COMPOSITION
-
Photography basics: Depth of Field and composition
Read more: Photography basics: Depth of Field and compositionDepth of field is the range within which focusing is resolved in a photo.
Aperture has a huge affect on to the depth of field.Changing the f-stops (f/#) of a lens will change aperture and as such the DOF.
f-stops are a just certain number which is telling you the size of the aperture. That’s how f-stop is related to aperture (and DOF).
If you increase f-stops, it will increase DOF, the area in focus (and decrease the aperture). On the other hand, decreasing the f-stop it will decrease DOF (and increase the aperture).
The red cone in the figure is an angular representation of the resolution of the system. Versus the dotted lines, which indicate the aperture coverage. Where the lines of the two cones intersect defines the total range of the depth of field.
This image explains why the longer the depth of field, the greater the range of clarity.
DESIGN
-
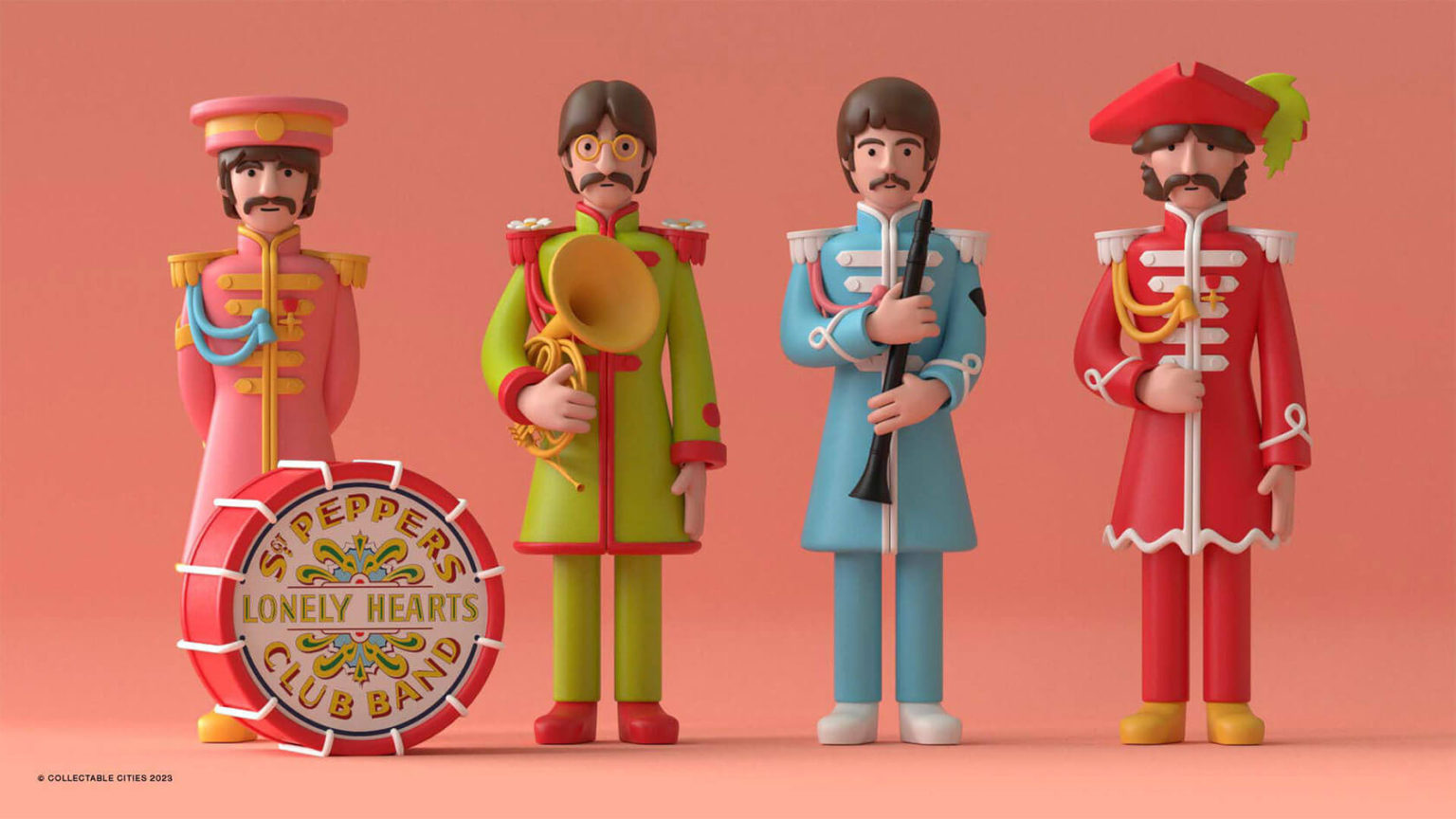
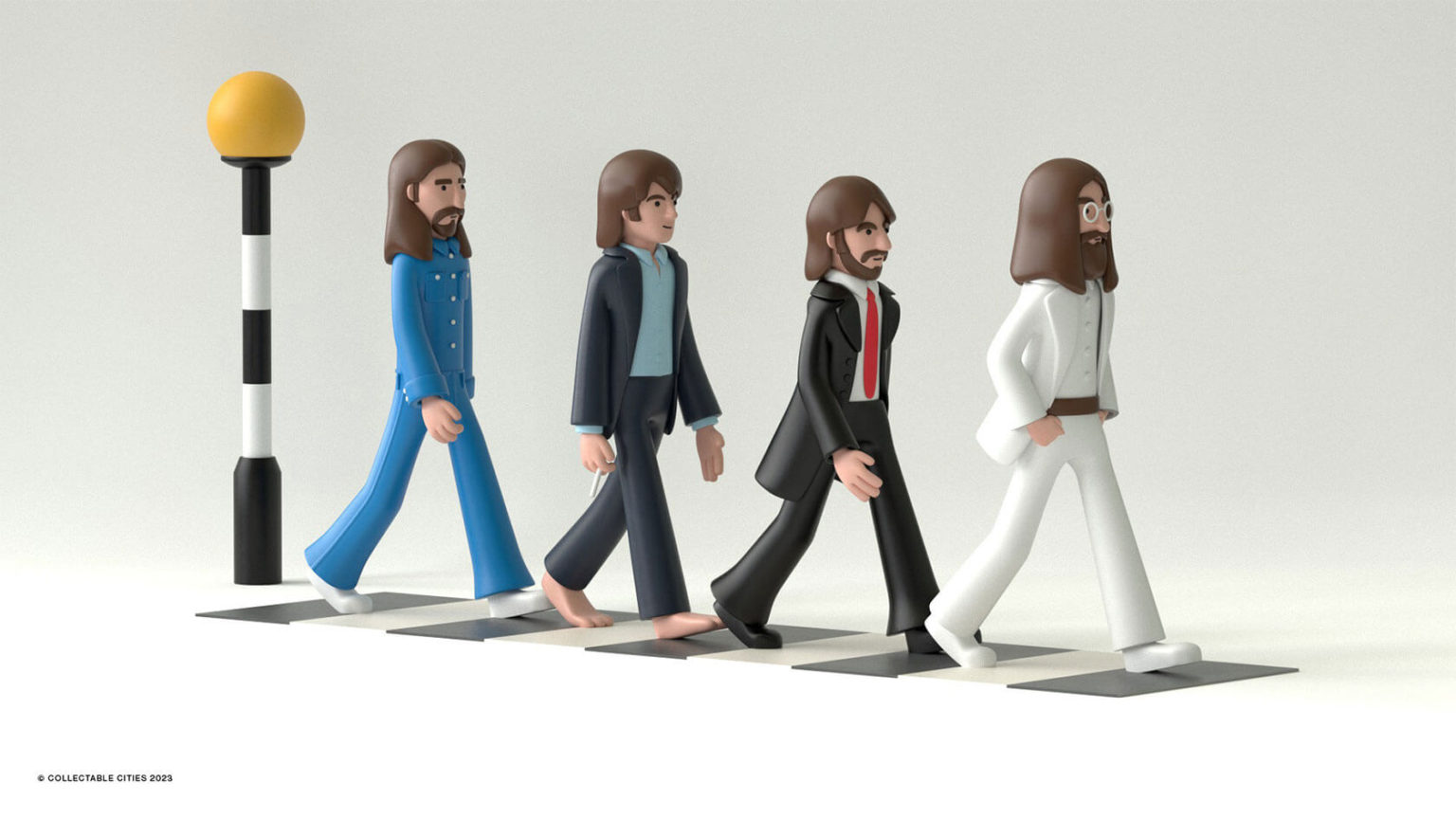
Creative duo Joseph Lattimer and Caitlin Derer Creates Absolutely Amazing The Beatles Collectable Toys
Read more: Creative duo Joseph Lattimer and Caitlin Derer Creates Absolutely Amazing The Beatles Collectable Toyshttps://designyoutrust.com/2024/11/artist-duo-creates-absolutely-amazing-the-beatles-collectable-toys



COLOR
-
The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t See
Read more: The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t Seewww.livescience.com/17948-red-green-blue-yellow-stunning-colors.html
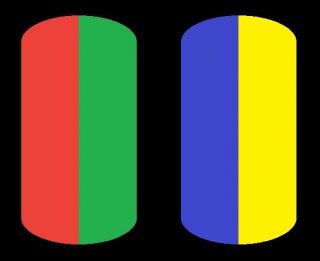
While the human eye has red, green, and blue-sensing cones, those cones are cross-wired in the retina to produce a luminance channel plus a red-green and a blue-yellow channel, and it’s data in that color space (known technically as “LAB”) that goes to the brain. That’s why we can’t perceive a reddish-green or a yellowish-blue, whereas such colors can be represented in the RGB color space used by digital cameras.
https://en.rockcontent.com/blog/the-use-of-yellow-in-data-design
The back of the retina is covered in light-sensitive neurons known as cone cells and rod cells. There are three types of cone cells, each sensitive to different ranges of light. These ranges overlap, but for convenience the cones are referred to as blue (short-wavelength), green (medium-wavelength), and red (long-wavelength). The rod cells are primarily used in low-light situations, so we’ll ignore those for now.
When light enters the eye and hits the cone cells, the cones get excited and send signals to the brain through the visual cortex. Different wavelengths of light excite different combinations of cones to varying levels, which generates our perception of color. You can see that the red cones are most sensitive to light, and the blue cones are least sensitive. The sensitivity of green and red cones overlaps for most of the visible spectrum.
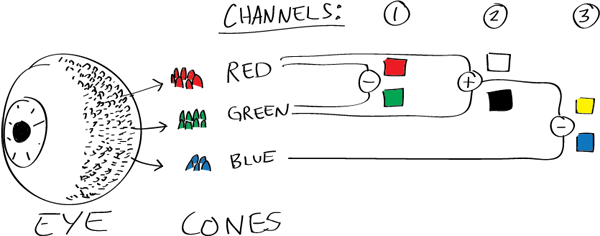
Here’s how your brain takes the signals of light intensity from the cones and turns it into color information. To see red or green, your brain finds the difference between the levels of excitement in your red and green cones. This is the red-green channel.
To get “brightness,” your brain combines the excitement of your red and green cones. This creates the luminance, or black-white, channel. To see yellow or blue, your brain then finds the difference between this luminance signal and the excitement of your blue cones. This is the yellow-blue channel.
From the calculations made in the brain along those three channels, we get four basic colors: blue, green, yellow, and red. Seeing blue is what you experience when low-wavelength light excites the blue cones more than the green and red.
Seeing green happens when light excites the green cones more than the red cones. Seeing red happens when only the red cones are excited by high-wavelength light.
Here’s where it gets interesting. Seeing yellow is what happens when BOTH the green AND red cones are highly excited near their peak sensitivity. This is the biggest collective excitement that your cones ever have, aside from seeing pure white.
Notice that yellow occurs at peak intensity in the graph to the right. Further, the lens and cornea of the eye happen to block shorter wavelengths, reducing sensitivity to blue and violet light.
-
What is a Gamut or Color Space and why do I need to know about CIE
Read more: What is a Gamut or Color Space and why do I need to know about CIEhttp://www.xdcam-user.com/2014/05/what-is-a-gamut-or-color-space-and-why-do-i-need-to-know-about-it/
In video terms gamut is normally related to as the full range of colours and brightness that can be either captured or displayed.
Generally speaking all color gamuts recommendations are trying to define a reasonable level of color representation based on available technology and hardware. REC-601 represents the old TVs. REC-709 is currently the most distributed solution. P3 is mainly available in movie theaters and is now being adopted in some of the best new 4K HDR TVs. Rec2020 (a wider space than P3 that improves on visibke color representation) and ACES (the full coverage of visible color) are other common standards which see major hardware development these days.
To compare and visualize different solution (across video and printing solutions), most developers use the CIE color model chart as a reference.
The CIE color model is a color space model created by the International Commission on Illumination known as the Commission Internationale de l’Elcairage (CIE) in 1931. It is also known as the CIE XYZ color space or the CIE 1931 XYZ color space.
This chart represents the first defined quantitative link between distributions of wavelengths in the electromagnetic visible spectrum, and physiologically perceived colors in human color vision. Or basically, the range of color a typical human eye can perceive through visible light.Note that while the human perception is quite wide, and generally speaking biased towards greens (we are apes after all), the amount of colors available through nature, generated through light reflection, tend to be a much smaller section. This is defined by the Pointer’s Chart.
In short. Color gamut is a representation of color coverage, used to describe data stored in images against available hardware and viewer technologies.
Camera color encoding from
https://www.slideshare.net/hpduiker/acescg-a-common-color-encoding-for-visual-effects-applicationsCIE 1976
http://bernardsmith.eu/computatrum/scan_and_restore_archive_and_print/scanning/
https://store.yujiintl.com/blogs/high-cri-led/understanding-cie1931-and-cie-1976
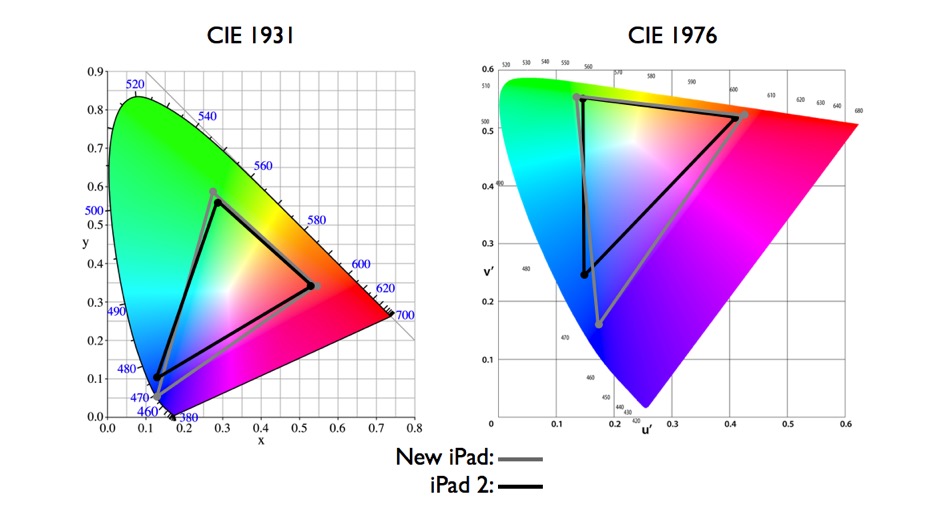
The CIE 1931 standard has been replaced by a CIE 1976 standard. Below we can see the significance of this.
People have observed that the biggest issue with CIE 1931 is the lack of uniformity with chromaticity, the three dimension color space in rectangular coordinates is not visually uniformed.
The CIE 1976 (also called CIELUV) was created by the CIE in 1976. It was put forward in an attempt to provide a more uniform color spacing than CIE 1931 for colors at approximately the same luminance
The CIE 1976 standard colour space is more linear and variations in perceived colour between different people has also been reduced. The disproportionately large green-turquoise area in CIE 1931, which cannot be generated with existing computer screens, has been reduced.
If we move from CIE 1931 to the CIE 1976 standard colour space we can see that the improvements made in the gamut for the “new” iPad screen (as compared to the “old” iPad 2) are more evident in the CIE 1976 colour space than in the CIE 1931 colour space, particularly in the blues from aqua to deep blue.
https://dot-color.com/2012/08/14/color-space-confusion/
Despite its age, CIE 1931, named for the year of its adoption, remains a well-worn and familiar shorthand throughout the display industry. CIE 1931 is the primary language of customers. When a customer says that their current display “can do 72% of NTSC,” they implicitly mean 72% of NTSC 1953 color gamut as mapped against CIE 1931.
LIGHTING
-
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
Read more: Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perceptionhttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
The Black Body Ultraviolet Catastrophe Experiment
In photography, color temperature describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a “blackbody” with that surface temperature. A blackbody is an object which absorbs all incident light — neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through.
The Sun closely approximates a black-body radiator. Another rough analogue of blackbody radiation in our day to day experience might be in heating a metal or stone: these are said to become “red hot” when they attain one temperature, and then “white hot” for even higher temperatures. Similarly, black bodies at different temperatures also have varying color temperatures of “white light.”
Despite its name, light which may appear white does not necessarily contain an even distribution of colors across the visible spectrum.
Although planets and stars are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, black-body radiation is used as a first approximation for the energy they emit. Black holes are near-perfect black bodies, and it is believed that they emit black-body radiation (called Hawking radiation), with a temperature that depends on the mass of the hole.
-
Photography basics: How Exposure Stops (Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO) Affect Your Photos – cheat cards
Read more: Photography basics: How Exposure Stops (Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO) Affect Your Photos – cheat cardsAlso see:
https://www.pixelsham.com/2018/11/22/exposure-value-measurements/
https://www.pixelsham.com/2016/03/03/f-stop-vs-t-stop/
An exposure stop is a unit measurement of Exposure as such it provides a universal linear scale to measure the increase and decrease in light, exposed to the image sensor, due to changes in shutter speed, iso and f-stop.
+-1 stop is a doubling or halving of the amount of light let in when taking a photo
1 EV (exposure value) is just another way to say one stop of exposure change.
https://www.photographymad.com/pages/view/what-is-a-stop-of-exposure-in-photography
Same applies to shutter speed, iso and aperture.
Doubling or halving your shutter speed produces an increase or decrease of 1 stop of exposure.
Doubling or halving your iso speed produces an increase or decrease of 1 stop of exposure.Details in the post
Collections
| Explore posts
| Design And Composition
| Featured AI
Popular Searches
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.


