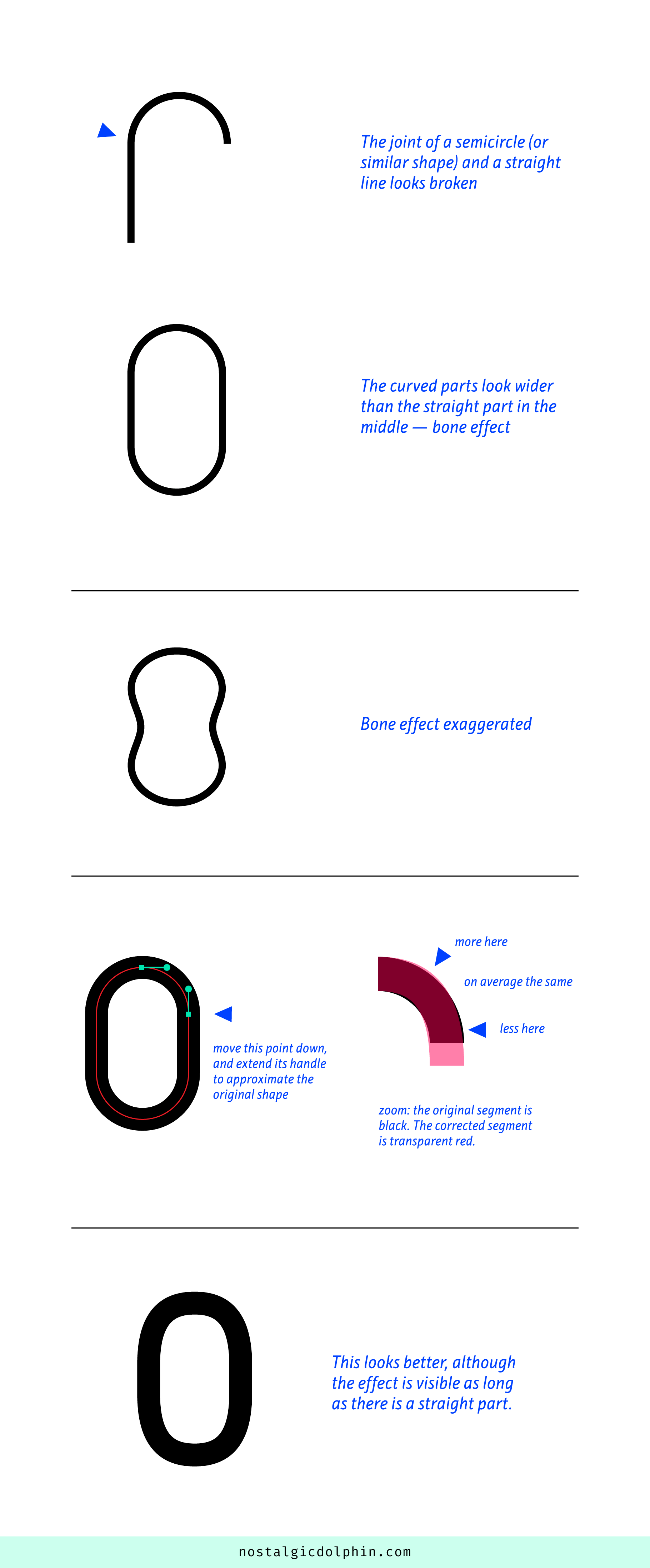
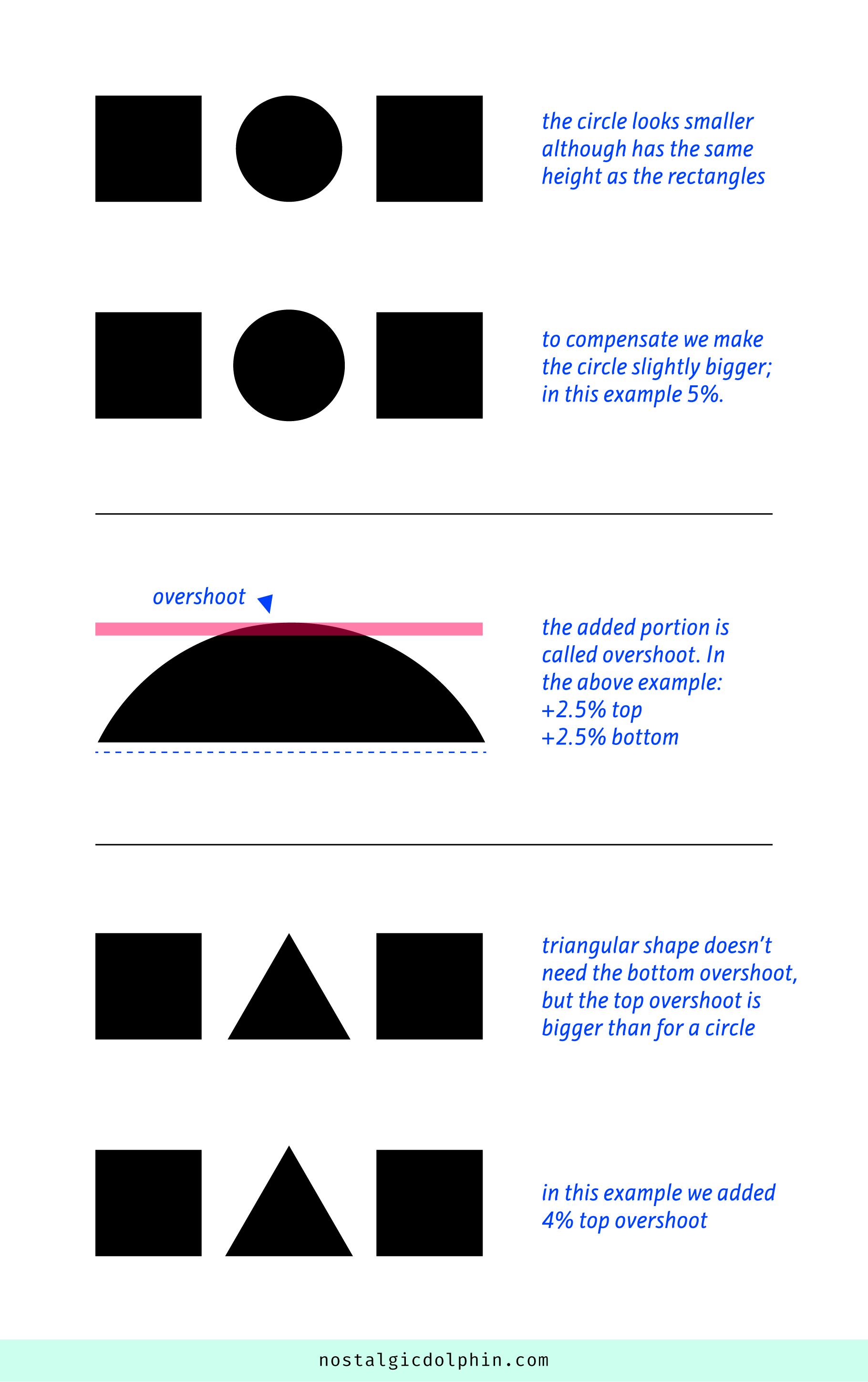
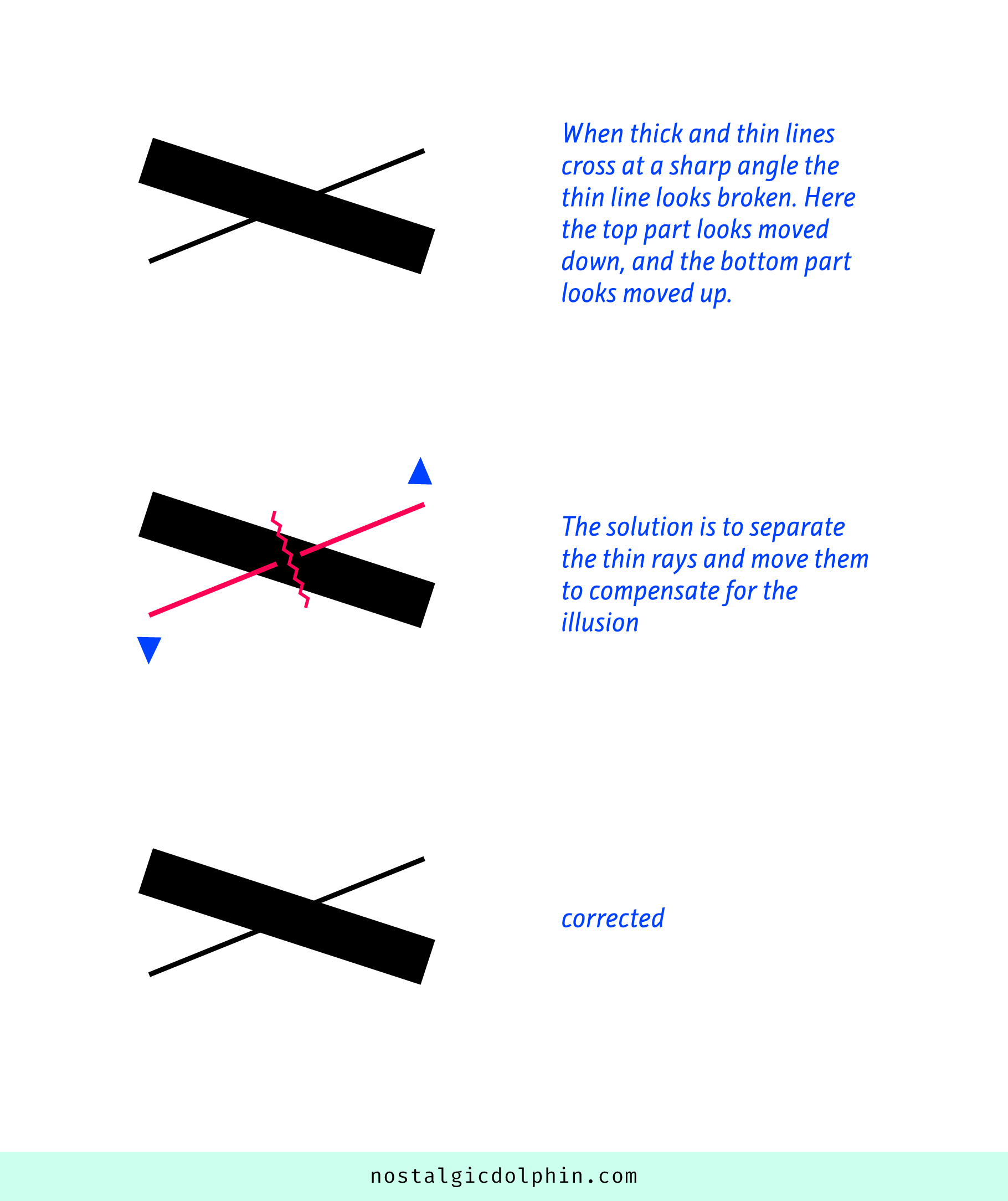
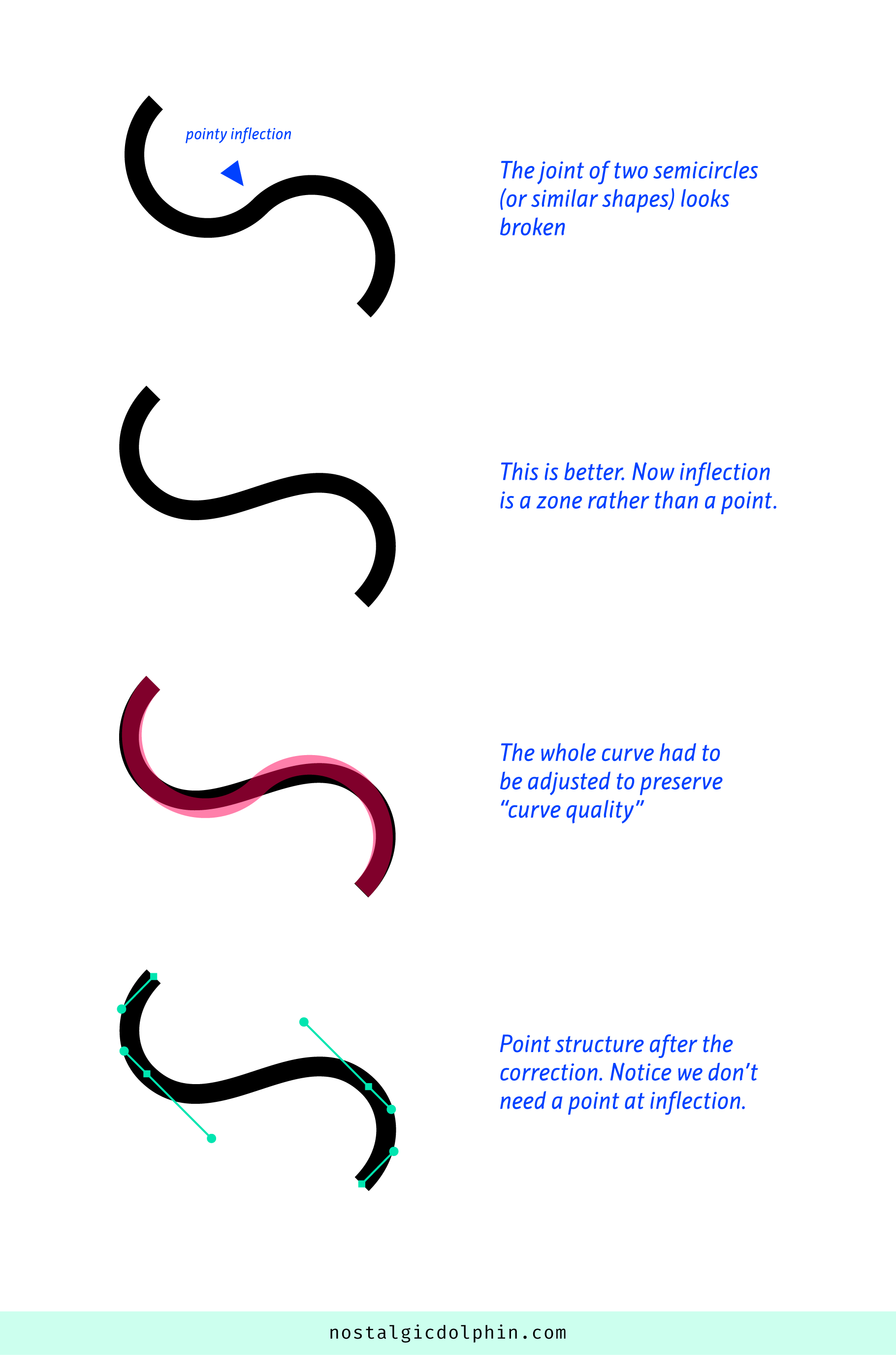COMPOSITION
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
DESIGN
-
Goga Tandashvili – bas-relief master
Read more: Goga Tandashvili – bas-relief master@moltenimmersiveart Goga Tandashvili is a master of the art of Bas-Relief. Using this technique, he creates stunning figures that are slightly raised from a flat surface, bringing scenes inspired by the natural world to life. #Art #Artists #GogaTandashvili #BasReliefSculpture #ArtInspiredByNature #ImpressionistArt #BasRelief #Sculptures #Sculptor #Molten #MoltenArt #MoltenImmersiveArt #MoltenAffect #Curation #Curator #ArtCuration #ArtCurator #DorothyDiStefano ♬ original sound – Molten Immersive Art -
Tokyo Prime 1 Studio 2022 + XM Studios Boots | Batman, Movies, Anime & Games Statues and Collectibles
Read more: Tokyo Prime 1 Studio 2022 + XM Studios Boots | Batman, Movies, Anime & Games Statues and Collectiblesnearly 140 statues at the booth from licenses including DC Comics, Lord of the Rings, Uncharted, The Last of Us, Bloodborne, Demon Souls, God of War, Jurassic Park, Godzilla, Predator, Aliens, Transformers, Berserk, Evangelion, My Hero Academia, Chainsaw Man, Attack on Titan, the DC movie universe, X-Men, Spider-man and much more
COLOR
LIGHTING
-
Romain Chauliac – LightIt a lighting script for Maya and Arnold
Read more: Romain Chauliac – LightIt a lighting script for Maya and ArnoldLightIt is a script for Maya and Arnold that will help you and improve your lighting workflow.
Thanks to preset studio lighting components (lights, backdrop…), high quality studio scenes and HDRI library manager.https://www.artstation.com/artwork/393emJ
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
How do LLMs like ChatGPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) work? Explained by Deep-Fake Ryan Gosling
-
AnimationXpress.com interviews Daniele Tosti for TheCgCareer.com channel
-
Mastering The Art Of Photography – PixelSham.com Photography Basics
-
Photography basics: How Exposure Stops (Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO) Affect Your Photos – cheat sheet cards
-
STOP FCC – SAVE THE FREE NET
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.