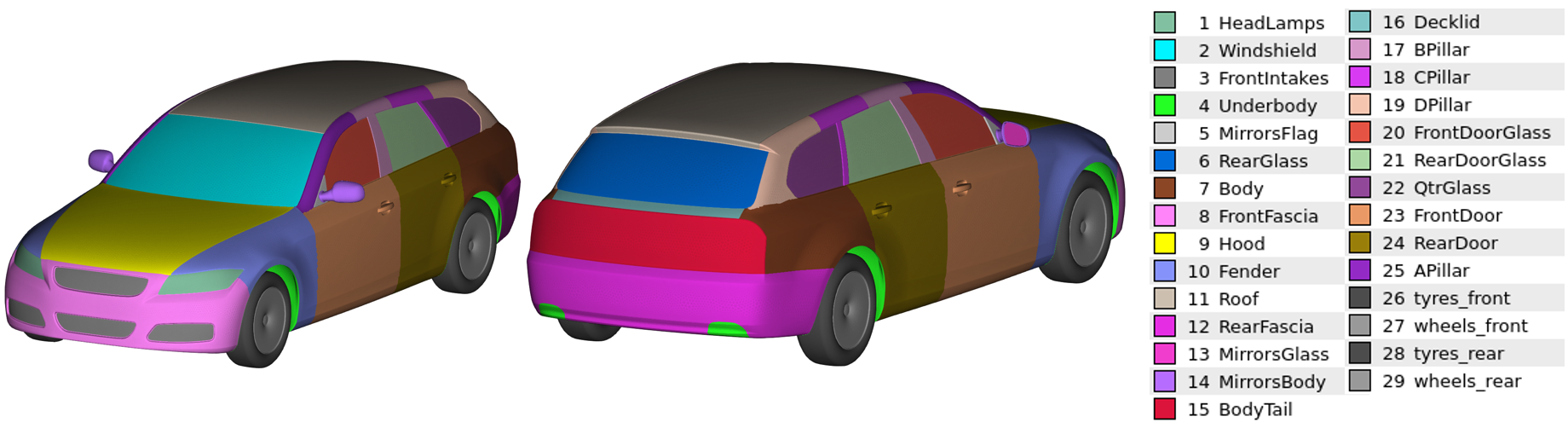
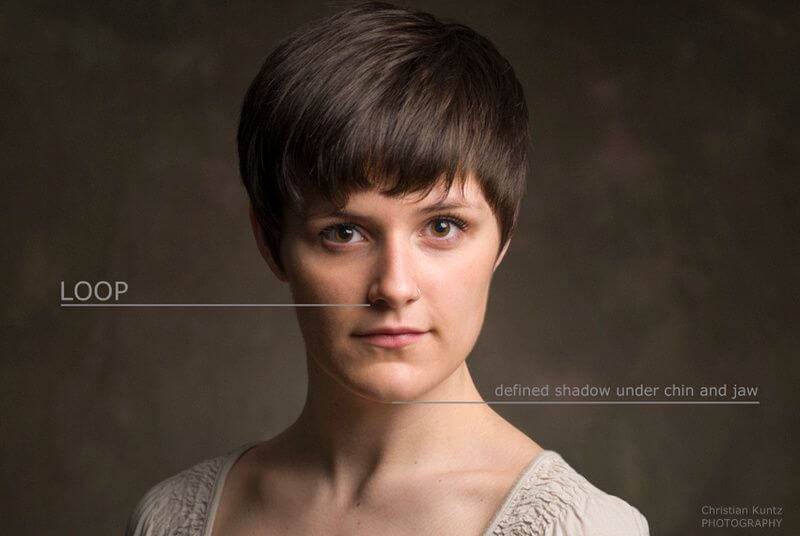
COMPOSITION
-
Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and film
Read more: Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and filmhttp://www.diyphotography.net/basic-lighting-techniques-need-know-photography-film/
Amongst the basic techniques, there’s…
1- Side lighting – Literally how it sounds, lighting a subject from the side when they’re faced toward you
2- Rembrandt lighting – Here the light is at around 45 degrees over from the front of the subject, raised and pointing down at 45 degrees
3- Back lighting – Again, how it sounds, lighting a subject from behind. This can help to add drama with silouettes
4- Rim lighting – This produces a light glowing outline around your subject
5- Key light – The main light source, and it’s not necessarily always the brightest light source
6- Fill light – This is used to fill in the shadows and provide detail that would otherwise be blackness
7- Cross lighting – Using two lights placed opposite from each other to light two subjects
DESIGN
-
A.I. Algorithm art fetches US$432,500 at Christie auction
Read more: A.I. Algorithm art fetches US$432,500 at Christie auctionwww.ctvnews.ca/entertainment/algorithm-art-fetches-us-432-500-at-christie-s-auction-1.4150620
www.christies.com/features/A-collaboration-between-two-artists-one-human-one-a-machine-9332-1.aspx

COLOR
-
Björn Ottosson – OKlch color space
Read more: Björn Ottosson – OKlch color spaceBjörn Ottosson proposed OKlch in 2020 to create a color space that can closely mimic how color is perceived by the human eye, predicting perceived lightness, chroma, and hue.
The OK in OKLCH stands for Optimal Color.
- L: Lightness (the perceived brightness of the color)
- C: Chroma (the intensity or saturation of the color)
- H: Hue (the actual color, such as red, blue, green, etc.)

Also read:
-
SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixing
Read more: SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixingInternally, Mixbox treats colors as real-life pigments using the Kubelka & Munk theory to predict realistic color behavior.
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/painter/
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox.pdf
https://github.com/scrtwpns/mixbox
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/docs/
-
The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t See
Read more: The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t Seewww.livescience.com/17948-red-green-blue-yellow-stunning-colors.html
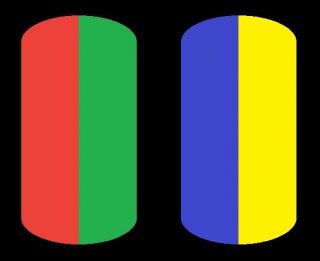
While the human eye has red, green, and blue-sensing cones, those cones are cross-wired in the retina to produce a luminance channel plus a red-green and a blue-yellow channel, and it’s data in that color space (known technically as “LAB”) that goes to the brain. That’s why we can’t perceive a reddish-green or a yellowish-blue, whereas such colors can be represented in the RGB color space used by digital cameras.
https://en.rockcontent.com/blog/the-use-of-yellow-in-data-design
The back of the retina is covered in light-sensitive neurons known as cone cells and rod cells. There are three types of cone cells, each sensitive to different ranges of light. These ranges overlap, but for convenience the cones are referred to as blue (short-wavelength), green (medium-wavelength), and red (long-wavelength). The rod cells are primarily used in low-light situations, so we’ll ignore those for now.
When light enters the eye and hits the cone cells, the cones get excited and send signals to the brain through the visual cortex. Different wavelengths of light excite different combinations of cones to varying levels, which generates our perception of color. You can see that the red cones are most sensitive to light, and the blue cones are least sensitive. The sensitivity of green and red cones overlaps for most of the visible spectrum.
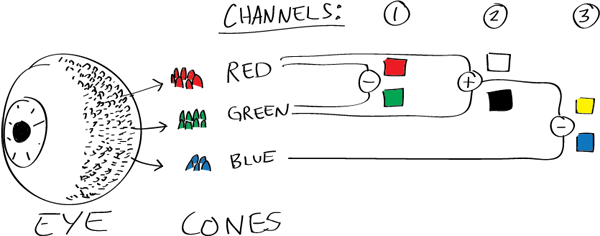
Here’s how your brain takes the signals of light intensity from the cones and turns it into color information. To see red or green, your brain finds the difference between the levels of excitement in your red and green cones. This is the red-green channel.
To get “brightness,” your brain combines the excitement of your red and green cones. This creates the luminance, or black-white, channel. To see yellow or blue, your brain then finds the difference between this luminance signal and the excitement of your blue cones. This is the yellow-blue channel.
From the calculations made in the brain along those three channels, we get four basic colors: blue, green, yellow, and red. Seeing blue is what you experience when low-wavelength light excites the blue cones more than the green and red.
Seeing green happens when light excites the green cones more than the red cones. Seeing red happens when only the red cones are excited by high-wavelength light.
Here’s where it gets interesting. Seeing yellow is what happens when BOTH the green AND red cones are highly excited near their peak sensitivity. This is the biggest collective excitement that your cones ever have, aside from seeing pure white.
Notice that yellow occurs at peak intensity in the graph to the right. Further, the lens and cornea of the eye happen to block shorter wavelengths, reducing sensitivity to blue and violet light.
-
If a blind person gained sight, could they recognize objects previously touched?
Read more: If a blind person gained sight, could they recognize objects previously touched?Blind people who regain their sight may find themselves in a world they don’t immediately comprehend. “It would be more like a sighted person trying to rely on tactile information,” Moore says.
Learning to see is a developmental process, just like learning language, Prof Cathleen Moore continues. “As far as vision goes, a three-and-a-half year old child is already a well-calibrated system.”
-
“Reality” is constructed by your brain. Here’s what that means, and why it matters.
Read more: “Reality” is constructed by your brain. Here’s what that means, and why it matters.“Fix your gaze on the black dot on the left side of this image. But wait! Finish reading this paragraph first. As you gaze at the left dot, try to answer this question: In what direction is the object on the right moving? Is it drifting diagonally, or is it moving up and down?”

What color are these strawberries?

Are A and B the same gray?

LIGHTING
-
domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRI
Read more: domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRIWhen collecting hdri make sure the data supports basic metadata, such as:
- Iso
- Aperture
- Exposure time or shutter time
- Color temperature
- Color space Exposure value (what the sensor receives of the sun intensity in lux)
- 7+ brackets (with 5 or 6 being the perceived balanced exposure)
In image processing, computer graphics, and photography, high dynamic range imaging (HDRI or just HDR) is a set of techniques that allow a greater dynamic range of luminances (a Photometry measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle) between the lightest and darkest areas of an image than standard digital imaging techniques or photographic methods. This wider dynamic range allows HDR images to represent more accurately the wide range of intensity levels found in real scenes ranging from direct sunlight to faint starlight and to the deepest shadows.
The two main sources of HDR imagery are computer renderings and merging of multiple photographs, which in turn are known as low dynamic range (LDR) or standard dynamic range (SDR) images. Tone Mapping (Look-up) techniques, which reduce overall contrast to facilitate display of HDR images on devices with lower dynamic range, can be applied to produce images with preserved or exaggerated local contrast for artistic effect. Photography
In photography, dynamic range is measured in Exposure Values (in photography, exposure value denotes all combinations of camera shutter speed and relative aperture that give the same exposure. The concept was developed in Germany in the 1950s) differences or stops, between the brightest and darkest parts of the image that show detail. An increase of one EV or one stop is a doubling of the amount of light.
The human response to brightness is well approximated by a Steven’s power law, which over a reasonable range is close to logarithmic, as described by the Weber�Fechner law, which is one reason that logarithmic measures of light intensity are often used as well.
HDR is short for High Dynamic Range. It’s a term used to describe an image which contains a greater exposure range than the “black” to “white” that 8 or 16-bit integer formats (JPEG, TIFF, PNG) can describe. Whereas these Low Dynamic Range images (LDR) can hold perhaps 8 to 10 f-stops of image information, HDR images can describe beyond 30 stops and stored in 32 bit images.

-
Fast, optimized ‘for’ pixel loops with OpenCV and Python to create tone mapped HDR images
Read more: Fast, optimized ‘for’ pixel loops with OpenCV and Python to create tone mapped HDR imageshttps://pyimagesearch.com/2017/08/28/fast-optimized-for-pixel-loops-with-opencv-and-python/
https://learnopencv.com/exposure-fusion-using-opencv-cpp-python/
Exposure Fusion is a method for combining images taken with different exposure settings into one image that looks like a tone mapped High Dynamic Range (HDR) image.
-
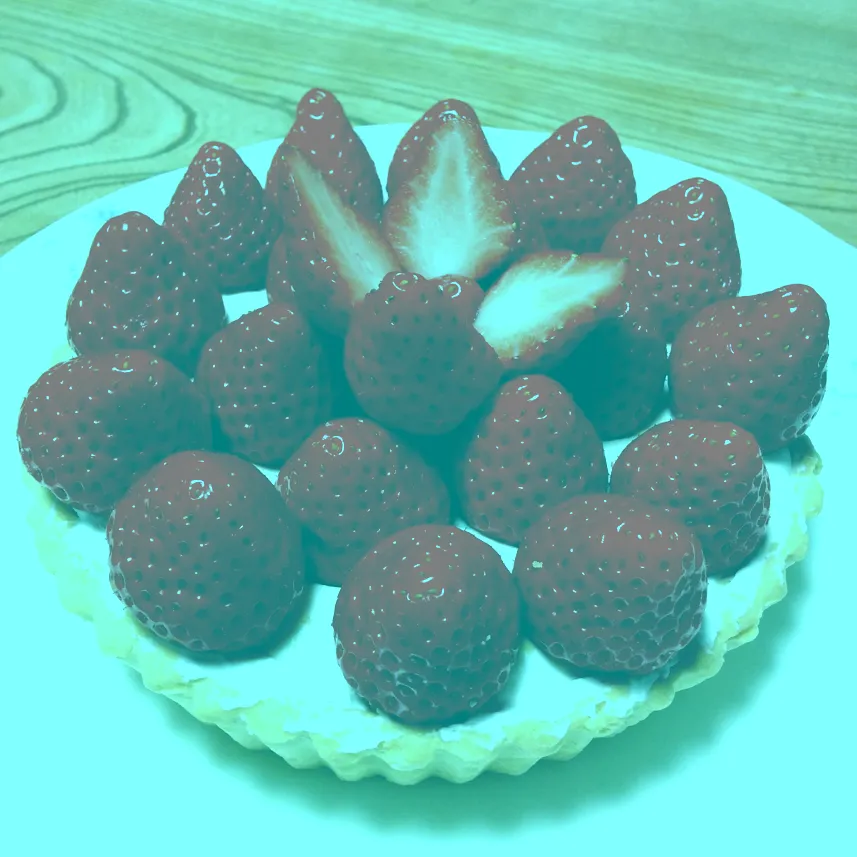
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Read more: What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…RASTERIZATION
Rasterisation (or rasterization) is the task of taking the information described in a vector graphics format OR the vertices of triangles making 3D shapes and converting them into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes), or in other words “rasterizing” vectors or 3D models onto a 2D plane for display on a computer screen.For each triangle of a 3D shape, you project the corners of the triangle on the virtual screen with some math (projective geometry). Then you have the position of the 3 corners of the triangle on the pixel screen. Those 3 points have texture coordinates, so you know where in the texture are the 3 corners. The cost is proportional to the number of triangles, and is only a little bit affected by the screen resolution.
In computer graphics, a raster graphics or bitmap image is a dot matrix data structure that represents a generally rectangular grid of pixels (points of color), viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium.
With rasterization, objects on the screen are created from a mesh of virtual triangles, or polygons, that create 3D models of objects. A lot of information is associated with each vertex, including its position in space, as well as information about color, texture and its “normal,” which is used to determine the way the surface of an object is facing.
Computers then convert the triangles of the 3D models into pixels, or dots, on a 2D screen. Each pixel can be assigned an initial color value from the data stored in the triangle vertices.
Further pixel processing or “shading,” including changing pixel color based on how lights in the scene hit the pixel, and applying one or more textures to the pixel, combine to generate the final color applied to a pixel.
The main advantage of rasterization is its speed. However, rasterization is simply the process of computing the mapping from scene geometry to pixels and does not prescribe a particular way to compute the color of those pixels. So it cannot take shading, especially the physical light, into account and it cannot promise to get a photorealistic output. That’s a big limitation of rasterization.
There are also multiple problems:
If you have two triangles one is behind the other, you will draw twice all the pixels. you only keep the pixel from the triangle that is closer to you (Z-buffer), but you still do the work twice.
The borders of your triangles are jagged as it is hard to know if a pixel is in the triangle or out. You can do some smoothing on those, that is anti-aliasing.
You have to handle every triangles (including the ones behind you) and then see that they do not touch the screen at all. (we have techniques to mitigate this where we only look at triangles that are in the field of view)
Transparency is hard to handle (you can’t just do an average of the color of overlapping transparent triangles, you have to do it in the right order)
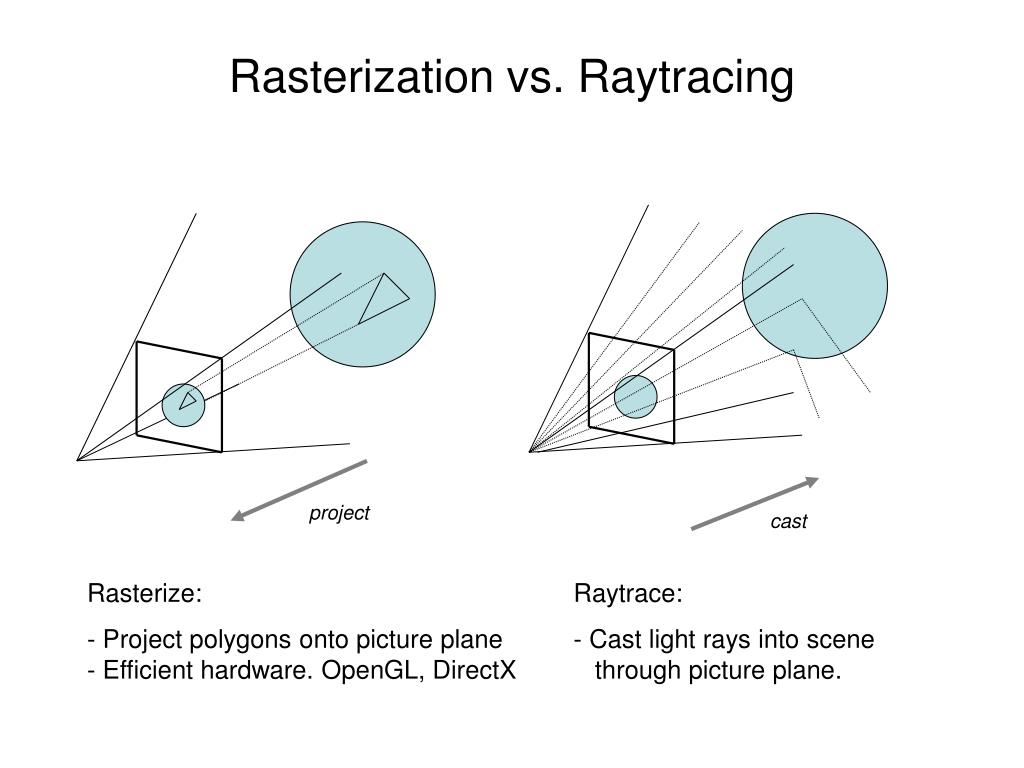
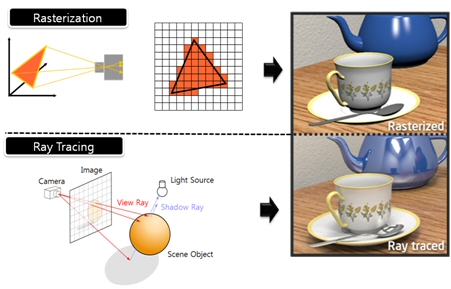
RAY CASTING
It is almost the exact reverse of rasterization: you start from the virtual screen instead of the vector or 3D shapes, and you project a ray, starting from each pixel of the screen, until it intersect with a triangle.The cost is directly correlated to the number of pixels in the screen and you need a really cheap way of finding the first triangle that intersect a ray. In the end, it is more expensive than rasterization but it will, by design, ignore the triangles that are out of the field of view.
You can use it to continue after the first triangle it hit, to take a little bit of the color of the next one, etc… This is useful to handle the border of the triangle cleanly (less jagged) and to handle transparency correctly.
RAYTRACING
Same idea as ray casting except once you hit a triangle you reflect on it and go into a different direction. The number of reflection you allow is the “depth” of your ray tracing. The color of the pixel can be calculated, based off the light source and all the polygons it had to reflect off of to get to that screen pixel.The easiest way to think of ray tracing is to look around you, right now. The objects you’re seeing are illuminated by beams of light. Now turn that around and follow the path of those beams backwards from your eye to the objects that light interacts with. That’s ray tracing.
Ray tracing is eye-oriented process that needs walking through each pixel looking for what object should be shown there, which is also can be described as a technique that follows a beam of light (in pixels) from a set point and simulates how it reacts when it encounters objects.
Compared with rasterization, ray tracing is hard to be implemented in real time, since even one ray can be traced and processed without much trouble, but after one ray bounces off an object, it can turn into 10 rays, and those 10 can turn into 100, 1000…The increase is exponential, and the the calculation for all these rays will be time consuming.
Historically, computer hardware hasn’t been fast enough to use these techniques in real time, such as in video games. Moviemakers can take as long as they like to render a single frame, so they do it offline in render farms. Video games have only a fraction of a second. As a result, most real-time graphics rely on the another technique called rasterization.
PATH TRACING
Path tracing can be used to solve more complex lighting situations.
Path tracing is a type of ray tracing. When using path tracing for rendering, the rays only produce a single ray per bounce. The rays do not follow a defined line per bounce (to a light, for example), but rather shoot off in a random direction. The path tracing algorithm then takes a random sampling of all of the rays to create the final image. This results in sampling a variety of different types of lighting.When a ray hits a surface it doesn’t trace a path to every light source, instead it bounces the ray off the surface and keeps bouncing it until it hits a light source or exhausts some bounce limit.
It then calculates the amount of light transferred all the way to the pixel, including any color information gathered from surfaces along the way.
It then averages out the values calculated from all the paths that were traced into the scene to get the final pixel color value.It requires a ton of computing power and if you don’t send out enough rays per pixel or don’t trace the paths far enough into the scene then you end up with a very spotty image as many pixels fail to find any light sources from their rays. So when you increase the the samples per pixel, you can see the image quality becomes better and better.
Ray tracing tends to be more efficient than path tracing. Basically, the render time of a ray tracer depends on the number of polygons in the scene. The more polygons you have, the longer it will take.
Meanwhile, the rendering time of a path tracer can be indifferent to the number of polygons, but it is related to light situation: If you add a light, transparency, translucence, or other shader effects, the path tracer will slow down considerably.blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2018/03/19/whats-difference-between-ray-tracing-rasterization/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rasterisation
https://www.quora.com/Whats-the-difference-between-ray-tracing-and-path-tracing
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
VFX pipeline – Render Wall management topics
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
-
Matt Gray – How to generate a profitable business
-
Film Production walk-through – pipeline – I want to make a … movie
-
AI Search – Find The Best AI Tools & Apps
-
QR code logos
-
Python and TCL: Tips and Tricks for Foundry Nuke
-
NVidia – High-Fidelity 3D Mesh Generation at Scale with Meshtron
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.