COMPOSITION
-
StudioBinder – Roger Deakins on How to Choose a Camera Lens — Cinematography Composition Techniques
Read more: StudioBinder – Roger Deakins on How to Choose a Camera Lens — Cinematography Composition Techniqueshttps://www.studiobinder.com/blog/camera-lens-buying-guide/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/e-books/camera-lenses-explained-volume-1-ebook
DESIGN
-
VQGAN + CLIP AI made Music Video for the song Canvas by Resonate
Read more: VQGAN + CLIP AI made Music Video for the song Canvas by Resonate” In this video, I utilized artificial intelligence to generate an animated music video for the song Canvas by Resonate. This tool allows anyone to generate beautiful images using only text as the input. My question was, what if I used song lyrics as input to the AI, can I make perfect music synchronized videos automatically with the push of a button? Let me know how you think the AI did in this visual interpretation of the song.
After getting caught up in the excitement around DALL·E2 (latest and greatest AI system, it’s INSANE), I searched for any way I could use similar image generation for music synchronization. Since DALL·E2 is not available to the public yet, my search led me to VQGAN + CLIP (Vector Quantized Generative Adversarial Network and Contrastive Language–Image Pre-training), before settling more specifically on Disco Diffusion V5.2 Turbo. If you don’t know what any of these words or acronyms mean, don’t worry, I was just as confused when I first started learning about this technology. I believe we’re reaching a turning point where entire industries are about to shift in reaction to this new process (which is essentially magic!).
DoodleChaos”
-
Kristina Kashtanova – “This is how GPT-4 sees and hears itself”
Read more: Kristina Kashtanova – “This is how GPT-4 sees and hears itself”“I used GPT-4 to describe itself. Then I used its description to generate an image, a video based on this image and a soundtrack.
Tools I used: GPT-4, Midjourney, Kaiber AI, Mubert, RunwayML
This is the description I used that GPT-4 had of itself as a prompt to text-to-image, image-to-video, and text-to-music. I put the video and sound together in RunwayML.
GPT-4 described itself as: “Imagine a sleek, metallic sphere with a smooth surface, representing the vast knowledge contained within the model. The sphere emits a soft, pulsating glow that shifts between various colors, symbolizing the dynamic nature of the AI as it processes information and generates responses. The sphere appears to float in a digital environment, surrounded by streams of data and code, reflecting the complex algorithms and computing power behind the AI”
COLOR
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
Read more: Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflowsDisplay Referred it is tied to the target hardware, as such it bakes color requirements into every type of media output request.
Scene Referred uses a common unified wide gamut and targeting audience through CDL and DI libraries instead.
So that color information stays untouched and only “transformed” as/when needed.Sources:
– Victor Perez – Color Management Fundamentals & ACES Workflows in Nuke
– https://z-fx.nl/ColorspACES.pdf
– Wicus
-
THOMAS MANSENCAL – The Apparent Simplicity of RGB Rendering
Read more: THOMAS MANSENCAL – The Apparent Simplicity of RGB Renderinghttps://thomasmansencal.substack.com/p/the-apparent-simplicity-of-rgb-rendering
The primary goal of physically-based rendering (PBR) is to create a simulation that accurately reproduces the imaging process of electro-magnetic spectrum radiation incident to an observer. This simulation should be indistinguishable from reality for a similar observer.
Because a camera is not sensitive to incident light the same way than a human observer, the images it captures are transformed to be colorimetric. A project might require infrared imaging simulation, a portion of the electro-magnetic spectrum that is invisible to us. Radically different observers might image the same scene but the act of observing does not change the intrinsic properties of the objects being imaged. Consequently, the physical modelling of the virtual scene should be independent of the observer.
-
Thomas Mansencal – Colour Science for Python
Read more: Thomas Mansencal – Colour Science for Pythonhttps://thomasmansencal.substack.com/p/colour-science-for-python
https://www.colour-science.org/
Colour is an open-source Python package providing a comprehensive number of algorithms and datasets for colour science. It is freely available under the BSD-3-Clause terms.
-
Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wrong
Read more: Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wronghttps://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorwrong/
Most software around us today are decent at accurately displaying colors. Processing of colors is another story unfortunately, and is often done badly.
To understand what the problem is, let’s start with an example of three ways of blending green and magenta:
- Perceptual blend – A smooth transition using a model designed to mimic human perception of color. The blending is done so that the perceived brightness and color varies smoothly and evenly.
- Linear blend – A model for blending color based on how light behaves physically. This type of blending can occur in many ways naturally, for example when colors are blended together by focus blur in a camera or when viewing a pattern of two colors at a distance.
- sRGB blend – This is how colors would normally be blended in computer software, using sRGB to represent the colors.
Let’s look at some more examples of blending of colors, to see how these problems surface more practically. The examples use strong colors since then the differences are more pronounced. This is using the same three ways of blending colors as the first example.
Instead of making it as easy as possible to work with color, most software make it unnecessarily hard, by doing image processing with representations not designed for it. Approximating the physical behavior of light with linear RGB models is one easy thing to do, but more work is needed to create image representations tailored for image processing and human perception.
Also see:
LIGHTING
-
Simulon – a Hollywood production studio app in the hands of an independent creator with access to consumer hardware, LDRi to HDRi through ML
Read more: Simulon – a Hollywood production studio app in the hands of an independent creator with access to consumer hardware, LDRi to HDRi through MLDivesh Naidoo: The video below was made with a live in-camera preview and auto-exposure matching, no camera solve, no HDRI capture and no manual compositing setup. Using the new Simulon phone app.
LDR to HDR through ML
https://simulon.typeform.com/betatest
Process example
-
HDRI Resources
Read more: HDRI ResourcesText2Light
- https://www.cgtrader.com/free-3d-models/exterior/other/10-free-hdr-panoramas-created-with-text2light-zero-shot
- https://frozenburning.github.io/projects/text2light/
- https://github.com/FrozenBurning/Text2Light
Royalty free links
- https://locationtextures.com/panoramas/
- http://www.noahwitchell.com/freebies
- https://polyhaven.com/hdris
- https://hdrmaps.com/
- https://www.ihdri.com/
- https://hdrihaven.com/
- https://www.domeble.com/
- http://www.hdrlabs.com/sibl/archive.html
- https://www.hdri-hub.com/hdrishop/hdri
- http://noemotionhdrs.net/hdrevening.html
- https://www.openfootage.net/hdri-panorama/
- https://www.zwischendrin.com/en/browse/hdri
Nvidia GauGAN360
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
Read more: HDRI Median Cut pluginwww.hdrlabs.com/picturenaut/plugins.html
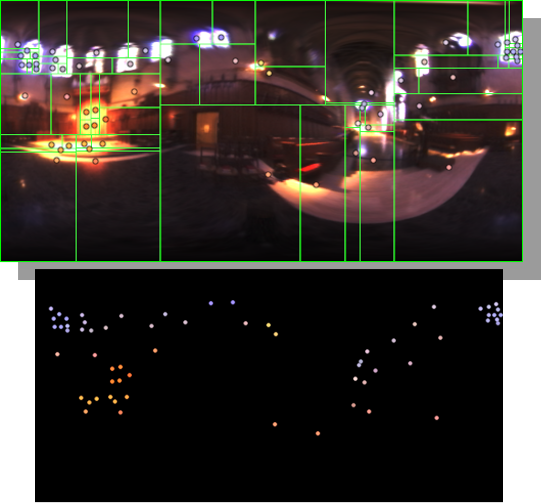
Note. The Median Cut algorithm is typically used for color quantization, which involves reducing the number of colors in an image while preserving its visual quality. It doesn’t directly provide a way to identify the brightest areas in an image. However, if you’re interested in identifying the brightest areas, you might want to look into other methods like thresholding, histogram analysis, or edge detection, through openCV for example.
Here is an openCV example:
# bottom left coordinates = 0,0 import numpy as np import cv2 # Load the HDR or EXR image image = cv2.imread('your_image_path.exr', cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED) # Load as-is without modification # Calculate the luminance from the HDR channels (assuming RGB format) luminance = np.dot(image[..., :3], [0.299, 0.587, 0.114]) # Set a threshold value based on estimated EV threshold_value = 2.4 # Estimated threshold value based on 4.8 EV # Apply the threshold to identify bright areas # Theluminancearray contains the calculated luminance values for each pixel in the image. # Thethreshold_valueis a user-defined value that represents a cutoff point, separating "bright" and "dark" areas in terms of perceived luminance.thresholded = (luminance > threshold_value) * 255 # Convert the thresholded image to uint8 for contour detection thresholded = thresholded.astype(np.uint8) # Find contours of the bright areas contours, _ = cv2.findContours(thresholded, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # Create a list to store the bounding boxes of bright areas bright_areas = [] # Iterate through contours and extract bounding boxes for contour in contours: x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour) # Adjust y-coordinate based on bottom-left origin y_bottom_left_origin = image.shape[0] - (y + h) bright_areas.append((x, y_bottom_left_origin, x + w, y_bottom_left_origin + h)) # Store as (x1, y1, x2, y2) # Print the identified bright areas print("Bright Areas (x1, y1, x2, y2):") for area in bright_areas: print(area)More details
Luminance and Exposure in an EXR Image:
- An EXR (Extended Dynamic Range) image format is often used to store high dynamic range (HDR) images that contain a wide range of luminance values, capturing both dark and bright areas.
- Luminance refers to the perceived brightness of a pixel in an image. In an RGB image, luminance is often calculated using a weighted sum of the red, green, and blue channels, where different weights are assigned to each channel to account for human perception.
- In an EXR image, the pixel values can represent radiometrically accurate scene values, including actual radiance or irradiance levels. These values are directly related to the amount of light emitted or reflected by objects in the scene.
The luminance line is calculating the luminance of each pixel in the image using a weighted sum of the red, green, and blue channels. The three float values [0.299, 0.587, 0.114] are the weights used to perform this calculation.
These weights are based on the concept of luminosity, which aims to approximate the perceived brightness of a color by taking into account the human eye’s sensitivity to different colors. The values are often derived from the NTSC (National Television System Committee) standard, which is used in various color image processing operations.
Here’s the breakdown of the float values:
- 0.299: Weight for the red channel.
- 0.587: Weight for the green channel.
- 0.114: Weight for the blue channel.
The weighted sum of these channels helps create a grayscale image where the pixel values represent the perceived brightness. This technique is often used when converting a color image to grayscale or when calculating luminance for certain operations, as it takes into account the human eye’s sensitivity to different colors.
For the threshold, remember that the exact relationship between EV values and pixel values can depend on the tone-mapping or normalization applied to the HDR image, as well as the dynamic range of the image itself.
To establish a relationship between exposure and the threshold value, you can consider the relationship between linear and logarithmic scales:
- Linear and Logarithmic Scales:
- Exposure values in an EXR image are often represented in logarithmic scales, such as EV (exposure value). Each increment in EV represents a doubling or halving of the amount of light captured.
- Threshold values for luminance thresholding are usually linear, representing an actual luminance level.
- Conversion Between Scales:
- To establish a mathematical relationship, you need to convert between the logarithmic exposure scale and the linear threshold scale.
- One common method is to use a power function. For instance, you can use a power function to convert EV to a linear intensity value.
threshold_value = base_value * (2 ** EV)Here,
EVis the exposure value,base_valueis a scaling factor that determines the relationship between EV and threshold_value, and2 ** EVis used to convert the logarithmic EV to a linear intensity value. - Choosing the Base Value:
- The
base_valuefactor should be determined based on the dynamic range of your EXR image and the specific luminance values you are dealing with. - You may need to experiment with different values of
base_valueto achieve the desired separation of bright areas from the rest of the image.
- The
Let’s say you have an EXR image with a dynamic range of 12 EV, which is a common range for many high dynamic range images. In this case, you want to set a threshold value that corresponds to a certain number of EV above the middle gray level (which is often considered to be around 0.18).
Here’s an example of how you might determine a
base_valueto achieve this:# Define the dynamic range of the image in EV dynamic_range = 12 # Choose the desired number of EV above middle gray for thresholding desired_ev_above_middle_gray = 2 # Calculate the threshold value based on the desired EV above middle gray threshold_value = 0.18 * (2 ** (desired_ev_above_middle_gray / dynamic_range)) print("Threshold Value:", threshold_value) -
IES Light Profiles and editing software
Read more: IES Light Profiles and editing softwarehttp://www.derekjenson.com/3d-blog/ies-light-profiles
https://ieslibrary.com/en/browse#ies
https://leomoon.com/store/shaders/ies-lights-pack
https://docs.arnoldrenderer.com/display/a5afmug/ai+photometric+light
IES profiles are useful for creating life-like lighting, as they can represent the physical distribution of light from any light source.
The IES format was created by the Illumination Engineering Society, and most lighting manufacturers provide IES profile for the lights they manufacture.
-
Composition and The Expressive Nature Of Light
Read more: Composition and The Expressive Nature Of Lighthttp://www.huffingtonpost.com/bill-danskin/post_12457_b_10777222.html
George Sand once said “ The artist vocation is to send light into the human heart.”
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Emmanuel Tsekleves – Writing Research Papers
-
UV maps
-
QR code logos
-
Sensitivity of human eye
-
Web vs Printing or digital RGB vs CMYK
-
Glossary of Lighting Terms – cheat sheet
-
Film Production walk-through – pipeline – I want to make a … movie
-
copypastecharacter.com – alphabets, special characters and symbols library
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.