COMPOSITION
-
StudioBinder – Roger Deakins on How to Choose a Camera Lens — Cinematography Composition Techniques
Read more: StudioBinder – Roger Deakins on How to Choose a Camera Lens — Cinematography Composition Techniqueshttps://www.studiobinder.com/blog/camera-lens-buying-guide/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/e-books/camera-lenses-explained-volume-1-ebook
DESIGN
COLOR
LIGHTING
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
As such, the color temperature of a light source is a numerical measurement of its color appearance. It is based on the principle that any object will emit light if it is heated to a high enough temperature, and that the color of that light will shift in a predictable manner as the temperature is increased. The system is based on the color changes of a theoretical “blackbody radiator” as it is heated from a cold black to a white hot state.
So, why do we measure the hue of the light as a “temperature”? This was started in the late 1800s, when the British physicist William Kelvin heated a block of carbon. It glowed in the heat, producing a range of different colors at different temperatures. The black cube first produced a dim red light, increasing to a brighter yellow as the temperature went up, and eventually produced a bright blue-white glow at the highest temperatures. In his honor, Color Temperatures are measured in degrees Kelvin, which are a variation on Centigrade degrees. Instead of starting at the temperature water freezes, the Kelvin scale starts at “absolute zero,” which is -273 Centigrade.
More about black bodies here: https://www.pixelsham.com/2013/03/14/black-body-color
Details in the post
-
LUX vs LUMEN vs NITS vs CANDELA – What is the difference
Read more: LUX vs LUMEN vs NITS vs CANDELA – What is the differenceMore details here: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
https://www.inhouseav.com.au/blog/beginners-guide-nits-lumens-brightness/

Candela
Candela is the basic unit of measure of the entire volume of light intensity from any point in a single direction from a light source. Note the detail: it measures the total volume of light within a certain beam angle and direction.
While the luminance of starlight is around 0.001 cd/m2, that of a sunlit scene is around 100,000 cd/m2, which is a hundred millions times higher. The luminance of the sun itself is approximately 1,000,000,000 cd/m2.NIT
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Candela_per_square_metre
The candela per square metre (symbol: cd/m2) is the unit of luminance in the International System of Units (SI). The unit is based on the candela, the SI unit of luminous intensity, and the square metre, the SI unit of area. The nit (symbol: nt) is a non-SI name also used for this unit (1 nt = 1 cd/m2).[1] The term nit is believed to come from the Latin word nitēre, “to shine”. As a measure of light emitted per unit area, this unit is frequently used to specify the brightness of a display device.
NIT and cd/m2 (candela power) represent the same thing and can be used interchangeably. One nit is equivalent to one candela per square meter, where the candela is the amount of light which has been emitted by a common tallow candle, but NIT is not part of the International System of Units (abbreviated SI, from Systeme International, in French).
It’s easiest to think of a TV as emitting light directly, in much the same way as the Sun does. Nits are simply the measurement of the level of light (luminance) in a given area which the emitting source sends to your eyes or a camera sensor.
The Nit can be considered a unit of visible-light intensity which is often used to specify the brightness level of an LCD.
1 Nit is approximately equal to 3.426 Lumens. To work out a comparable number of Nits to Lumens, you need to multiply the number of Nits by 3.426. If you know the number of Lumens, and wish to know the Nits, simply divide the number of Lumens by 3.426.
Most consumer desktop LCDs have Nits of 200 to 300, the average TV most likely has an output capability of between 100 and 200 Nits, and an HDR TV ranges from 400 to 1,500 Nits.
Virtual Production sets currently sport around 6000 NIT ceiling and 1000 NIT wall panels.The ambient brightness of a sunny day with clear blue skies is between 7000-10,000 nits (between 3000-7000 nits for overcast skies and indirect sunlight).
A bright sunny day can have specular highlights that reach over 100,000 nits. Direct sunlight is around 1,600,000,000 nits.
10,000 nits is also the typical brightness of a fluorescent tube – bright, but not painful to look at.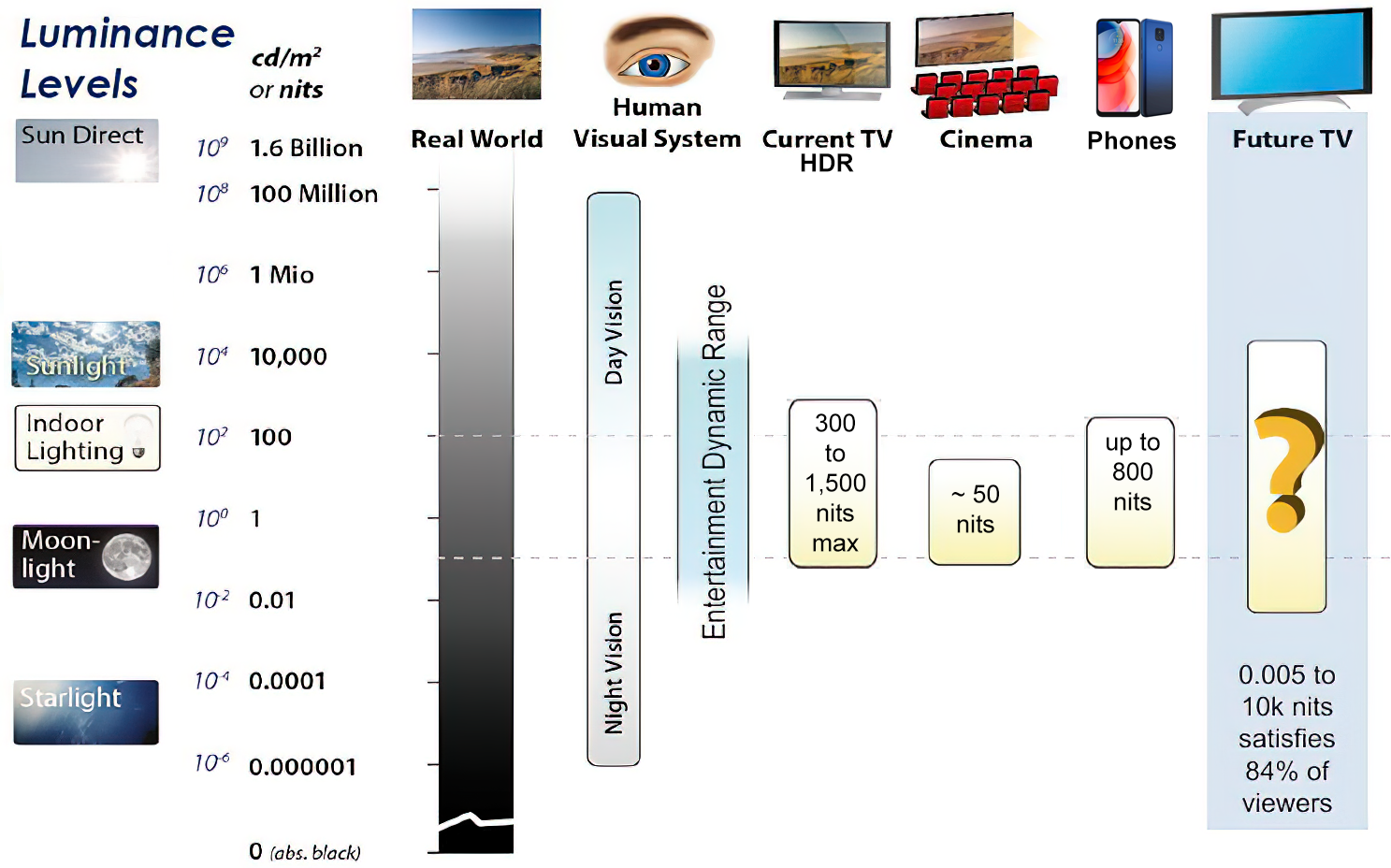
https://www.displaydaily.com/article/display-daily/dolby-vision-vs-hdr10-clarified
Tests showed that a “black level” of 0.005 nits (cd/m²) satisfied the vast majority of viewers. While 0.005 nits is very close to true black, Griffis says Dolby can go down to a black of 0.0001 nits, even though there is no need or ability for displays to get that dark today.
How bright is white? Dolby says the range of 0.005 nits – 10,000 nits satisfied 84% of the viewers in their viewing tests.
The brightest consumer HDR displays today are about 1,500 nits. Professional displays where HDR content is color-graded can achieve up to 4,000 nits peak brightness.High brightness that would be in danger of damaging the eye would be in the neighborhood of 250,000 nits.
Lumens
Lumen is a measure of how much light is emitted (luminance, luminous flux) by an object. It indicates the total potential amount of light from a light source that is visible to the human eye.
Lumen is commonly used in the context of light bulbs or video-projectors as a metric for their brightness power.Lumen is used to describe light output, and about video projectors, it is commonly referred to as ANSI Lumens. Simply put, lumens is how to find out how bright a LED display is. The higher the lumens, the brighter to display!
Technically speaking, a Lumen is the SI unit of luminous flux, which is equal to the amount of light which is emitted per second in a unit solid angle of one steradian from a uniform source of one-candela intensity radiating in all directions.
LUX
Lux (lx) or often Illuminance, is a photometric unit along a given area, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts. It is the measure of light at a specific distance within a specific area at that distance. Often used to measure the incidental sun’s intensity.
-
Photography basics: Solid Angle measures
Read more: Photography basics: Solid Angle measureshttp://www.calculator.org/property.aspx?name=solid+angle
A measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point. Thus. A measure for objects in the sky. Useful to retuen the size of the sun and moon… and in perspective, how much of their contribution to lighting. Solid angle can be represented in ‘angular diameter’ as well.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle
http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/steradian.html
A solid angle is expressed in a dimensionless unit called a steradian (symbol: sr). By default in terms of the total celestial sphere and before atmospheric’s scattering, the Sun and the Moon subtend fractional areas of 0.000546% (Sun) and 0.000531% (Moon).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle#Sun_and_Moon
On earth the sun is likely closer to 0.00011 solid angle after athmospheric scattering. The sun as perceived from earth has a diameter of 0.53 degrees. This is about 0.000064 solid angle.
http://www.numericana.com/answer/angles.htm
The mean angular diameter of the full moon is 2q = 0.52° (it varies with time around that average, by about 0.009°). This translates into a solid angle of 0.0000647 sr, which means that the whole night sky covers a solid angle roughly one hundred thousand times greater than the full moon.
More info
http://lcogt.net/spacebook/using-angles-describe-positions-and-apparent-sizes-objects
http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/glossary/def.php.s=topic_astronomy
Angular Size
The apparent size of an object as seen by an observer; expressed in units of degrees (of arc), arc minutes, or arc seconds. The moon, as viewed from the Earth, has an angular diameter of one-half a degree.
The angle covered by the diameter of the full moon is about 31 arcmin or 1/2°, so astronomers would say the Moon’s angular diameter is 31 arcmin, or the Moon subtends an angle of 31 arcmin.
Collections
| Explore posts
| Design And Composition
| Featured AI
Popular Searches
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.


