COMPOSITION
-
9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camera
Read more: 9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camerahttps://www.flexclip.com/learn/cinematic-video.html
- Frame Your Shots to Create Depth
- Create Shallow Depth of Field
- Avoid Shaky Footage and Use Flexible Camera Movements
- Properly Use Slow Motion
- Use Cinematic Lighting Techniques
- Apply Color Grading
- Use Cinematic Music and SFX
- Add Cinematic Fonts and Text Effects
- Create the Cinematic Bar at the Top and the Bottom

-
SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source program
Read more: SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source programhttp://slowmovideo.granjow.net/
slowmoVideo is an OpenSource program that creates slow-motion videos from your footage.
Slow motion cinematography is the result of playing back frames for a longer duration than they were exposed. For example, if you expose 240 frames of film in one second, then play them back at 24 fps, the resulting movie is 10 times longer (slower) than the original filmed event….
Film cameras are relatively simple mechanical devices that allow you to crank up the speed to whatever rate the shutter and pull-down mechanism allow. Some film cameras can operate at 2,500 fps or higher (although film shot in these cameras often needs some readjustment in postproduction). Video, on the other hand, is always captured, recorded, and played back at a fixed rate, with a current limit around 60fps. This makes extreme slow motion effects harder to achieve (and less elegant) on video, because slowing down the video results in each frame held still on the screen for a long time, whereas with high-frame-rate film there are plenty of frames to fill the longer durations of time. On video, the slow motion effect is more like a slide show than smooth, continuous motion.
One obvious solution is to shoot film at high speed, then transfer it to video (a case where film still has a clear advantage, sorry George). Another possibility is to cross dissolve or blur from one frame to the next. This adds a smooth transition from one still frame to the next. The blur reduces the sharpness of the image, and compared to slowing down images shot at a high frame rate, this is somewhat of a cheat. However, there isn’t much you can do about it until video can be recorded at much higher rates. Of course, many film cameras can’t shoot at high frame rates either, so the whole super-slow-motion endeavor is somewhat specialized no matter what medium you are using. (There are some high speed digital cameras available now that allow you to capture lots of digital frames directly to your computer, so technology is starting to catch up with film. However, this feature isn’t going to appear in consumer camcorders any time soon.)
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat SheetWhere is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
What type of lighting?-> High key lighting.
Features bright, even illumination and few conspicuous shadows. This lighting key is often used in musicals and comedies.Low key lighting
Features diffused shadows and atmospheric pools of light. This lighting key is often used in mysteries and thrillers.High contrast lighting
Features harsh shafts of lights and dramatic streaks of blackness. This type of lighting is often used in tragedies and melodramas.What type of shot?
Extreme long shot
Taken from a great distance, showing much of the locale. Ifpeople are included in these shots, they usually appear as mere specks-> Long shot
Corresponds to the space between the audience and the stage in a live theater. The long shots show the characters and some of the locale.Full shot
Range with just enough space to contain the human body in full. The full shot shows the character and a minimal amount of the locale.Medium shot
Shows the human figure from the knees or waist up.Close-Up
Concentrates on a relatively small object and show very little if any locale.Extreme close-up
Focuses on an unnaturally small portion of an object, giving that part great detail and symbolic significance.What angle?
Bird’s-eye view.
The shot is photographed directly from above. This type of shot can be disorienting, and the people photographed seem insignificant.High angle.
This angle reduces the size of the objects photographed. A person photographed from this angle seems harmless and insignificant, but to a lesser extent than with the bird’s-eye view.-> Eye-level shot.
The clearest view of an object, but seldom intrinsically dramatic, because it tends to be the norm.Low angle.
This angle increases high and a sense of verticality, heightening the importance of the object photographed. A person shot from this angle is given a sense of power and respect.Oblique angle.
For this angle, the camera is tilted laterally, giving the image a slanted appearance. Oblique angles suggest tension, transition, a impending movement. They are also called canted or dutch angles.What is the dominant color?
The use of color in this shot is symbolic. The scene is set in warehouse. Both the set and characters are blues, blacks and whites.
This was intentional allowing for the scenes and shots with blood to have a great level of contrast.
What is the Lens/Filter/Stock?
Telephoto lens.
A lens that draws objects closer but also diminishes the illusion of depth.Wide-angle lens.
A lens that takes in a broad area and increases the illusion of depth but sometimes distorts the edges of the image.Fast film stock.
Highly sensitive to light, it can register an image with little illumination. However, the final product tends to be grainy.Slow film stock.
Relatively insensitive to light, it requires a great deal of illumination. The final product tends to look polished.The lens is not wide-angle because there isn’t a great sense of depth, nor are several planes in focus. The lens is probably long but not necessarily a telephoto lens because the depth isn’t inordinately compressed.
The stock is fast because of the grainy quality of the image.
Subsidiary Contrast; where does the eye go next?
The two guns.
How much visual information is packed into the image? Is the texture stark, moderate, or highly detailed?
Minimalist clutter in the warehouse allows a focus on a character driven thriller.
What is the Composition?
Horizontal.
Compositions based on horizontal lines seem visually at rest and suggest placidity or peacefulness.Vertical.
Compositions based on vertical lines seem visually at rest and suggest strength.-> Diagonal.
Compositions based on diagonal, or oblique, lines seem dynamic and suggest tension or anxiety.-> Binary. Binary structures emphasize parallelism.
Triangle.
Triadic compositions stress the dynamic interplay among three mainCircle.
Circular compositions suggest security and enclosure.Is the form open or closed? Does the image suggest a window that arbitrarily isolates a fragment of the scene? Or a proscenium arch, in which the visual elements are carefully arranged and held in balance?
The most nebulous of all the categories of mise en scene, the type of form is determined by how consciously structured the mise en scene is. Open forms stress apparently simple techniques, because with these unself-conscious methods the filmmaker is able to emphasize the immediate, the familiar, the intimate aspects of reality. In open-form images, the frame tends to be deemphasized. In closed form images, all the necessary information is carefully structured within the confines of the frame. Space seems enclosed and self-contained rather than continuous.
Could argue this is a proscenium arch because this is such a classic shot with parallels and juxtapositions.
Is the framing tight or loose? Do the character have no room to move around, or can they move freely without impediments?
Shots where the characters are placed at the edges of the frame and have little room to move around within the frame are considered tight.
Longer shots, in which characters have room to move around within the frame, are considered loose and tend to suggest freedom.
Center-framed giving us the entire scene showing isolation, place and struggle.
Depth of Field. On how many planes is the image composed (how many are in focus)? Does the background or foreground comment in any way on the mid-ground?
Standard DOF, one background and clearly defined foreground.
Which way do the characters look vis-a-vis the camera?
An actor can be photographed in any of five basic positions, each conveying different psychological overtones.
Full-front (facing the camera):
the position with the most intimacy. The character is looking in our direction, inviting our complicity.Quarter Turn:
the favored position of most filmmakers. This position offers a high degree of intimacy but with less emotional involvement than the full-front.-> Profile (looking of the frame left or right):
More remote than the quarter turn, the character in profile seems unaware of being observed, lost in his or her own thoughts.Three-quarter Turn:
More anonymous than the profile, this position is useful for conveying a character’s unfriendly or antisocial feelings, for in effect, the character is partially turning his or her back on us, rejecting our interest.Back to Camera:
The most anonymous of all positions, this position is often used to suggest a character’s alienation from the world. When a character has his or her back to the camera, we can only guess what’s taking place internally, conveying a sense of concealment, or mystery.How much space is there between the characters?
Extremely close, for a gunfight.
The way people use space can be divided into four proxemic patterns.
Intimate distances.
The intimate distance ranges from skin contact to about eighteen inches away. This is the distance of physical involvement–of love, comfort, and tenderness between individuals.-> Personal distances.
The personal distance ranges roughly from eighteen inches away to about four feet away. These distances tend to be reserved for friends and acquaintances. Personal distances preserve the privacy between individuals, yet these rages don’t necessarily suggest exclusion, as intimate distances often do.Social distances.
The social distance rages from four feet to about twelve feet. These distances are usually reserved for impersonal business and casual social gatherings. It’s a friendly range in most cases, yet somewhat more formal than the personal distance.Public distances.
The public distance extends from twelve feet to twenty-five feet or more. This range tends to be formal and rather detached.
DESIGN
-
Japanese Designer Tomoo Yamaji Offers 3D Printed Transformer Kit, Stingray, Through Shapeways
Read more: Japanese Designer Tomoo Yamaji Offers 3D Printed Transformer Kit, Stingray, Through Shapewayshttps://3dprint.com/55799/transformer-kit-shapeways/
http://www.shapeways.com/product/5YHJL6XSZ/t060101-stingray?li=shareProduct
-
James Gerde – The way the leaves dance in the rain
Read more: James Gerde – The way the leaves dance in the rainhttps://www.instagram.com/gerdegotit/reel/C6s-2r2RgSu/
Since spending a lot of time recently with SDXL I’ve since made my way back to SD 1.5
While the models overall have less fidelity. There is just no comparing to the current motion models we have available for animatediff with 1.5 models.
To date this is one of my favorite pieces. Not because I think it’s even the best it can be. But because the workflow adjustments unlocked some very important ideas I can’t wait to try out.
Performance by @silkenkelly and @itxtheballerina on IG
COLOR
-
Akiyoshi Kitaoka – Surround biased illumination perception
Read more: Akiyoshi Kitaoka – Surround biased illumination perceptionhttps://x.com/AkiyoshiKitaoka/status/1798705648001327209
The left face appears whitish and the right one blackish, but they are made up of the same luminance.
https://community.wolfram.com/groups/-/m/t/3191015
Illusory staircase Gelb effect
https://www.psy.ritsumei.ac.jp/akitaoka/illgelbe.html -
Björn Ottosson – OKlch color space
Read more: Björn Ottosson – OKlch color spaceBjörn Ottosson proposed OKlch in 2020 to create a color space that can closely mimic how color is perceived by the human eye, predicting perceived lightness, chroma, and hue.
The OK in OKLCH stands for Optimal Color.
- L: Lightness (the perceived brightness of the color)
- C: Chroma (the intensity or saturation of the color)
- H: Hue (the actual color, such as red, blue, green, etc.)

Also read:
-
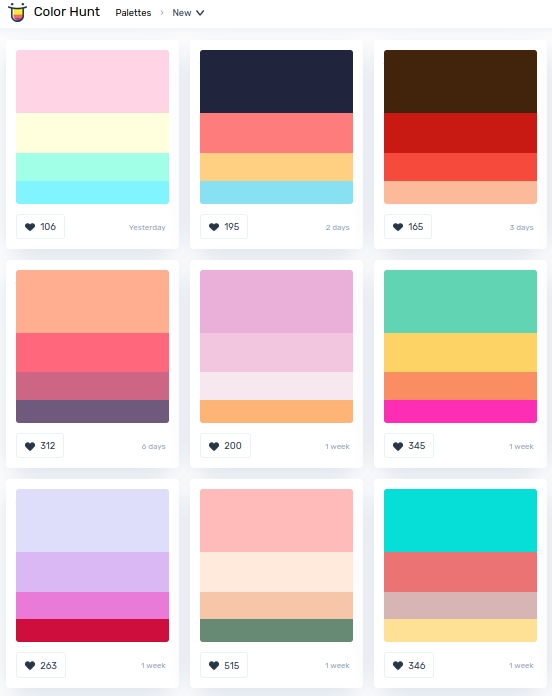
colorhunt.co
Read more: colorhunt.coColor Hunt is a free and open platform for color inspiration with thousands of trendy hand-picked color palettes.
-
Weta Digital – Manuka Raytracer and Gazebo GPU renderers – pipeline
Read more: Weta Digital – Manuka Raytracer and Gazebo GPU renderers – pipelinehttps://jo.dreggn.org/home/2018_manuka.pdf
http://www.fxguide.com/featured/manuka-weta-digitals-new-renderer/

The Manuka rendering architecture has been designed in the spirit of the classic reyes rendering architecture. In its core, reyes is based on stochastic rasterisation of micropolygons, facilitating depth of field, motion blur, high geometric complexity,and programmable shading.
This is commonly achieved with Monte Carlo path tracing, using a paradigm often called shade-on-hit, in which the renderer alternates tracing rays with running shaders on the various ray hits. The shaders take the role of generating the inputs of the local material structure which is then used bypath sampling logic to evaluate contributions and to inform what further rays to cast through the scene.
Over the years, however, the expectations have risen substantially when it comes to image quality. Computing pictures which are indistinguishable from real footage requires accurate simulation of light transport, which is most often performed using some variant of Monte Carlo path tracing. Unfortunately this paradigm requires random memory accesses to the whole scene and does not lend itself well to a rasterisation approach at all.
Manuka is both a uni-directional and bidirectional path tracer and encompasses multiple importance sampling (MIS). Interestingly, and importantly for production character skin work, it is the first major production renderer to incorporate spectral MIS in the form of a new ‘Hero Spectral Sampling’ technique, which was recently published at Eurographics Symposium on Rendering 2014.
Manuka propose a shade-before-hit paradigm in-stead and minimise I/O strain (and some memory costs) on the system, leveraging locality of reference by running pattern generation shaders before we execute light transport simulation by path sampling, “compressing” any bvh structure as needed, and as such also limiting duplication of source data.
The difference with reyes is that instead of baking colors into the geometry like in Reyes, manuka bakes surface closures. This means that light transport is still calculated with path tracing, but all texture lookups etc. are done up-front and baked into the geometry.The main drawback with this method is that geometry has to be tessellated to its highest, stable topology before shading can be evaluated properly. As such, the high cost to first pixel. Even a basic 4 vertices square becomes a much more complex model with this approach.
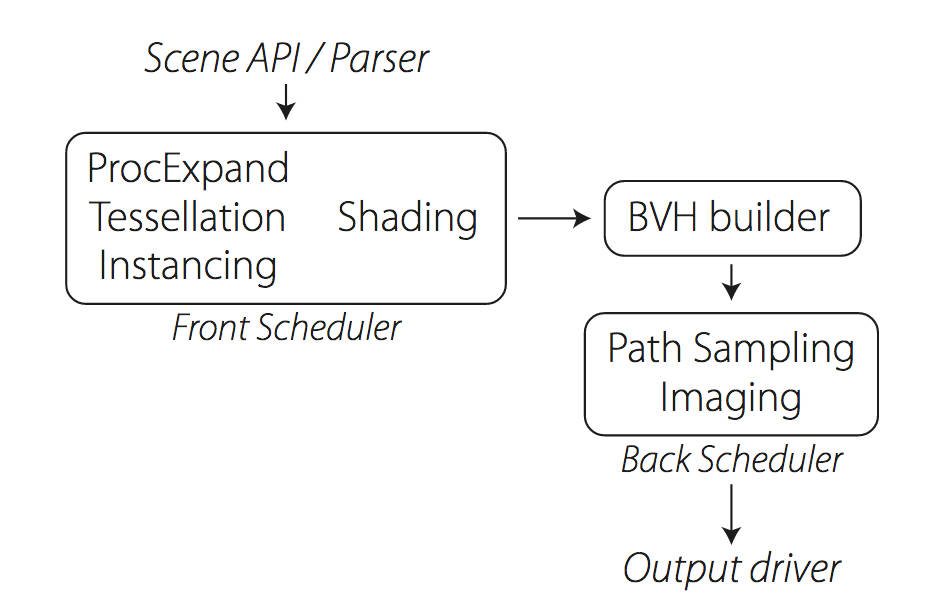
Manuka use the RenderMan Shading Language (rsl) for programmable shading [Pixar Animation Studios 2015], but we do not invoke rsl shaders when intersecting a ray with a surface (often called shade-on-hit). Instead, we pre-tessellate and pre-shade all the input geometry in the front end of the renderer.
This way, we can efficiently order shading computations to sup-port near-optimal texture locality, vectorisation, and parallelism. This system avoids repeated evaluation of shaders at the same surface point, and presents a minimal amount of memory to be accessed during light transport time. An added benefit is that the acceleration structure for ray tracing (abounding volume hierarchy, bvh) is built once on the final tessellated geometry, which allows us to ray trace more efficiently than multi-level bvhs and avoids costly caching of on-demand tessellated micropolygons and the associated scheduling issues.For the shading reasons above, in terms of AOVs, the studio approach is to succeed at combining complex shading with ray paths in the render rather than pass a multi-pass render to compositing.
For the Spectral Rendering component. The light transport stage is fully spectral, using a continuously sampled wavelength which is traced with each path and used to apply the spectral camera sensitivity of the sensor. This allows for faithfully support any degree of observer metamerism as the camera footage they are intended to match as well as complex materials which require wavelength dependent phenomena such as diffraction, dispersion, interference, iridescence, or chromatic extinction and Rayleigh scattering in participating media.
As opposed to the original reyes paper, we use bilinear interpolation of these bsdf inputs later when evaluating bsdfs per pathv ertex during light transport4. This improves temporal stability of geometry which moves very slowly with respect to the pixel raster
In terms of the pipeline, everything rendered at Weta was already completely interwoven with their deep data pipeline. Manuka very much was written with deep data in mind. Here, Manuka not so much extends the deep capabilities, rather it fully matches the already extremely complex and powerful setup Weta Digital already enjoy with RenderMan. For example, an ape in a scene can be selected, its ID is available and a NUKE artist can then paint in 3D say a hand and part of the way up the neutral posed ape.
We called our system Manuka, as a respectful nod to reyes: we had heard a story froma former ILM employee about how reyes got its name from how fond the early Pixar people were of their lunches at Point Reyes, and decided to name our system after our surrounding natural environment, too. Manuka is a kind of tea tree very common in New Zealand which has very many very small leaves, in analogy to micropolygons ina tree structure for ray tracing. It also happens to be the case that Weta Digital’s main site is on Manuka Street.

-
Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Colorists
Read more: Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Coloristshttps://www.tobiamontanari.com/memory-colors-an-essential-tool-for-colorists/
“Memory colors are colors that are universally associated with specific objects, elements or scenes in our environment. They are the colors that we expect to see in specific situations: these colors are based on our expectation of how certain objects should look based on our past experiences and memories.
For instance, we associate specific hues, saturation and brightness values with human skintones and a slight variation can significantly affect the way we perceive a scene.
Similarly, we expect blue skies to have a particular hue, green trees to be a specific shade and so on.
Memory colors live inside of our brains and we often impose them onto what we see. By considering them during the grading process, the resulting image will be more visually appealing and won’t distract the viewer from the intended message of the story. Even a slight deviation from memory colors in a movie can create a sense of discordance, ultimately detracting from the viewer’s experience.”
-
Space bodies’ components and light spectroscopy
Read more: Space bodies’ components and light spectroscopywww.plutorules.com/page-111-space-rocks.html
This help’s us understand the composition of components in/on solar system bodies.
Dips in the observed light spectrum, also known as, lines of absorption occur as gasses absorb energy from light at specific points along the light spectrum.
These dips or darkened zones (lines of absorption) leave a finger print which identify elements and compounds.
In this image the dark absorption bands appear as lines of emission which occur as the result of emitted not reflected (absorbed) light.
Lines of absorption
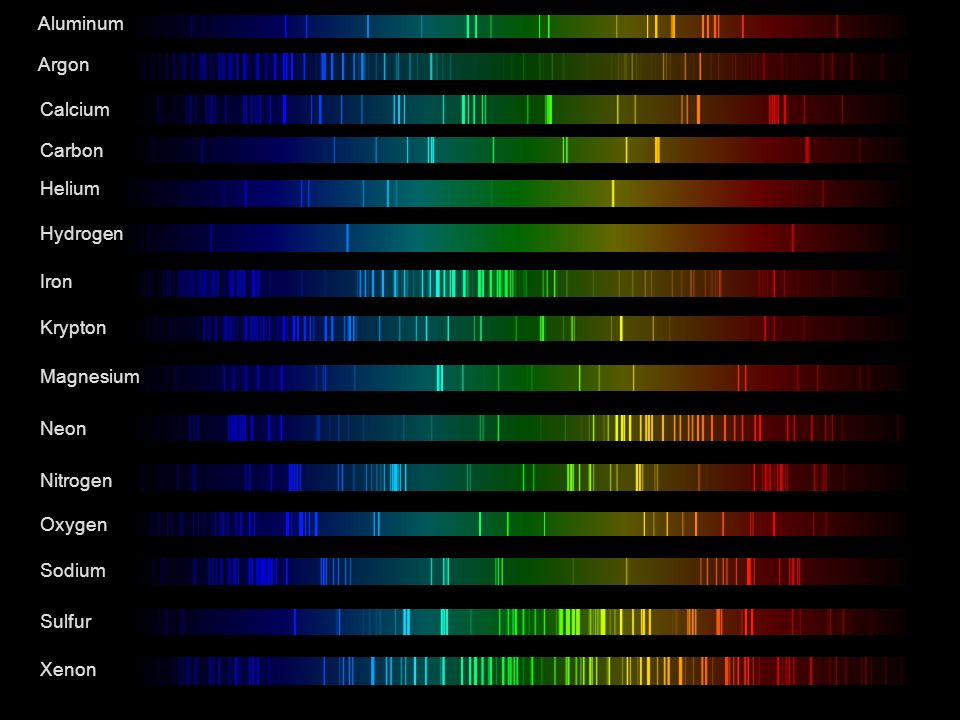 Lines of emission
Lines of emission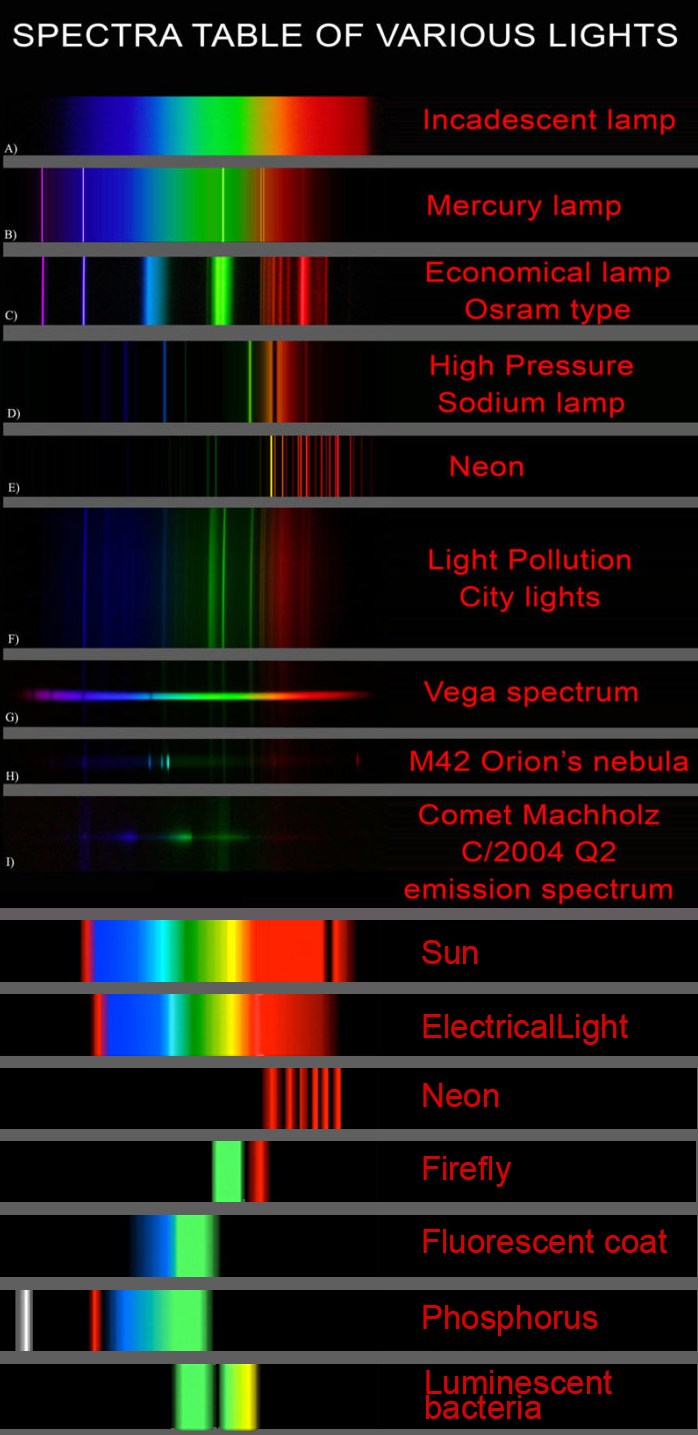
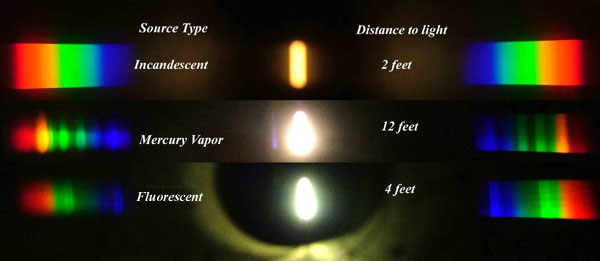

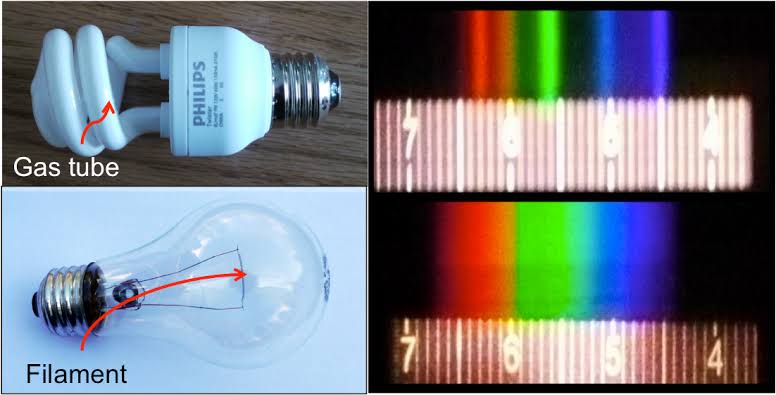
LIGHTING
-
7 Easy Portrait Lighting Setups
Read more: 7 Easy Portrait Lighting SetupsButterfly
Loop
Rembrandt
Split
Rim
Broad
Short
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat SheetWhere is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
What type of lighting?-> High key lighting.
Features bright, even illumination and few conspicuous shadows. This lighting key is often used in musicals and comedies.Low key lighting
Features diffused shadows and atmospheric pools of light. This lighting key is often used in mysteries and thrillers.High contrast lighting
Features harsh shafts of lights and dramatic streaks of blackness. This type of lighting is often used in tragedies and melodramas.What type of shot?
Extreme long shot
Taken from a great distance, showing much of the locale. Ifpeople are included in these shots, they usually appear as mere specks-> Long shot
Corresponds to the space between the audience and the stage in a live theater. The long shots show the characters and some of the locale.Full shot
Range with just enough space to contain the human body in full. The full shot shows the character and a minimal amount of the locale.Medium shot
Shows the human figure from the knees or waist up.Close-Up
Concentrates on a relatively small object and show very little if any locale.Extreme close-up
Focuses on an unnaturally small portion of an object, giving that part great detail and symbolic significance.What angle?
Bird’s-eye view.
The shot is photographed directly from above. This type of shot can be disorienting, and the people photographed seem insignificant.High angle.
This angle reduces the size of the objects photographed. A person photographed from this angle seems harmless and insignificant, but to a lesser extent than with the bird’s-eye view.-> Eye-level shot.
The clearest view of an object, but seldom intrinsically dramatic, because it tends to be the norm.Low angle.
This angle increases high and a sense of verticality, heightening the importance of the object photographed. A person shot from this angle is given a sense of power and respect.Oblique angle.
For this angle, the camera is tilted laterally, giving the image a slanted appearance. Oblique angles suggest tension, transition, a impending movement. They are also called canted or dutch angles.What is the dominant color?
The use of color in this shot is symbolic. The scene is set in warehouse. Both the set and characters are blues, blacks and whites.
This was intentional allowing for the scenes and shots with blood to have a great level of contrast.
What is the Lens/Filter/Stock?
Telephoto lens.
A lens that draws objects closer but also diminishes the illusion of depth.Wide-angle lens.
A lens that takes in a broad area and increases the illusion of depth but sometimes distorts the edges of the image.Fast film stock.
Highly sensitive to light, it can register an image with little illumination. However, the final product tends to be grainy.Slow film stock.
Relatively insensitive to light, it requires a great deal of illumination. The final product tends to look polished.The lens is not wide-angle because there isn’t a great sense of depth, nor are several planes in focus. The lens is probably long but not necessarily a telephoto lens because the depth isn’t inordinately compressed.
The stock is fast because of the grainy quality of the image.
Subsidiary Contrast; where does the eye go next?
The two guns.
How much visual information is packed into the image? Is the texture stark, moderate, or highly detailed?
Minimalist clutter in the warehouse allows a focus on a character driven thriller.
What is the Composition?
Horizontal.
Compositions based on horizontal lines seem visually at rest and suggest placidity or peacefulness.Vertical.
Compositions based on vertical lines seem visually at rest and suggest strength.-> Diagonal.
Compositions based on diagonal, or oblique, lines seem dynamic and suggest tension or anxiety.-> Binary. Binary structures emphasize parallelism.
Triangle.
Triadic compositions stress the dynamic interplay among three mainCircle.
Circular compositions suggest security and enclosure.Is the form open or closed? Does the image suggest a window that arbitrarily isolates a fragment of the scene? Or a proscenium arch, in which the visual elements are carefully arranged and held in balance?
The most nebulous of all the categories of mise en scene, the type of form is determined by how consciously structured the mise en scene is. Open forms stress apparently simple techniques, because with these unself-conscious methods the filmmaker is able to emphasize the immediate, the familiar, the intimate aspects of reality. In open-form images, the frame tends to be deemphasized. In closed form images, all the necessary information is carefully structured within the confines of the frame. Space seems enclosed and self-contained rather than continuous.
Could argue this is a proscenium arch because this is such a classic shot with parallels and juxtapositions.
Is the framing tight or loose? Do the character have no room to move around, or can they move freely without impediments?
Shots where the characters are placed at the edges of the frame and have little room to move around within the frame are considered tight.
Longer shots, in which characters have room to move around within the frame, are considered loose and tend to suggest freedom.
Center-framed giving us the entire scene showing isolation, place and struggle.
Depth of Field. On how many planes is the image composed (how many are in focus)? Does the background or foreground comment in any way on the mid-ground?
Standard DOF, one background and clearly defined foreground.
Which way do the characters look vis-a-vis the camera?
An actor can be photographed in any of five basic positions, each conveying different psychological overtones.
Full-front (facing the camera):
the position with the most intimacy. The character is looking in our direction, inviting our complicity.Quarter Turn:
the favored position of most filmmakers. This position offers a high degree of intimacy but with less emotional involvement than the full-front.-> Profile (looking of the frame left or right):
More remote than the quarter turn, the character in profile seems unaware of being observed, lost in his or her own thoughts.Three-quarter Turn:
More anonymous than the profile, this position is useful for conveying a character’s unfriendly or antisocial feelings, for in effect, the character is partially turning his or her back on us, rejecting our interest.Back to Camera:
The most anonymous of all positions, this position is often used to suggest a character’s alienation from the world. When a character has his or her back to the camera, we can only guess what’s taking place internally, conveying a sense of concealment, or mystery.How much space is there between the characters?
Extremely close, for a gunfight.
The way people use space can be divided into four proxemic patterns.
Intimate distances.
The intimate distance ranges from skin contact to about eighteen inches away. This is the distance of physical involvement–of love, comfort, and tenderness between individuals.-> Personal distances.
The personal distance ranges roughly from eighteen inches away to about four feet away. These distances tend to be reserved for friends and acquaintances. Personal distances preserve the privacy between individuals, yet these rages don’t necessarily suggest exclusion, as intimate distances often do.Social distances.
The social distance rages from four feet to about twelve feet. These distances are usually reserved for impersonal business and casual social gatherings. It’s a friendly range in most cases, yet somewhat more formal than the personal distance.Public distances.
The public distance extends from twelve feet to twenty-five feet or more. This range tends to be formal and rather detached. -
Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmic
Read more: Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmicacademy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-1
academy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-2
Local copy:
-
DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ball
Read more: DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ballhttps://diffusionlight.github.io/
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight?tab=MIT-1-ov-file#readme
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/15pC4qb9mEtRYsW3utXkk-jnaeVxUy-0S
“a simple yet effective technique to estimate lighting in a single input image. Current techniques rely heavily on HDR panorama datasets to train neural networks to regress an input with limited field-of-view to a full environment map. However, these approaches often struggle with real-world, uncontrolled settings due to the limited diversity and size of their datasets. To address this problem, we leverage diffusion models trained on billions of standard images to render a chrome ball into the input image. Despite its simplicity, this task remains challenging: the diffusion models often insert incorrect or inconsistent objects and cannot readily generate images in HDR format. Our research uncovers a surprising relationship between the appearance of chrome balls and the initial diffusion noise map, which we utilize to consistently generate high-quality chrome balls. We further fine-tune an LDR difusion model (Stable Diffusion XL) with LoRA, enabling it to perform exposure bracketing for HDR light estimation. Our method produces convincing light estimates across diverse settings and demonstrates superior generalization to in-the-wild scenarios.”

-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. …
Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
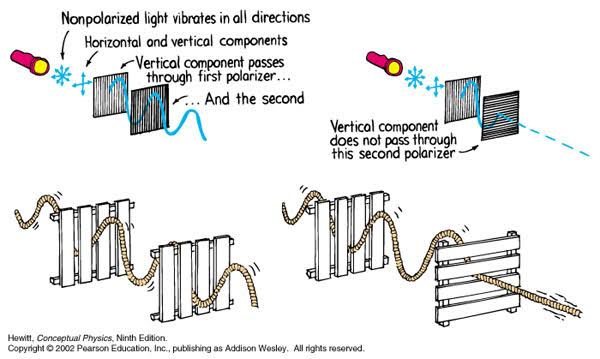
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
The most common use of polarized technology is to reduce lighting complexity on the subject.
Details such as glare and hard edges are not removed, but greatly reduced.This method is usually used in VFX to capture raw images with the least amount of specular diffusion or pollution, thus allowing artists to infer detail back through typical shading and rendering techniques and on demand.
Light reflected from a non-metallic surface becomes polarized; this effect is maximum at Brewster’s angle, about 56° from the vertical for common glass.
A polarizer rotated to pass only light polarized in the direction perpendicular to the reflected light will absorb much of it. This absorption allows glare reflected from, for example, a body of water or a road to be reduced. Reflections from shiny surfaces (e.g. vegetation, sweaty skin, water surfaces, glass) are also reduced. This allows the natural color and detail of what is beneath to come through. Reflections from a window into a dark interior can be much reduced, allowing it to be seen through. (The same effects are available for vision by using polarizing sunglasses.)
www.physicsclassroom.com/class/light/u12l1e.cfm
Some of the light coming from the sky is polarized (bees use this phenomenon for navigation). The electrons in the air molecules cause a scattering of sunlight in all directions. This explains why the sky is not dark during the day. But when looked at from the sides, the light emitted from a specific electron is totally polarized.[3] Hence, a picture taken in a direction at 90 degrees from the sun can take advantage of this polarization.
Use of a polarizing filter, in the correct direction, will filter out the polarized component of skylight, darkening the sky; the landscape below it, and clouds, will be less affected, giving a photograph with a darker and more dramatic sky, and emphasizing the clouds.

There are two types of polarizing filters readily available, linear and “circular”, which have exactly the same effect photographically. But the metering and auto-focus sensors in certain cameras, including virtually all auto-focus SLRs, will not work properly with linear polarizers because the beam splitters used to split off the light for focusing and metering are polarization-dependent.
Polarizing filters reduce the light passed through to the film or sensor by about one to three stops (2–8×) depending on how much of the light is polarized at the filter angle selected. Auto-exposure cameras will adjust for this by widening the aperture, lengthening the time the shutter is open, and/or increasing the ASA/ISO speed of the camera.
www.adorama.com/alc/nd-filter-vs-polarizer-what%25e2%2580%2599s-the-difference
Neutral Density (ND) filters help control image exposure by reducing the light that enters the camera so that you can have more control of your depth of field and shutter speed. Polarizers or polarizing filters work in a similar way, but the difference is that they selectively let light waves of a certain polarization pass through. This effect helps create more vivid colors in an image, as well as manage glare and reflections from water surfaces. Both are regarded as some of the best filters for landscape and travel photography as they reduce the dynamic range in high-contrast images, thus enabling photographers to capture more realistic and dramatic sceneries.
shopfelixgray.com/blog/polarized-vs-non-polarized-sunglasses/
www.eyebuydirect.com/blog/difference-polarized-nonpolarized-sunglasses/
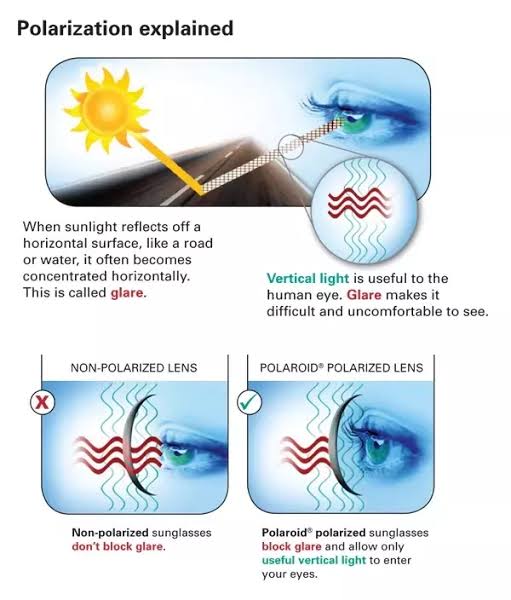
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
The exposure meter in the camera does not know whether the subject itself is bright or not. It simply measures the amount of light that comes in, and makes a guess based on that. The camera will aim for 18% gray independently, meaning if you take a photo of an entirely white surface, and an entirely black surface you should get two identical images which both are gray (at least in theory). Thus enters the Macbeth chart.
<!–more–>
Note that Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
http://www.rags-int-inc.com/PhotoTechStuff/MacbethTarget/
https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b4/CIE1931xy_ColorChecker_SMIL.svg
RGB coordinates of the Macbeth ColorChecker
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/0e03/251ad1e6d3c3fb9cb0b1f9754351a959e065.pdf
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.