COMPOSITION
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat SheetWhere is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
What type of lighting?-> High key lighting.
Features bright, even illumination and few conspicuous shadows. This lighting key is often used in musicals and comedies.Low key lighting
Features diffused shadows and atmospheric pools of light. This lighting key is often used in mysteries and thrillers.High contrast lighting
Features harsh shafts of lights and dramatic streaks of blackness. This type of lighting is often used in tragedies and melodramas.What type of shot?
Extreme long shot
Taken from a great distance, showing much of the locale. Ifpeople are included in these shots, they usually appear as mere specks-> Long shot
Corresponds to the space between the audience and the stage in a live theater. The long shots show the characters and some of the locale.Full shot
Range with just enough space to contain the human body in full. The full shot shows the character and a minimal amount of the locale.Medium shot
Shows the human figure from the knees or waist up.Close-Up
Concentrates on a relatively small object and show very little if any locale.Extreme close-up
Focuses on an unnaturally small portion of an object, giving that part great detail and symbolic significance.What angle?
Bird’s-eye view.
The shot is photographed directly from above. This type of shot can be disorienting, and the people photographed seem insignificant.High angle.
This angle reduces the size of the objects photographed. A person photographed from this angle seems harmless and insignificant, but to a lesser extent than with the bird’s-eye view.-> Eye-level shot.
The clearest view of an object, but seldom intrinsically dramatic, because it tends to be the norm.Low angle.
This angle increases high and a sense of verticality, heightening the importance of the object photographed. A person shot from this angle is given a sense of power and respect.Oblique angle.
For this angle, the camera is tilted laterally, giving the image a slanted appearance. Oblique angles suggest tension, transition, a impending movement. They are also called canted or dutch angles.What is the dominant color?
The use of color in this shot is symbolic. The scene is set in warehouse. Both the set and characters are blues, blacks and whites.
This was intentional allowing for the scenes and shots with blood to have a great level of contrast.
What is the Lens/Filter/Stock?
Telephoto lens.
A lens that draws objects closer but also diminishes the illusion of depth.Wide-angle lens.
A lens that takes in a broad area and increases the illusion of depth but sometimes distorts the edges of the image.Fast film stock.
Highly sensitive to light, it can register an image with little illumination. However, the final product tends to be grainy.Slow film stock.
Relatively insensitive to light, it requires a great deal of illumination. The final product tends to look polished.The lens is not wide-angle because there isn’t a great sense of depth, nor are several planes in focus. The lens is probably long but not necessarily a telephoto lens because the depth isn’t inordinately compressed.
The stock is fast because of the grainy quality of the image.
Subsidiary Contrast; where does the eye go next?
The two guns.
How much visual information is packed into the image? Is the texture stark, moderate, or highly detailed?
Minimalist clutter in the warehouse allows a focus on a character driven thriller.
What is the Composition?
Horizontal.
Compositions based on horizontal lines seem visually at rest and suggest placidity or peacefulness.Vertical.
Compositions based on vertical lines seem visually at rest and suggest strength.-> Diagonal.
Compositions based on diagonal, or oblique, lines seem dynamic and suggest tension or anxiety.-> Binary. Binary structures emphasize parallelism.
Triangle.
Triadic compositions stress the dynamic interplay among three mainCircle.
Circular compositions suggest security and enclosure.Is the form open or closed? Does the image suggest a window that arbitrarily isolates a fragment of the scene? Or a proscenium arch, in which the visual elements are carefully arranged and held in balance?
The most nebulous of all the categories of mise en scene, the type of form is determined by how consciously structured the mise en scene is. Open forms stress apparently simple techniques, because with these unself-conscious methods the filmmaker is able to emphasize the immediate, the familiar, the intimate aspects of reality. In open-form images, the frame tends to be deemphasized. In closed form images, all the necessary information is carefully structured within the confines of the frame. Space seems enclosed and self-contained rather than continuous.
Could argue this is a proscenium arch because this is such a classic shot with parallels and juxtapositions.
Is the framing tight or loose? Do the character have no room to move around, or can they move freely without impediments?
Shots where the characters are placed at the edges of the frame and have little room to move around within the frame are considered tight.
Longer shots, in which characters have room to move around within the frame, are considered loose and tend to suggest freedom.
Center-framed giving us the entire scene showing isolation, place and struggle.
Depth of Field. On how many planes is the image composed (how many are in focus)? Does the background or foreground comment in any way on the mid-ground?
Standard DOF, one background and clearly defined foreground.
Which way do the characters look vis-a-vis the camera?
An actor can be photographed in any of five basic positions, each conveying different psychological overtones.
Full-front (facing the camera):
the position with the most intimacy. The character is looking in our direction, inviting our complicity.Quarter Turn:
the favored position of most filmmakers. This position offers a high degree of intimacy but with less emotional involvement than the full-front.-> Profile (looking of the frame left or right):
More remote than the quarter turn, the character in profile seems unaware of being observed, lost in his or her own thoughts.Three-quarter Turn:
More anonymous than the profile, this position is useful for conveying a character’s unfriendly or antisocial feelings, for in effect, the character is partially turning his or her back on us, rejecting our interest.Back to Camera:
The most anonymous of all positions, this position is often used to suggest a character’s alienation from the world. When a character has his or her back to the camera, we can only guess what’s taking place internally, conveying a sense of concealment, or mystery.How much space is there between the characters?
Extremely close, for a gunfight.
The way people use space can be divided into four proxemic patterns.
Intimate distances.
The intimate distance ranges from skin contact to about eighteen inches away. This is the distance of physical involvement–of love, comfort, and tenderness between individuals.-> Personal distances.
The personal distance ranges roughly from eighteen inches away to about four feet away. These distances tend to be reserved for friends and acquaintances. Personal distances preserve the privacy between individuals, yet these rages don’t necessarily suggest exclusion, as intimate distances often do.Social distances.
The social distance rages from four feet to about twelve feet. These distances are usually reserved for impersonal business and casual social gatherings. It’s a friendly range in most cases, yet somewhat more formal than the personal distance.Public distances.
The public distance extends from twelve feet to twenty-five feet or more. This range tends to be formal and rather detached.
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Björn Ottosson – OKHSV and OKHSL – Two new color spaces for color picking
Read more: Björn Ottosson – OKHSV and OKHSL – Two new color spaces for color pickinghttps://bottosson.github.io/misc/colorpicker
https://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorpicker/
https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2024/10/interview-bjorn-ottosson-creator-oklab-color-space/
One problem with sRGB is that in a gradient between blue and white, it becomes a bit purple in the middle of the transition. That’s because sRGB really isn’t created to mimic how the eye sees colors; rather, it is based on how CRT monitors work. That means it works with certain frequencies of red, green, and blue, and also the non-linear coding called gamma. It’s a miracle it works as well as it does, but it’s not connected to color perception. When using those tools, you sometimes get surprising results, like purple in the gradient.
There were also attempts to create simple models matching human perception based on XYZ, but as it turned out, it’s not possible to model all color vision that way. Perception of color is incredibly complex and depends, among other things, on whether it is dark or light in the room and the background color it is against. When you look at a photograph, it also depends on what you think the color of the light source is. The dress is a typical example of color vision being very context-dependent. It is almost impossible to model this perfectly.
I based Oklab on two other color spaces, CIECAM16 and IPT. I used the lightness and saturation prediction from CIECAM16, which is a color appearance model, as a target. I actually wanted to use the datasets used to create CIECAM16, but I couldn’t find them.
IPT was designed to have better hue uniformity. In experiments, they asked people to match light and dark colors, saturated and unsaturated colors, which resulted in a dataset for which colors, subjectively, have the same hue. IPT has a few other issues but is the basis for hue in Oklab.
In the Munsell color system, colors are described with three parameters, designed to match the perceived appearance of colors: Hue, Chroma and Value. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. Modern color spaces and models, such as CIELAB, Cam16 and Björn Ottosson own Oklab, are very similar in their construction.
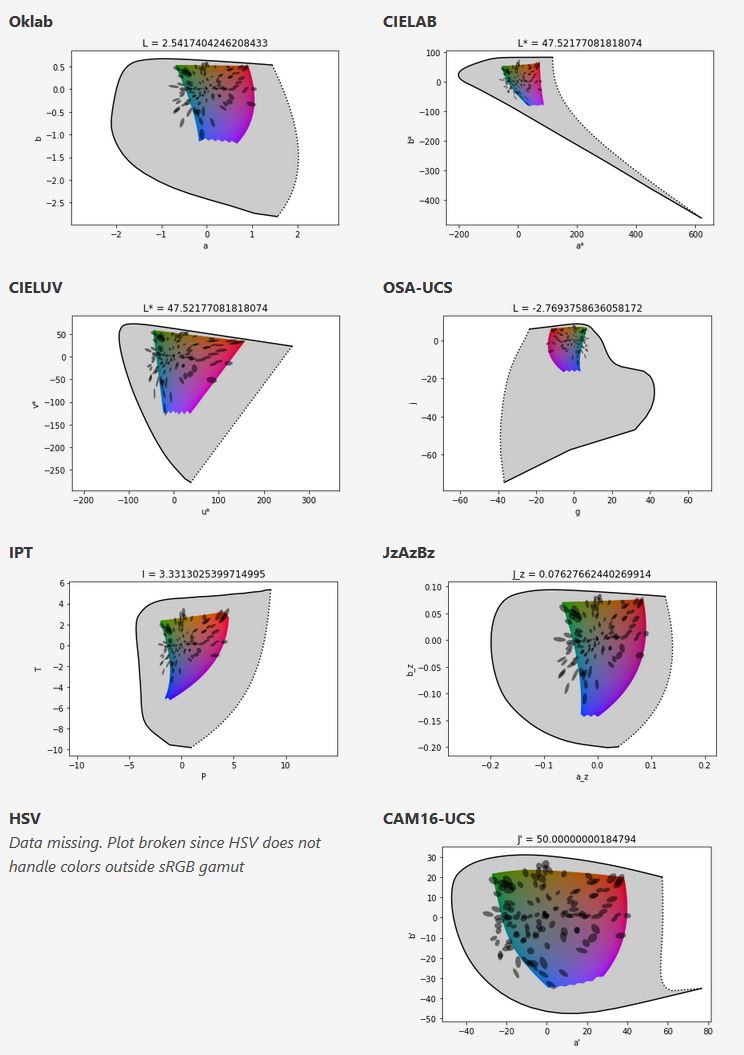
By far the most used color spaces today for color picking are HSL and HSV, two representations introduced in the classic 1978 paper “Color Spaces for Computer Graphics”. HSL and HSV designed to roughly correlate with perceptual color properties while being very simple and cheap to compute.
Today HSL and HSV are most commonly used together with the sRGB color space.

One of the main advantages of HSL and HSV over the different Lab color spaces is that they map the sRGB gamut to a cylinder. This makes them easy to use since all parameters can be changed independently, without the risk of creating colors outside of the target gamut.
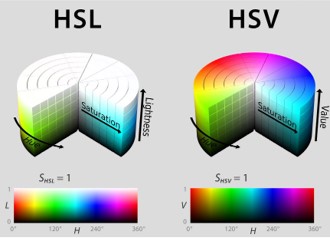
The main drawback on the other hand is that their properties don’t match human perception particularly well.
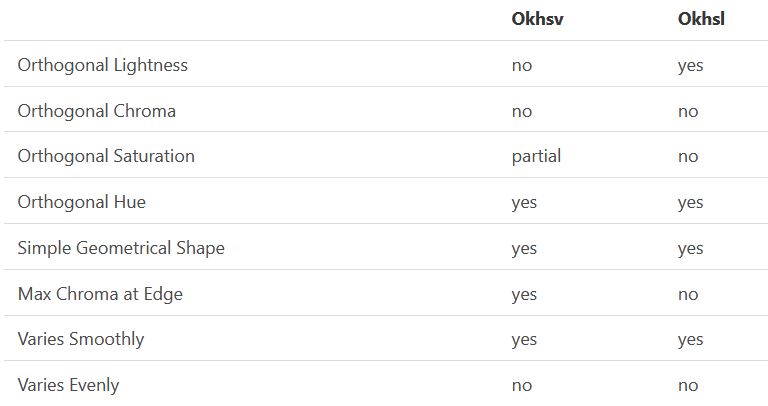
Reconciling these conflicting goals perfectly isn’t possible, but given that HSV and HSL don’t use anything derived from experiments relating to human perception, creating something that makes a better tradeoff does not seem unreasonable.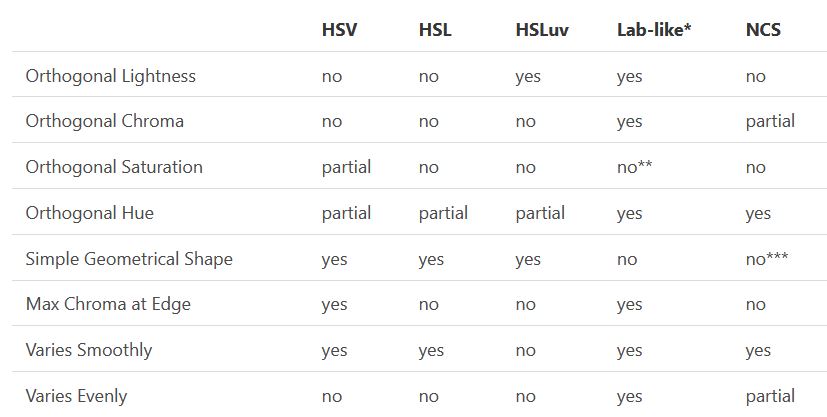
With this new lightness estimate, we are ready to look into the construction of Okhsv and Okhsl.
-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. … Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
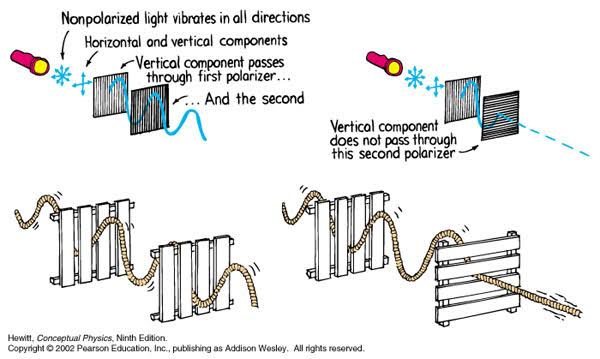
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
Light reflected from a non-metallic surface becomes polarized; this effect is maximum at Brewster’s angle, about 56° from the vertical for common glass.
A polarizer rotated to pass only light polarized in the direction perpendicular to the reflected light will absorb much of it. This absorption allows glare reflected from, for example, a body of water or a road to be reduced. Reflections from shiny surfaces (e.g. vegetation, sweaty skin, water surfaces, glass) are also reduced. This allows the natural color and detail of what is beneath to come through. Reflections from a window into a dark interior can be much reduced, allowing it to be seen through. (The same effects are available for vision by using polarizing sunglasses.)
www.physicsclassroom.com/class/light/u12l1e.cfm
Some of the light coming from the sky is polarized (bees use this phenomenon for navigation). The electrons in the air molecules cause a scattering of sunlight in all directions. This explains why the sky is not dark during the day. But when looked at from the sides, the light emitted from a specific electron is totally polarized.[3] Hence, a picture taken in a direction at 90 degrees from the sun can take advantage of this polarization. Use of a polarizing filter, in the correct direction, will filter out the polarized component of skylight, darkening the sky; the landscape below it, and clouds, will be less affected, giving a photograph with a darker and more dramatic sky, and emphasizing the clouds.

There are two types of polarizing filters readily available, linear and “circular”, which have exactly the same effect photographically. But the metering and auto-focus sensors in certain cameras, including virtually all auto-focus SLRs, will not work properly with linear polarizers because the beam splitters used to split off the light for focusing and metering are polarization-dependent.
Polarizing filters reduce the light passed through to the film or sensor by about one to three stops (2–8×) depending on how much of the light is polarized at the filter angle selected. Auto-exposure cameras will adjust for this by widening the aperture, lengthening the time the shutter is open, and/or increasing the ASA/ISO speed of the camera.
www.adorama.com/alc/nd-filter-vs-polarizer-what%25e2%2580%2599s-the-difference
Neutral Density (ND) filters help control image exposure by reducing the light that enters the camera so that you can have more control of your depth of field and shutter speed. Polarizers or polarizing filters work in a similar way, but the difference is that they selectively let light waves of a certain polarization pass through. This effect helps create more vivid colors in an image, as well as manage glare and reflections from water surfaces. Both are regarded as some of the best filters for landscape and travel photography as they reduce the dynamic range in high-contrast images, thus enabling photographers to capture more realistic and dramatic sceneries.
shopfelixgray.com/blog/polarized-vs-non-polarized-sunglasses/
www.eyebuydirect.com/blog/difference-polarized-nonpolarized-sunglasses/
-
The Color of Infinite Temperature
Read more: The Color of Infinite TemperatureThis is the color of something infinitely hot.
Of course you’d instantly be fried by gamma rays of arbitrarily high frequency, but this would be its spectrum in the visible range.
johncarlosbaez.wordpress.com/2022/01/16/the-color-of-infinite-temperature/
This is also the color of a typical neutron star. They’re so hot they look the same.
It’s also the color of the early Universe!This was worked out by David Madore.
The color he got is sRGB(148,177,255).
www.htmlcsscolor.com/hex/94B1FFAnd according to the experts who sip latte all day and make up names for colors, this color is called ‘Perano’.
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
Read more: Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminancehttps://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…) -
Sensitivity of human eye
Read more: Sensitivity of human eyehttp://www.wikilectures.eu/index.php/Spectral_sensitivity_of_the_human_eye
http://www.normankoren.com/Human_spectral_sensitivity_small.jpg
Spectral sensitivity of eye is influenced by light intensity. And the light intensity determines the level of activity of cones cell and rod cell. This is the main characteristic of human vision. Sensitivity to individual colors, in other words, wavelengths of the light spectrum, is explained by the RGB (red-green-blue) theory. This theory assumed that there are three kinds of cones. It’s selectively sensitive to red (700-630 nm), green (560-500 nm), and blue (490-450 nm) light. And their mutual interaction allow to perceive all colors of the spectrum.
http://weeklysciencequiz.blogspot.com/2013/01/violet-skies-are-for-birds.html

Sensitivity of human eye Sensitivity of human eyes to light increase with the decrease in light intensity. In day-light condition, the cones cell is responding to this condition. And the eye is most sensitive at 555 nm. In darkness condition, the rod cell is responding to this condition. And the eye is most sensitive at 507 nm.
As light intensity decreases, cone function changes more effective way. And when decrease the light intensity, it prompt to accumulation of rhodopsin. Furthermore, in activates rods, it allow to respond to stimuli of light in much lower intensity.
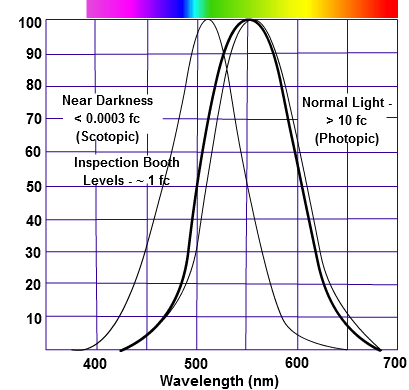
The three curves in the figure above shows the normalized response of an average human eye to various amounts of ambient light. The shift in sensitivity occurs because two types of photoreceptors called cones and rods are responsible for the eye’s response to light. The curve on the right shows the eye’s response under normal lighting conditions and this is called the photopic response. The cones respond to light under these conditions.
As mentioned previously, cones are composed of three different photo pigments that enable color perception. This curve peaks at 555 nanometers, which means that under normal lighting conditions, the eye is most sensitive to a yellowish-green color. When the light levels drop to near total darkness, the response of the eye changes significantly as shown by the scotopic response curve on the left. At this level of light, the rods are most active and the human eye is more sensitive to the light present, and less sensitive to the range of color. Rods are highly sensitive to light but are comprised of a single photo pigment, which accounts for the loss in ability to discriminate color. At this very low light level, sensitivity to blue, violet, and ultraviolet is increased, but sensitivity to yellow and red is reduced. The heavier curve in the middle represents the eye’s response at the ambient light level found in a typical inspection booth. This curve peaks at 550 nanometers, which means the eye is most sensitive to yellowish-green color at this light level. Fluorescent penetrant inspection materials are designed to fluoresce at around 550 nanometers to produce optimal sensitivity under dim lighting conditions.
LIGHTING
-
Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution function
Read more: Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution functionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bidirectional_reflectance_distribution_function
The bidirectional reflectance distribution function is a four-dimensional function that defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface
http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~zhu/tutorial/An_Introduction_to_BRDF-Based_Lighting.pdf
In general, when light interacts with matter, a complicated light-matter dynamic occurs. This interaction depends on the physical characteristics of the light as well as the physical composition and characteristics of the matter.
That is, some of the incident light is reflected, some of the light is transmitted, and another portion of the light is absorbed by the medium itself.
A BRDF describes how much light is reflected when light makes contact with a certain material. Similarly, a BTDF (Bi-directional Transmission Distribution Function) describes how much light is transmitted when light makes contact with a certain material
http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~smr/cs348c-97/surveypaper.html
It is difficult to establish exactly how far one should go in elaborating the surface model. A truly complete representation of the reflective behavior of a surface might take into account such phenomena as polarization, scattering, fluorescence, and phosphorescence, all of which might vary with position on the surface. Therefore, the variables in this complete function would be:
incoming and outgoing angle incoming and outgoing wavelength incoming and outgoing polarization (both linear and circular) incoming and outgoing position (which might differ due to subsurface scattering) time delay between the incoming and outgoing light ray
Collections
| Explore posts
| Design And Composition
| Featured AI
Popular Searches
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.

