range) image format is often used to store high dynamic range (HDR) images that contain a wide range of luminance values, capturing both dark and bright areas.
- Luminance refers to the perceived brightness of a pixel in an image. In an RGB image, luminance is often calculated using a weighted sum of the red, green, and blue channels, where different weights are assigned to each channel to account for human perception.
- In an EXR image, the pixel values can represent radiometrically accurate scene values, including actual radiance or irradiance levels. These values are directly related to the amount of light emitted or reflected by objects in the scene.
The luminance line is calculating the luminance of each pixel in the image using a weighted sum of the red, green, and blue channels. The three float values [0.299, 0.587, 0.114] are the weights used to perform this calculation.
These weights are based on the concept of luminosity, which aims to approximate the perceived brightness of a color by taking into account the human eye’s sensitivity to different colors. The values are often derived from the NTSC (National Television System Committee) standard, which is used in various color image processing operations.
Here’s the breakdown of the float values:
- 0.299: Weight for the red channel.
- 0.587: Weight for the green channel.
- 0.114: Weight for the blue channel.
The weighted sum of these channels helps create a grayscale image where the pixel values represent the perceived brightness. This technique is often used when converting a color image to grayscale or when calculating luminance for certain operations, as it takes into account the human eye’s sensitivity to different colors.
For the threshold, remember that the exact relationship between EV values and pixel values can depend on the tone-mapping or normalization applied to the HDR image, as well as the dynamic range of the image itself.
To establish a relationship between exposure and the threshold value, you can consider the relationship between linear and logarithmic scales:
- Linear and Logarithmic Scales:
- Exposure values in an EXR image are often represented in logarithmic scales, such as EV (exposure value). Each increment in EV represents a doubling or halving of the amount of light captured.
- Threshold values for luminance thresholding are usually linear, representing an actual luminance level.
- Conversion Between Scales:
- To establish a mathematical relationship, you need to convert between the logarithmic exposure scale and the linear threshold scale.
- One common method is to use a power function. For instance, you can use a power function to convert EV to a linear intensity value.
threshold_value = base_value * (2 ** EV)Here,
EVis the exposure value,base_valueis a scaling factor that determines the relationship between EV and threshold_value, and2 ** EVis used to convert the logarithmic EV to a linear intensity value. - Choosing the Base Value:
- The
base_valuefactor should be determined based on the dynamic range of your EXR image and the specific luminance values you are dealing with. - You may need to experiment with different values of
base_valueto achieve the desired separation of bright areas from the rest of the image.
- The
Let’s say you have an EXR image with a dynamic range of 12 EV, which is a common range for many high dynamic range images. In this case, you want to set a threshold value that corresponds to a certain number of EV above the middle gray level (which is often considered to be around 0.18).
Here’s an example of how you might determine a
base_valueto achieve this:# Define the dynamic range of the image in EV dynamic_range = 12 # Choose the desired number of EV above middle gray for thresholding desired_ev_above_middle_gray = 2 # Calculate the threshold value based on the desired EV above middle gray threshold_value = 0.18 * (2 ** (desired_ev_above_middle_gray / dynamic_range)) print("Threshold Value:", threshold_value)
Collections
| Explore posts
| Design And Composition
| Featured AI
Popular Searches
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.



