COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Björn Ottosson – OKlch color space
Read more: Björn Ottosson – OKlch color spaceBjörn Ottosson proposed OKlch in 2020 to create a color space that can closely mimic how color is perceived by the human eye, predicting perceived lightness, chroma, and hue.
The OK in OKLCH stands for Optimal Color.
- L: Lightness (the perceived brightness of the color)
- C: Chroma (the intensity or saturation of the color)
- H: Hue (the actual color, such as red, blue, green, etc.)

Also read:
-
colorhunt.co
Read more: colorhunt.coColor Hunt is a free and open platform for color inspiration with thousands of trendy hand-picked color palettes.
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…) -
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
Read more: Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflowsDisplay Referred it is tied to the target hardware, as such it bakes color requirements into every type of media output request.
Scene Referred uses a common unified wide gamut and targeting audience through CDL and DI libraries instead.
So that color information stays untouched and only “transformed” as/when needed.Sources:
– Victor Perez – Color Management Fundamentals & ACES Workflows in Nuke
– https://z-fx.nl/ColorspACES.pdf
– Wicus
-
PBR Color Reference List for Materials – by Grzegorz Baran
Read more: PBR Color Reference List for Materials – by Grzegorz Baran“The list should be helpful for every material artist who work on PBR materials as it contains over 200 color values measured with PCE-RGB2 1002 Color Spectrometer device and presented in linear and sRGB (2.2) gamma space.
All color values, HUE and Saturation in this list come from measurements taken with PCE-RGB2 1002 Color Spectrometer device and are presented in linear and sRGB (2.2) gamma space (more info at the end of this video) I calculated Relative Luminance and Luminance values based on captured color using my own equation which takes color based luminance perception into consideration. Bare in mind that there is no ‘one’ color per substance as nothing in nature is even 100% uniform and any value in +/-10% range from these should be considered as correct one. Therefore this list should be always considered as a color reference for material’s albedos, not ulitimate and absolute truth.“
LIGHTING
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet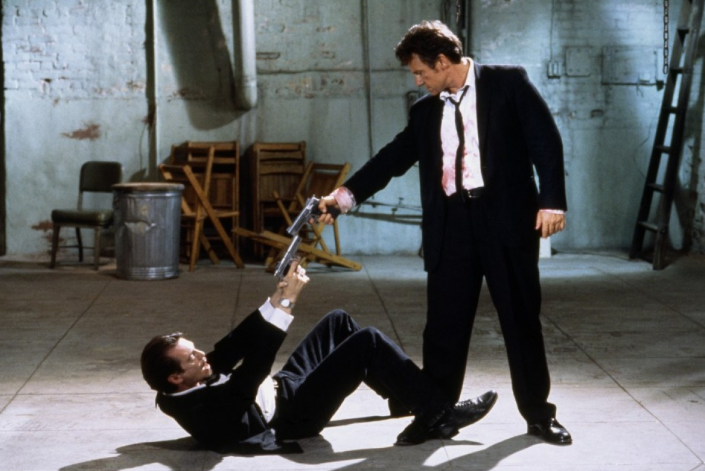
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.







