COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
LIGHTING
-
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
Read more: Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perceptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
The Black Body Ultraviolet Catastrophe Experiment
In photography, color temperature describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a “blackbody” with that surface temperature. A blackbody is an object which absorbs all incident light — neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through.
The Sun closely approximates a black-body radiator. Another rough analogue of blackbody radiation in our day to day experience might be in heating a metal or stone: these are said to become “red hot” when they attain one temperature, and then “white hot” for even higher temperatures. Similarly, black bodies at different temperatures also have varying color temperatures of “white light.”
Despite its name, light which may appear white does not necessarily contain an even distribution of colors across the visible spectrum.
Although planets and stars are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, black-body radiation is used as a first approximation for the energy they emit. Black holes are near-perfect black bodies, and it is believed that they emit black-body radiation (called Hawking radiation), with a temperature that depends on the mass of the hole.
-
LUX vs LUMEN vs NITS vs CANDELA – What is the difference
Read more: LUX vs LUMEN vs NITS vs CANDELA – What is the differenceMore details here: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
https://www.inhouseav.com.au/blog/beginners-guide-nits-lumens-brightness/

Candela
Candela is the basic unit of measure of the entire volume of light intensity from any point in a single direction from a light source. Note the detail: it measures the total volume of light within a certain beam angle and direction.
While the luminance of starlight is around 0.001 cd/m2, that of a sunlit scene is around 100,000 cd/m2, which is a hundred millions times higher. The luminance of the sun itself is approximately 1,000,000,000 cd/m2.NIT
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Candela_per_square_metre
The candela per square metre (symbol: cd/m2) is the unit of luminance in the International System of Units (SI). The unit is based on the candela, the SI unit of luminous intensity, and the square metre, the SI unit of area. The nit (symbol: nt) is a non-SI name also used for this unit (1 nt = 1 cd/m2).[1] The term nit is believed to come from the Latin word nitēre, “to shine”. As a measure of light emitted per unit area, this unit is frequently used to specify the brightness of a display device.
NIT and cd/m2 (candela power) represent the same thing and can be used interchangeably. One nit is equivalent to one candela per square meter, where the candela is the amount of light which has been emitted by a common tallow candle, but NIT is not part of the International System of Units (abbreviated SI, from Systeme International, in French).
It’s easiest to think of a TV as emitting light directly, in much the same way as the Sun does. Nits are simply the measurement of the level of light (luminance) in a given area which the emitting source sends to your eyes or a camera sensor.
The Nit can be considered a unit of visible-light intensity which is often used to specify the brightness level of an LCD.
1 Nit is approximately equal to 3.426 Lumens. To work out a comparable number of Nits to Lumens, you need to multiply the number of Nits by 3.426. If you know the number of Lumens, and wish to know the Nits, simply divide the number of Lumens by 3.426.
Most consumer desktop LCDs have Nits of 200 to 300, the average TV most likely has an output capability of between 100 and 200 Nits, and an HDR TV ranges from 400 to 1,500 Nits.
Virtual Production sets currently sport around 6000 NIT ceiling and 1000 NIT wall panels.The ambient brightness of a sunny day with clear blue skies is between 7000-10,000 nits (between 3000-7000 nits for overcast skies and indirect sunlight).
A bright sunny day can have specular highlights that reach over 100,000 nits. Direct sunlight is around 1,600,000,000 nits.
10,000 nits is also the typical brightness of a fluorescent tube – bright, but not painful to look at.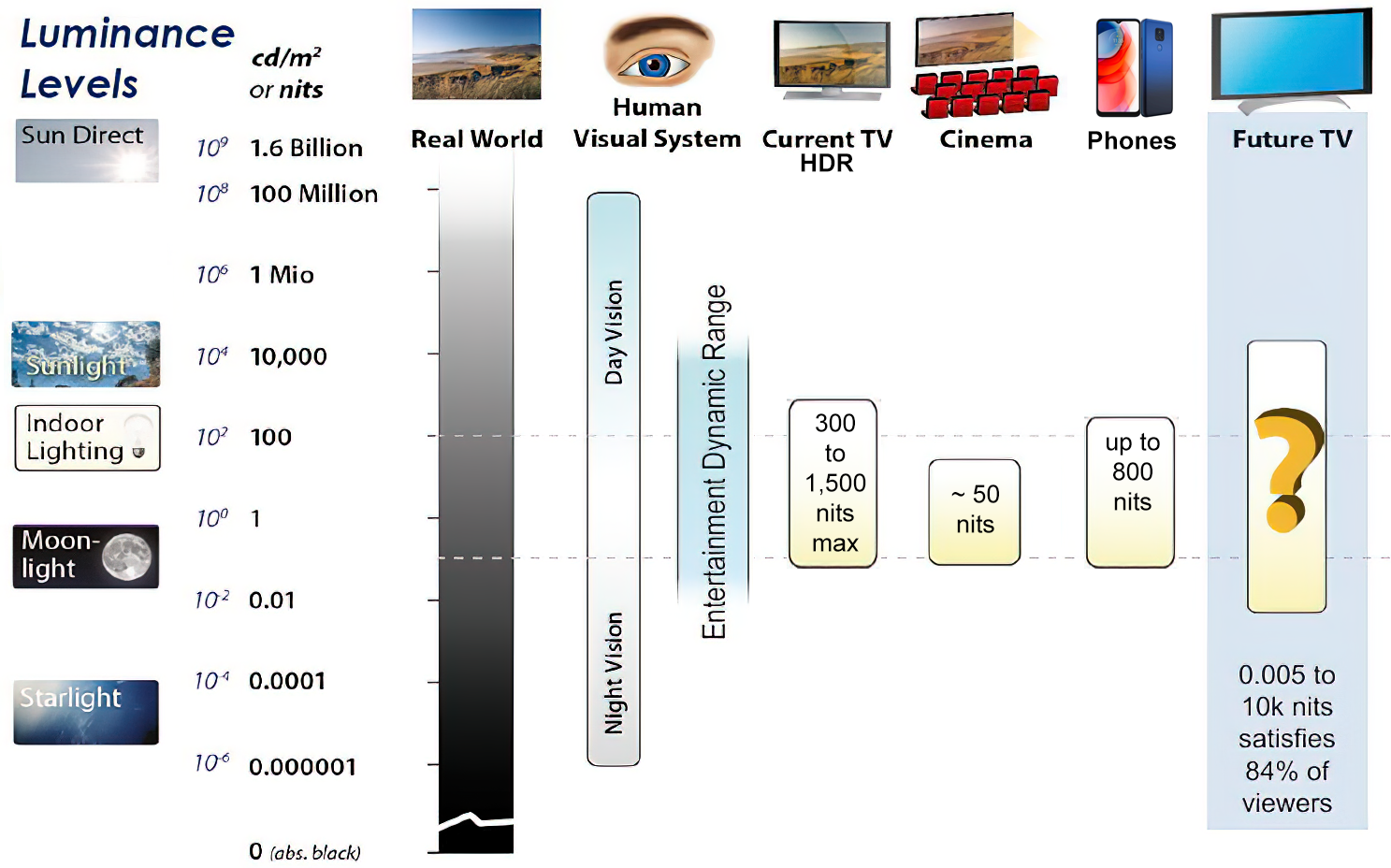
https://www.displaydaily.com/article/display-daily/dolby-vision-vs-hdr10-clarified
Tests showed that a “black level” of 0.005 nits (cd/m²) satisfied the vast majority of viewers. While 0.005 nits is very close to true black, Griffis says Dolby can go down to a black of 0.0001 nits, even though there is no need or ability for displays to get that dark today.
How bright is white? Dolby says the range of 0.005 nits – 10,000 nits satisfied 84% of the viewers in their viewing tests.
The brightest consumer HDR displays today are about 1,500 nits. Professional displays where HDR content is color-graded can achieve up to 4,000 nits peak brightness.High brightness that would be in danger of damaging the eye would be in the neighborhood of 250,000 nits.
Lumens
Lumen is a measure of how much light is emitted (luminance, luminous flux) by an object. It indicates the total potential amount of light from a light source that is visible to the human eye.
Lumen is commonly used in the context of light bulbs or video-projectors as a metric for their brightness power.Lumen is used to describe light output, and about video projectors, it is commonly referred to as ANSI Lumens. Simply put, lumens is how to find out how bright a LED display is. The higher the lumens, the brighter to display!
Technically speaking, a Lumen is the SI unit of luminous flux, which is equal to the amount of light which is emitted per second in a unit solid angle of one steradian from a uniform source of one-candela intensity radiating in all directions.
LUX
Lux (lx) or often Illuminance, is a photometric unit along a given area, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts. It is the measure of light at a specific distance within a specific area at that distance. Often used to measure the incidental sun’s intensity.
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
Read more: HDRI Median Cut pluginwww.hdrlabs.com/picturenaut/plugins.html
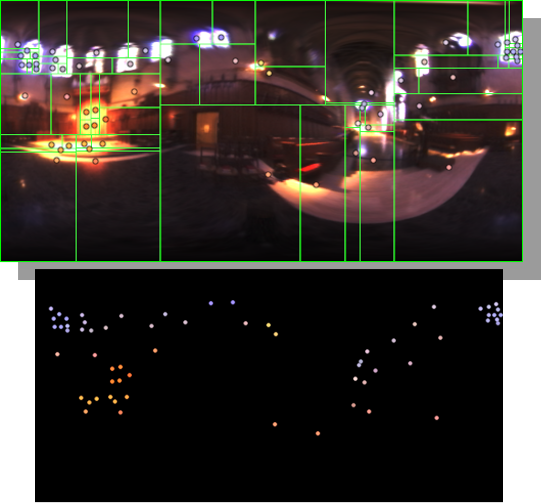
Note. The Median Cut algorithm is typically used for color quantization, which involves reducing the number of colors in an image while preserving its visual quality. It doesn’t directly provide a way to identify the brightest areas in an image. However, if you’re interested in identifying the brightest areas, you might want to look into other methods like thresholding, histogram analysis, or edge detection, through openCV for example.
Here is an openCV example:
# bottom left coordinates = 0,0 import numpy as np import cv2 # Load the HDR or EXR image image = cv2.imread('your_image_path.exr', cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED) # Load as-is without modification # Calculate the luminance from the HDR channels (assuming RGB format) luminance = np.dot(image[..., :3], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114]) # Set a threshold value based on estimated EV threshold_value = 2.4 # Estimated threshold value based on 4.8 EV # Apply the threshold to identify bright areas # Theluminancearray contains the calculated luminance values for each pixel in the image. # Thethreshold_valueis a user-defined value that represents a cutoff point, separating "bright" and "dark" areas in terms of perceived luminance.thresholded = (luminance > threshold_value) * 255 # Convert the thresholded image to uint8 for contour detection thresholded = thresholded.astype(np.uint8) # Find contours of the bright areas contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresholded, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # Create a list to store the bounding boxes of bright areas bright_areas = [] # Iterate through contours and extract bounding boxes for contour in contours: x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour) # Adjust y-coordinate based on bottom-left origin y_bottom_left_origin = image.shape[0] - (y + h) bright_areas.append((x, y_bottom_left_origin, x + w, y_bottom_left_origin + h)) # Store as (x1, y1, x2, y2) # Print the identified bright areas print("Bright Areas (x1, y1, x2, y2):") for area in bright_areas: print(area)More details
Luminance and Exposure in an EXR Image:
- An EXR (Extended Dynamic Range) image format is often used to store high dynamic range (HDR) images that contain a wide range of luminance values, capturing both dark and bright areas.
- Luminance refers to the perceived brightness of a pixel in an image. In an RGB image, luminance is often calculated using a weighted sum of the red, green, and blue channels, where different weights are assigned to each channel to account for human perception.
- In an EXR image, the pixel values can represent radiometrically accurate scene values, including actual radiance or irradiance levels. These values are directly related to the amount of light emitted or reflected by objects in the scene.
The luminance line is calculating the luminance of each pixel in the image using a weighted sum of the red, green, and blue channels. The three float values [0.299, 0.587, 0.114] are the weights used to perform this calculation.
These weights are based on the concept of luminosity, which aims to approximate the perceived brightness of a color by taking into account the human eye’s sensitivity to different colors. The values are often derived from the NTSC (National Television System Committee) standard, which is used in various color image processing operations.
Here’s the breakdown of the float values:
- 0.299: Weight for the red channel.
- 0.587: Weight for the green channel.
- 0.114: Weight for the blue channel.
The weighted sum of these channels helps create a grayscale image where the pixel values represent the perceived brightness. This technique is often used when converting a color image to grayscale or when calculating luminance for certain operations, as it takes into account the human eye’s sensitivity to different colors.
For the threshold, remember that the exact relationship between EV values and pixel values can depend on the tone-mapping or normalization applied to the HDR image, as well as the dynamic range of the image itself.
To establish a relationship between exposure and the threshold value, you can consider the relationship between linear and logarithmic scales:
- Linear and Logarithmic Scales:
- Exposure values in an EXR image are often represented in logarithmic scales, such as EV (exposure value). Each increment in EV represents a doubling or halving of the amount of light captured.
- Threshold values for luminance thresholding are usually linear, representing an actual luminance level.
- Conversion Between Scales:
- To establish a mathematical relationship, you need to convert between the logarithmic exposure scale and the linear threshold scale.
- One common method is to use a power function. For instance, you can use a power function to convert EV to a linear intensity value.
threshold_value = base_value * (2 ** EV)Here,
EVis the exposure value,base_valueis a scaling factor that determines the relationship between EV and threshold_value, and2 ** EVis used to convert the logarithmic EV to a linear intensity value. - Choosing the Base Value:
- The
base_valuefactor should be determined based on the dynamic range of your EXR image and the specific luminance values you are dealing with. - You may need to experiment with different values of
base_valueto achieve the desired separation of bright areas from the rest of the image.
- The
Let’s say you have an EXR image with a dynamic range of 12 EV, which is a common range for many high dynamic range images. In this case, you want to set a threshold value that corresponds to a certain number of EV above the middle gray level (which is often considered to be around 0.18).
Here’s an example of how you might determine a
base_valueto achieve this:# Define the dynamic range of the image in EV dynamic_range = 12 # Choose the desired number of EV above middle gray for thresholding desired_ev_above_middle_gray = 2 # Calculate the threshold value based on the desired EV above middle gray threshold_value = 0.18 * (2 ** (desired_ev_above_middle_gray / dynamic_range)) print("Threshold Value:", threshold_value)
Collections
| Explore posts
| Design And Composition
| Featured AI
Popular Searches
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.



