COMPOSITION
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
-
Key/Fill ratios and scene composition using false colors
Read more: Key/Fill ratios and scene composition using false colorsTo measure the contrast ratio you will need a light meter. The process starts with you measuring the main source of light, or the key light.
Get a reading from the brightest area on the face of your subject. Then, measure the area lit by the secondary light, or fill light. To make sense of what you have just measured you have to understand that the information you have just gathered is in F-stops, a measure of light. With each additional F-stop, for example going one stop from f/1.4 to f/2.0, you create a doubling of light. The reverse is also true; moving one stop from f/8.0 to f/5.6 results in a halving of the light.
Let’s say you grabbed a measurement from your key light of f/8.0. Then, when you measured your fill light area, you get a reading of f/4.0. This will lead you to a contrast ratio of 4:1 because there are two stops between f/4.0 and f/8.0 and each stop doubles the amount of light. In other words, two stops x twice the light per stop = four times as much light at f/8.0 than at f/4.0.
theslantedlens.com/2017/lighting-ratios-photo-video/
Examples in the post
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Image rendering bit depth
Read more: Image rendering bit depthThe terms 16-bit, 16-bit float, and 32-bit refer to different data formats used to store and represent image information, as bits per pixel.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_depth
In color technology, color depth also known as bit depth, is either the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel, OR the number of bits used for each color component of a single pixel.
When referring to a pixel, the concept can be defined as bits per pixel (bpp).
When referring to a color component, the concept can be defined as bits per component, bits per channel, bits per color (all three abbreviated bpc), and also bits per pixel component, bits per color channel or bits per sample (bps). Modern standards tend to use bits per component, but historical lower-depth systems used bits per pixel more often.
Color depth is only one aspect of color representation, expressing the precision with which the amount of each primary can be expressed; the other aspect is how broad a range of colors can be expressed (the gamut). The definition of both color precision and gamut is accomplished with a color encoding specification which assigns a digital code value to a location in a color space.
-
mmColorTarget – Nuke Gizmo for color matching a MacBeth chart
Read more: mmColorTarget – Nuke Gizmo for color matching a MacBeth charthttps://www.marcomeyer-vfx.de/posts/2014-04-11-mmcolortarget-nuke-gizmo/
https://www.marcomeyer-vfx.de/posts/mmcolortarget-nuke-gizmo/
https://vimeo.com/9.1652466e+07
https://www.nukepedia.com/gizmos/colour/mmcolortarget
-
SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixing
Read more: SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixingInternally, Mixbox treats colors as real-life pigments using the Kubelka & Munk theory to predict realistic color behavior.
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/painter/
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox.pdf
https://github.com/scrtwpns/mixbox
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/docs/
-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. … Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
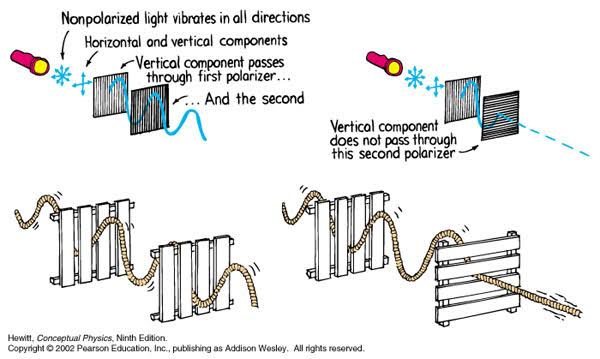
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
Light reflected from a non-metallic surface becomes polarized; this effect is maximum at Brewster’s angle, about 56° from the vertical for common glass.
A polarizer rotated to pass only light polarized in the direction perpendicular to the reflected light will absorb much of it. This absorption allows glare reflected from, for example, a body of water or a road to be reduced. Reflections from shiny surfaces (e.g. vegetation, sweaty skin, water surfaces, glass) are also reduced. This allows the natural color and detail of what is beneath to come through. Reflections from a window into a dark interior can be much reduced, allowing it to be seen through. (The same effects are available for vision by using polarizing sunglasses.)
www.physicsclassroom.com/class/light/u12l1e.cfm
Some of the light coming from the sky is polarized (bees use this phenomenon for navigation). The electrons in the air molecules cause a scattering of sunlight in all directions. This explains why the sky is not dark during the day. But when looked at from the sides, the light emitted from a specific electron is totally polarized.[3] Hence, a picture taken in a direction at 90 degrees from the sun can take advantage of this polarization. Use of a polarizing filter, in the correct direction, will filter out the polarized component of skylight, darkening the sky; the landscape below it, and clouds, will be less affected, giving a photograph with a darker and more dramatic sky, and emphasizing the clouds.

There are two types of polarizing filters readily available, linear and “circular”, which have exactly the same effect photographically. But the metering and auto-focus sensors in certain cameras, including virtually all auto-focus SLRs, will not work properly with linear polarizers because the beam splitters used to split off the light for focusing and metering are polarization-dependent.
Polarizing filters reduce the light passed through to the film or sensor by about one to three stops (2–8×) depending on how much of the light is polarized at the filter angle selected. Auto-exposure cameras will adjust for this by widening the aperture, lengthening the time the shutter is open, and/or increasing the ASA/ISO speed of the camera.
www.adorama.com/alc/nd-filter-vs-polarizer-what%25e2%2580%2599s-the-difference
Neutral Density (ND) filters help control image exposure by reducing the light that enters the camera so that you can have more control of your depth of field and shutter speed. Polarizers or polarizing filters work in a similar way, but the difference is that they selectively let light waves of a certain polarization pass through. This effect helps create more vivid colors in an image, as well as manage glare and reflections from water surfaces. Both are regarded as some of the best filters for landscape and travel photography as they reduce the dynamic range in high-contrast images, thus enabling photographers to capture more realistic and dramatic sceneries.
shopfelixgray.com/blog/polarized-vs-non-polarized-sunglasses/
www.eyebuydirect.com/blog/difference-polarized-nonpolarized-sunglasses/
LIGHTING
-
Unity 3D resources
Read more: Unity 3D resources
http://answers.unity3d.com/questions/12321/how-can-i-start-learning-unity-fast-list-of-tutori.html
If you have no previous experience with Unity, start with these six video tutorials which give a quick overview of the Unity interface and some important features http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/video/
-
domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRI
Read more: domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRIWhen collecting hdri make sure the data supports basic metadata, such as:
- Iso
- Aperture
- Exposure time or shutter time
- Color temperature
- Color space Exposure value (what the sensor receives of the sun intensity in lux)
- 7+ brackets (with 5 or 6 being the perceived balanced exposure)
In image processing, computer graphics, and photography, high dynamic range imaging (HDRI or just HDR) is a set of techniques that allow a greater dynamic range of luminances (a Photometry measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle) between the lightest and darkest areas of an image than standard digital imaging techniques or photographic methods. This wider dynamic range allows HDR images to represent more accurately the wide range of intensity levels found in real scenes ranging from direct sunlight to faint starlight and to the deepest shadows.
The two main sources of HDR imagery are computer renderings and merging of multiple photographs, which in turn are known as low dynamic range (LDR) or standard dynamic range (SDR) images. Tone Mapping (Look-up) techniques, which reduce overall contrast to facilitate display of HDR images on devices with lower dynamic range, can be applied to produce images with preserved or exaggerated local contrast for artistic effect. Photography
In photography, dynamic range is measured in Exposure Values (in photography, exposure value denotes all combinations of camera shutter speed and relative aperture that give the same exposure. The concept was developed in Germany in the 1950s) differences or stops, between the brightest and darkest parts of the image that show detail. An increase of one EV or one stop is a doubling of the amount of light.
The human response to brightness is well approximated by a Steven’s power law, which over a reasonable range is close to logarithmic, as described by the Weber�Fechner law, which is one reason that logarithmic measures of light intensity are often used as well.
HDR is short for High Dynamic Range. It’s a term used to describe an image which contains a greater exposure range than the “black” to “white” that 8 or 16-bit integer formats (JPEG, TIFF, PNG) can describe. Whereas these Low Dynamic Range images (LDR) can hold perhaps 8 to 10 f-stops of image information, HDR images can describe beyond 30 stops and stored in 32 bit images.
Collections
| Explore posts
| Design And Composition
| Featured AI
Popular Searches
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.


