COMPOSITION
-
Photography basics: Depth of Field and composition
Read more: Photography basics: Depth of Field and compositionDepth of field is the range within which focusing is resolved in a photo.
Aperture has a huge affect on to the depth of field.Changing the f-stops (f/#) of a lens will change aperture and as such the DOF.
f-stops are a just certain number which is telling you the size of the aperture. That’s how f-stop is related to aperture (and DOF).
If you increase f-stops, it will increase DOF, the area in focus (and decrease the aperture). On the other hand, decreasing the f-stop it will decrease DOF (and increase the aperture).
The red cone in the figure is an angular representation of the resolution of the system. Versus the dotted lines, which indicate the aperture coverage. Where the lines of the two cones intersect defines the total range of the depth of field.
This image explains why the longer the depth of field, the greater the range of clarity.
-
Key/Fill ratios and scene composition using false colors
Read more: Key/Fill ratios and scene composition using false colorsTo measure the contrast ratio you will need a light meter. The process starts with you measuring the main source of light, or the key light.
Get a reading from the brightest area on the face of your subject. Then, measure the area lit by the secondary light, or fill light. To make sense of what you have just measured you have to understand that the information you have just gathered is in F-stops, a measure of light. With each additional F-stop, for example going one stop from f/1.4 to f/2.0, you create a doubling of light. The reverse is also true; moving one stop from f/8.0 to f/5.6 results in a halving of the light.
Let’s say you grabbed a measurement from your key light of f/8.0. Then, when you measured your fill light area, you get a reading of f/4.0. This will lead you to a contrast ratio of 4:1 because there are two stops between f/4.0 and f/8.0 and each stop doubles the amount of light. In other words, two stops x twice the light per stop = four times as much light at f/8.0 than at f/4.0.
theslantedlens.com/2017/lighting-ratios-photo-video/
Examples in the post
-
7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition
Read more: 7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition1. Watch every frame of raw footage twice. On the second time, take notes. If you don’t do this and try to start developing a scene premature, then it’s a big disservice to yourself and to the director, actors and production crew.
2. Nurture the relationships with the director. You are the secondary person in the relationship. Be calm and continually offer solutions. Get the main intention of the film as soon as possible from the director.
3. Organize your media so that you can find any shot instantly.
4. Factor in extra time for renders, exports, errors and crashes.
5. Attempt edits and ideas that shouldn’t work. It just might work. Until you do it and watch it, you won’t know. Don’t rule out ideas just because they don’t make sense in your mind.
6. Spend more time on your audio. It’s the glue of your edit. AUDIO SAVES EVERYTHING. Create fluid and seamless audio under your video.
7. Make cuts for the scene, but always in context for the whole film. Have a macro and a micro view at all times.
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat SheetWhere is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
What type of lighting?-> High key lighting.
Features bright, even illumination and few conspicuous shadows. This lighting key is often used in musicals and comedies.Low key lighting
Features diffused shadows and atmospheric pools of light. This lighting key is often used in mysteries and thrillers.High contrast lighting
Features harsh shafts of lights and dramatic streaks of blackness. This type of lighting is often used in tragedies and melodramas.What type of shot?
Extreme long shot
Taken from a great distance, showing much of the locale. Ifpeople are included in these shots, they usually appear as mere specks-> Long shot
Corresponds to the space between the audience and the stage in a live theater. The long shots show the characters and some of the locale.Full shot
Range with just enough space to contain the human body in full. The full shot shows the character and a minimal amount of the locale.Medium shot
Shows the human figure from the knees or waist up.Close-Up
Concentrates on a relatively small object and show very little if any locale.Extreme close-up
Focuses on an unnaturally small portion of an object, giving that part great detail and symbolic significance.What angle?
Bird’s-eye view.
The shot is photographed directly from above. This type of shot can be disorienting, and the people photographed seem insignificant.High angle.
This angle reduces the size of the objects photographed. A person photographed from this angle seems harmless and insignificant, but to a lesser extent than with the bird’s-eye view.-> Eye-level shot.
The clearest view of an object, but seldom intrinsically dramatic, because it tends to be the norm.Low angle.
This angle increases high and a sense of verticality, heightening the importance of the object photographed. A person shot from this angle is given a sense of power and respect.Oblique angle.
For this angle, the camera is tilted laterally, giving the image a slanted appearance. Oblique angles suggest tension, transition, a impending movement. They are also called canted or dutch angles.What is the dominant color?
The use of color in this shot is symbolic. The scene is set in warehouse. Both the set and characters are blues, blacks and whites.
This was intentional allowing for the scenes and shots with blood to have a great level of contrast.
What is the Lens/Filter/Stock?
Telephoto lens.
A lens that draws objects closer but also diminishes the illusion of depth.Wide-angle lens.
A lens that takes in a broad area and increases the illusion of depth but sometimes distorts the edges of the image.Fast film stock.
Highly sensitive to light, it can register an image with little illumination. However, the final product tends to be grainy.Slow film stock.
Relatively insensitive to light, it requires a great deal of illumination. The final product tends to look polished.The lens is not wide-angle because there isn’t a great sense of depth, nor are several planes in focus. The lens is probably long but not necessarily a telephoto lens because the depth isn’t inordinately compressed.
The stock is fast because of the grainy quality of the image.
Subsidiary Contrast; where does the eye go next?
The two guns.
How much visual information is packed into the image? Is the texture stark, moderate, or highly detailed?
Minimalist clutter in the warehouse allows a focus on a character driven thriller.
What is the Composition?
Horizontal.
Compositions based on horizontal lines seem visually at rest and suggest placidity or peacefulness.Vertical.
Compositions based on vertical lines seem visually at rest and suggest strength.-> Diagonal.
Compositions based on diagonal, or oblique, lines seem dynamic and suggest tension or anxiety.-> Binary. Binary structures emphasize parallelism.
Triangle.
Triadic compositions stress the dynamic interplay among three mainCircle.
Circular compositions suggest security and enclosure.Is the form open or closed? Does the image suggest a window that arbitrarily isolates a fragment of the scene? Or a proscenium arch, in which the visual elements are carefully arranged and held in balance?
The most nebulous of all the categories of mise en scene, the type of form is determined by how consciously structured the mise en scene is. Open forms stress apparently simple techniques, because with these unself-conscious methods the filmmaker is able to emphasize the immediate, the familiar, the intimate aspects of reality. In open-form images, the frame tends to be deemphasized. In closed form images, all the necessary information is carefully structured within the confines of the frame. Space seems enclosed and self-contained rather than continuous.
Could argue this is a proscenium arch because this is such a classic shot with parallels and juxtapositions.
Is the framing tight or loose? Do the character have no room to move around, or can they move freely without impediments?
Shots where the characters are placed at the edges of the frame and have little room to move around within the frame are considered tight.
Longer shots, in which characters have room to move around within the frame, are considered loose and tend to suggest freedom.
Center-framed giving us the entire scene showing isolation, place and struggle.
Depth of Field. On how many planes is the image composed (how many are in focus)? Does the background or foreground comment in any way on the mid-ground?
Standard DOF, one background and clearly defined foreground.
Which way do the characters look vis-a-vis the camera?
An actor can be photographed in any of five basic positions, each conveying different psychological overtones.
Full-front (facing the camera):
the position with the most intimacy. The character is looking in our direction, inviting our complicity.Quarter Turn:
the favored position of most filmmakers. This position offers a high degree of intimacy but with less emotional involvement than the full-front.-> Profile (looking of the frame left or right):
More remote than the quarter turn, the character in profile seems unaware of being observed, lost in his or her own thoughts.Three-quarter Turn:
More anonymous than the profile, this position is useful for conveying a character’s unfriendly or antisocial feelings, for in effect, the character is partially turning his or her back on us, rejecting our interest.Back to Camera:
The most anonymous of all positions, this position is often used to suggest a character’s alienation from the world. When a character has his or her back to the camera, we can only guess what’s taking place internally, conveying a sense of concealment, or mystery.How much space is there between the characters?
Extremely close, for a gunfight.
The way people use space can be divided into four proxemic patterns.
Intimate distances.
The intimate distance ranges from skin contact to about eighteen inches away. This is the distance of physical involvement–of love, comfort, and tenderness between individuals.-> Personal distances.
The personal distance ranges roughly from eighteen inches away to about four feet away. These distances tend to be reserved for friends and acquaintances. Personal distances preserve the privacy between individuals, yet these rages don’t necessarily suggest exclusion, as intimate distances often do.Social distances.
The social distance rages from four feet to about twelve feet. These distances are usually reserved for impersonal business and casual social gatherings. It’s a friendly range in most cases, yet somewhat more formal than the personal distance.Public distances.
The public distance extends from twelve feet to twenty-five feet or more. This range tends to be formal and rather detached.
DESIGN
-
Mike Mitchell x Marvel x Mondo – Iconic portraits of Marvel’s huge stable of heroes and villains
Read more: Mike Mitchell x Marvel x Mondo – Iconic portraits of Marvel’s huge stable of heroes and villainshttps://mondoshop.com/blogs/gallery/16910155-mike-mitchell-x-marvel-x-mondo
https://time.com/69659/marvel-comics-mike-mitchell-artist-portraits/
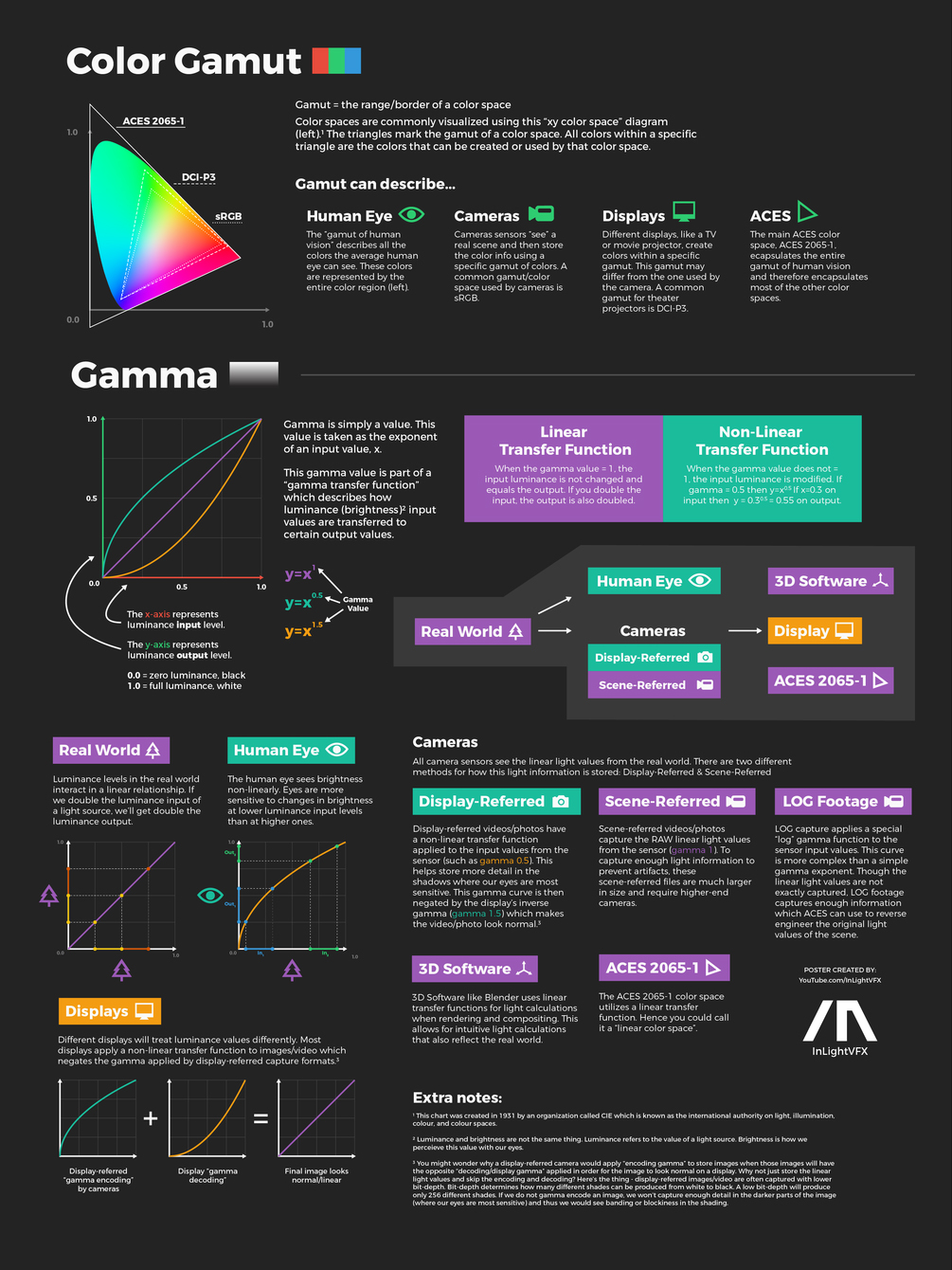
COLOR
-
Anders Langlands – Render Color Spaces
Read more: Anders Langlands – Render Color Spaceshttps://www.colour-science.org/anders-langlands/
This page compares images rendered in Arnold using spectral rendering and different sets of colourspace primaries: Rec.709, Rec.2020, ACES and DCI-P3. The SPD data for the GretagMacbeth Color Checker are the measurements of Noburu Ohta, taken from Mansencal, Mauderer and Parsons (2014) colour-science.org.
-
About green screens
Read more: About green screenshackaday.com/2015/02/07/how-green-screen-worked-before-computers/
www.newtek.com/blog/tips/best-green-screen-materials/
www.chromawall.com/blog//chroma-key-green
Chroma Key Green, the color of green screens is also known as Chroma Green and is valued at approximately 354C in the Pantone color matching system (PMS).
Chroma Green can be broken down in many different ways. Here is green screen green as other values useful for both physical and digital production:
Green Screen as RGB Color Value: 0, 177, 64
Green Screen as CMYK Color Value: 81, 0, 92, 0
Green Screen as Hex Color Value: #00b140
Green Screen as Websafe Color Value: #009933Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
Illuminate your green screen with an uniform source with less than 2/3 EV variation.
The level of brightness at any given f-stop should be equivalent to a 90% white card under the same lighting. -
Photography basics: Why Use a (MacBeth) Color Chart?
Read more: Photography basics: Why Use a (MacBeth) Color Chart?Start here: https://www.pixelsham.com/2013/05/09/gretagmacbeth-color-checker-numeric-values/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-a-color-checker-tool/
In LightRoom
in Final Cut
in Nuke
Note: In Foundry’s Nuke, the software will map 18% gray to whatever your center f/stop is set to in the viewer settings (f/8 by default… change that to EV by following the instructions below).
You can experiment with this by attaching an Exposure node to a Constant set to 0.18, setting your viewer read-out to Spotmeter, and adjusting the stops in the node up and down. You will see that a full stop up or down will give you the respective next value on the aperture scale (f8, f11, f16 etc.).One stop doubles or halves the amount or light that hits the filmback/ccd, so everything works in powers of 2.
So starting with 0.18 in your constant, you will see that raising it by a stop will give you .36 as a floating point number (in linear space), while your f/stop will be f/11 and so on.If you set your center stop to 0 (see below) you will get a relative readout in EVs, where EV 0 again equals 18% constant gray.
In other words. Setting the center f-stop to 0 means that in a neutral plate, the middle gray in the macbeth chart will equal to exposure value 0. EV 0 corresponds to an exposure time of 1 sec and an aperture of f/1.0.
This will set the sun usually around EV12-17 and the sky EV1-4 , depending on cloud coverage.
To switch Foundry’s Nuke’s SpotMeter to return the EV of an image, click on the main viewport, and then press s, this opens the viewer’s properties. Now set the center f-stop to 0 in there. And the SpotMeter in the viewport will change from aperture and fstops to EV.
LIGHTING
-
Vahan Sosoyan MakeHDR – an OpenFX open source plug-in for merging multiple LDR images into a single HDRI
Read more: Vahan Sosoyan MakeHDR – an OpenFX open source plug-in for merging multiple LDR images into a single HDRIhttps://github.com/Sosoyan/make-hdr
Feature notes
- Merge up to 16 inputs with 8, 10 or 12 bit depth processing
- User friendly logarithmic Tone Mapping controls within the tool
- Advanced controls such as Sampling rate and Smoothness
Available at cross platform on Linux, MacOS and Windows Works consistent in compositing applications like Nuke, Fusion, Natron.
NOTE: The goal is to clean the initial individual brackets before or at merging time as much as possible.
This means:- keeping original shooting metadata
- de-fringing
- removing aberration (through camera lens data or automatically)
- at 32 bit
- in ACEScg (or ACES) wherever possible
-
Ethan Roffler interviews CG Supervisor Daniele Tosti
Read more: Ethan Roffler interviews CG Supervisor Daniele TostiEthan Roffler
I recently had the honor of interviewing this VFX genius and gained great insight into what it takes to work in the entertainment industry. Keep in mind, these questions are coming from an artist’s perspective but can be applied to any creative individual looking for some wisdom from a professional. So grab a drink, sit back, and enjoy this fun and insightful conversation.
Ethan
To start, I just wanted to say thank you so much for taking the time for this interview!Daniele
My pleasure.
When I started my career I struggled to find help. Even people in the industry at the time were not that helpful. Because of that, I decided very early on that I was going to do exactly the opposite. I spend most of my weekends talking or helping students. ;)Ethan
That’s awesome! I have also come across the same struggle! Just a heads up, this will probably be the most informal interview you’ll ever have haha! Okay, so let’s start with a small introduction!Daniele
Short introduction: I worked very hard and got lucky enough to work on great shows with great people. ;) Slightly longer version: I started working for a TV channel, very early, while I was learning about CG. Slowly made my way across the world, working along very great people and amazing shows. I learned that to be successful in this business, you have to really love what you do as much as respecting the people around you. What you do will improve to the final product; the way you work with people will make a difference in your life.
Ethan
How long have you been an artist?Daniele
Loaded question. I believe I am still trying and craving to be one. After each production I finish I realize how much I still do not know. And how many things I would like to try. I guess in my CG Sup and generalist world, being an artist is about learning as much about the latest technologies and production cycles as I can, then putting that in practice. Having said that, I do consider myself a cinematographer first, as I have been doing that for about 25 years now.Ethan
Words of true wisdom, the more I know the less I know:) How did you get your start in the industry?
How did you break into such a competitive field?Daniele
There were not many schools when I started. It was all about a few magazines, some books, and pushing software around trying to learn how to make pretty images. Opportunities opened because of that knowledge! The true break was learning to work hard to achieve a Suspension of Disbelief in my work that people would recognize as such. It’s not something everyone can do, but I was fortunate to not be scared of working hard, being a quick learner and having very good supervisors and colleagues to learn from.Ethan
Which do you think is better, having a solid art degree or a strong portfolio?Daniele
Very good question. A strong portfolio will get you a job now. A solid strong degree will likely get you a job for a longer period. Let me digress here; Working as an artist is not about being an artist, it’s about making money as an artist. Most people fail to make that difference and have either a poor career or lack the understanding to make a stable one. One should never mix art with working as an artist. You can do both only if you understand business and are fair to yourself.
Ethan
That’s probably the most helpful answer to that question I have ever heard.
What’s some advice you can offer to someone just starting out who wants to break into the industry?Daniele
Breaking in the industry is not just about knowing your art. It’s about knowing good business practices. Prepare a good demo reel based on the skill you are applying for; research all the places where you want to apply and why; send as many reels around; follow up each reel with a phone call. Business is all about right time, right place.Ethan
A follow-up question to that is: Would you consider it a bad practice to send your demo reels out in mass quantity rather than focusing on a handful of companies to research and apply for?Daniele
Depends how desperate you are… I would say research is a must. To improve your options, you need to know which company is working on what and what skills they are after. If you were selling vacuum cleaners you probably would not want to waste energy contacting shoemakers or cattle farmers.Ethan
What do you think the biggest killer of creativity and productivity is for you?Daniele
Money…If you were thinking as an artist. ;) If you were thinking about making money as an artist… then I would say “thinking that you work alone”.Ethan
Best. Answer. Ever.
What are ways you fight complacency and maintain fresh ideas, outlooks, and perspectivesDaniele
Two things: Challenge yourself to go outside your comfort zone. And think outside of the box.Ethan
What are the ways/habits you have that challenge yourself to get out of your comfort zone and think outside the box?Daniele
If you think you are a good character painter, pick up a camera and go take pictures of amazing landscapes. If you think you are good only at painting or sketching, learn how to code in python. If you cannot solve a problem, that being a project or a person, learn to ask for help or learn about looking at the problem from various perspectives. If you are introvert, learn to be extrovert. And vice versa. And so on…
Ethan
How do you avoid burnout?Daniele
Oh… I wish I learned about this earlier. I think anyone that has a passion in something is at risk of burning out. Artists, more than many, because we see the world differently and our passion goes deep. You avoid burnouts by thinking that you are in a long term plan and that you have an obligation to pay or repay your talent by supporting and cherishing yourself and your family, not your paycheck. You do this by treating your art as a business and using business skills when dealing with your career and using artistic skills only when you are dealing with a project itself.Ethan
Looking back, what was a big defining moment for you?Daniele
Recognizing that people around you, those being colleagues, friends or family, come first.
It changed my career overnight.Ethan
Who are some of your personal heroes?Daniele
Too many to list. Most recently… James Cameron; Joe Letteri; Lawrence Krauss; Richard Dawkins. Because they all mix science, art, and poetry in their own way.Ethan
Last question:
What’s your dream job? ;)Daniele
Teaching artists to be better at being business people… as it will help us all improve our lives and the careers we took…
Being a VFX artist is fundamentally based on mistrust.
This because schedules, pipelines, technology, creative calls… all have a native and naive instability to them that causes everyone to grow a genuine but beneficial lack of trust in the status quo. This is a fine balance act to build into your character. The VFX motto: “Love everyone but trust no one” is born on that.
-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. … Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
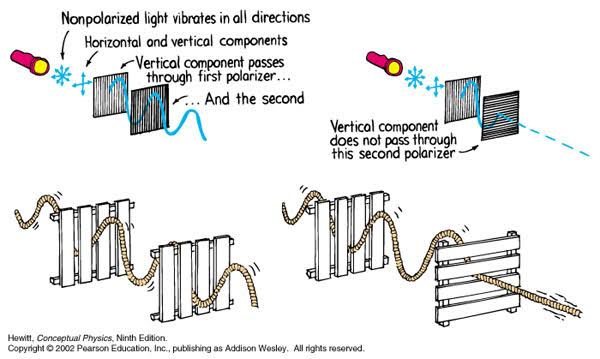
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
Light reflected from a non-metallic surface becomes polarized; this effect is maximum at Brewster’s angle, about 56° from the vertical for common glass.
A polarizer rotated to pass only light polarized in the direction perpendicular to the reflected light will absorb much of it. This absorption allows glare reflected from, for example, a body of water or a road to be reduced. Reflections from shiny surfaces (e.g. vegetation, sweaty skin, water surfaces, glass) are also reduced. This allows the natural color and detail of what is beneath to come through. Reflections from a window into a dark interior can be much reduced, allowing it to be seen through. (The same effects are available for vision by using polarizing sunglasses.)
www.physicsclassroom.com/class/light/u12l1e.cfm
Some of the light coming from the sky is polarized (bees use this phenomenon for navigation). The electrons in the air molecules cause a scattering of sunlight in all directions. This explains why the sky is not dark during the day. But when looked at from the sides, the light emitted from a specific electron is totally polarized.[3] Hence, a picture taken in a direction at 90 degrees from the sun can take advantage of this polarization. Use of a polarizing filter, in the correct direction, will filter out the polarized component of skylight, darkening the sky; the landscape below it, and clouds, will be less affected, giving a photograph with a darker and more dramatic sky, and emphasizing the clouds.

There are two types of polarizing filters readily available, linear and “circular”, which have exactly the same effect photographically. But the metering and auto-focus sensors in certain cameras, including virtually all auto-focus SLRs, will not work properly with linear polarizers because the beam splitters used to split off the light for focusing and metering are polarization-dependent.
Polarizing filters reduce the light passed through to the film or sensor by about one to three stops (2–8×) depending on how much of the light is polarized at the filter angle selected. Auto-exposure cameras will adjust for this by widening the aperture, lengthening the time the shutter is open, and/or increasing the ASA/ISO speed of the camera.
www.adorama.com/alc/nd-filter-vs-polarizer-what%25e2%2580%2599s-the-difference
Neutral Density (ND) filters help control image exposure by reducing the light that enters the camera so that you can have more control of your depth of field and shutter speed. Polarizers or polarizing filters work in a similar way, but the difference is that they selectively let light waves of a certain polarization pass through. This effect helps create more vivid colors in an image, as well as manage glare and reflections from water surfaces. Both are regarded as some of the best filters for landscape and travel photography as they reduce the dynamic range in high-contrast images, thus enabling photographers to capture more realistic and dramatic sceneries.
shopfelixgray.com/blog/polarized-vs-non-polarized-sunglasses/
www.eyebuydirect.com/blog/difference-polarized-nonpolarized-sunglasses/
Collections
| Explore posts
| Design And Composition
| Featured AI
Popular Searches
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
-
Kling 1.6 and competitors – advanced tests and comparisons
-
The Perils of Technical Debt – Understanding Its Impact on Security, Usability, and Stability
-
Film Production walk-through – pipeline – I want to make a … movie
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.