COMPOSITION
-
9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camera
Read more: 9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camerahttps://www.flexclip.com/learn/cinematic-video.html
- Frame Your Shots to Create Depth
- Create Shallow Depth of Field
- Avoid Shaky Footage and Use Flexible Camera Movements
- Properly Use Slow Motion
- Use Cinematic Lighting Techniques
- Apply Color Grading
- Use Cinematic Music and SFX
- Add Cinematic Fonts and Text Effects
- Create the Cinematic Bar at the Top and the Bottom

DESIGN
COLOR
-
About green screens
Read more: About green screenshackaday.com/2015/02/07/how-green-screen-worked-before-computers/
www.newtek.com/blog/tips/best-green-screen-materials/
www.chromawall.com/blog//chroma-key-green
Chroma Key Green, the color of green screens is also known as Chroma Green and is valued at approximately 354C in the Pantone color matching system (PMS).
Chroma Green can be broken down in many different ways. Here is green screen green as other values useful for both physical and digital production:
Green Screen as RGB Color Value: 0, 177, 64
Green Screen as CMYK Color Value: 81, 0, 92, 0
Green Screen as Hex Color Value: #00b140
Green Screen as Websafe Color Value: #009933Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
Illuminate your green screen with an uniform source with less than 2/3 EV variation.
The level of brightness at any given f-stop should be equivalent to a 90% white card under the same lighting. -
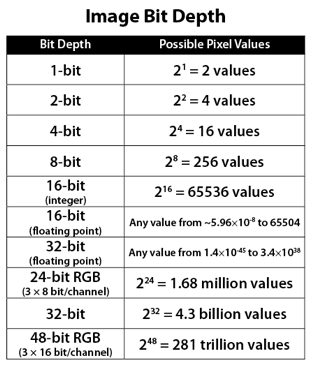
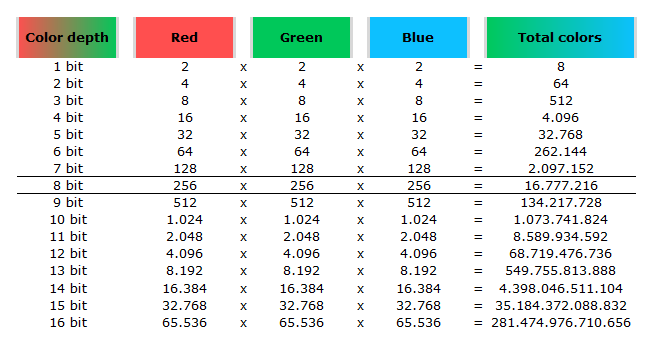
Image rendering bit depth
Read more: Image rendering bit depthThe terms 8-bit, 16-bit, 16-bit float, and 32-bit refer to different data formats used to store and represent image information, as bits per pixel.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_depth
In color technology, color depth also known as bit depth, is either the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel, OR the number of bits used for each color component of a single pixel.
When referring to a pixel, the concept can be defined as bits per pixel (bpp).
When referring to a color component, the concept can be defined as bits per component, bits per channel, bits per color (all three abbreviated bpc), and also bits per pixel component, bits per color channel or bits per sample (bps). Modern standards tend to use bits per component, but historical lower-depth systems used bits per pixel more often.
Color depth is only one aspect of color representation, expressing the precision with which the amount of each primary can be expressed; the other aspect is how broad a range of colors can be expressed (the gamut). The definition of both color precision and gamut is accomplished with a color encoding specification which assigns a digital code value to a location in a color space.

Here’s a simple explanation of each.
8-bit images (i.e. 24 bits per pixel for a color image) are considered Low Dynamic Range.
They can store around 5 stops of light and each pixel carry a value from 0 (black) to 255 (white).
As a comparison, DSLR cameras can capture ~12-15 stops of light and they use RAW files to store the information.16-bit: This format is commonly referred to as “half-precision.” It uses 16 bits of data to represent color values for each pixel. With 16 bits, you can have 65,536 discrete levels of color, allowing for relatively high precision and smooth gradients. However, it has a limited dynamic range, meaning it cannot accurately represent extremely bright or dark values. It is commonly used for regular images and textures.
16-bit float: This format is an extension of the 16-bit format but uses floating-point numbers instead of fixed integers. Floating-point numbers allow for more precise calculations and a larger dynamic range. In this case, the 16 bits are used to store both the color value and the exponent, which controls the range of values that can be represented. The 16-bit float format provides better accuracy and a wider dynamic range than regular 16-bit, making it useful for high-dynamic-range imaging (HDRI) and computations that require more precision.
32-bit: (i.e. 96 bits per pixel for a color image) are considered High Dynamic Range. This format, also known as “full-precision” or “float,” uses 32 bits to represent color values and offers the highest precision and dynamic range among the three options. With 32 bits, you have a significantly larger number of discrete levels, allowing for extremely accurate color representation, smooth gradients, and a wide range of brightness values. It is commonly used for professional rendering, visual effects, and scientific applications where maximum precision is required.
Bits and HDR coverage
High Dynamic Range (HDR) images are designed to capture a wide range of luminance values, from the darkest shadows to the brightest highlights, in order to reproduce a scene with more accuracy and detail. The bit depth of an image refers to the number of bits used to represent each pixel’s color information. When comparing 32-bit float and 16-bit float HDR images, the drop in accuracy primarily relates to the precision of the color information.
A 32-bit float HDR image offers a higher level of precision compared to a 16-bit float HDR image. In a 32-bit float format, each color channel (red, green, and blue) is represented by 32 bits, allowing for a larger range of values to be stored. This increased precision enables the image to retain more details and subtleties in color and luminance.
On the other hand, a 16-bit float HDR image utilizes 16 bits per color channel, resulting in a reduced range of values that can be represented. This lower precision leads to a loss of fine details and color nuances, especially in highly contrasted areas of the image where there are significant differences in luminance.
The drop in accuracy between 32-bit and 16-bit float HDR images becomes more noticeable as the exposure range of the scene increases. Exposure range refers to the span between the darkest and brightest areas of an image. In scenes with a limited exposure range, where the luminance differences are relatively small, the loss of accuracy may not be as prominent or perceptible. These images usually are around 8-10 exposure levels.
However, in scenes with a wide exposure range, such as a landscape with deep shadows and bright highlights, the reduced precision of a 16-bit float HDR image can result in visible artifacts like color banding, posterization, and loss of detail in both shadows and highlights. The image may exhibit abrupt transitions between tones or colors, which can appear unnatural and less realistic.
To provide a rough estimate, it is often observed that exposure values beyond approximately ±6 to ±8 stops from the middle gray (18% reflectance) may be more prone to accuracy issues in a 16-bit float format. This range may vary depending on the specific implementation and encoding scheme used.
To summarize, the drop in accuracy between 32-bit and 16-bit float HDR images is mainly related to the reduced precision of color information. This decrease in precision becomes more apparent in scenes with a wide exposure range, affecting the representation of fine details and leading to visible artifacts in the image.
In practice, this means that exposure values beyond a certain range will experience a loss of accuracy and detail when stored in a 16-bit float format. The exact range at which this loss occurs depends on the encoding scheme and the specific implementation. However, in general, extremely bright or extremely dark values that fall outside the representable range may be subject to quantization errors, resulting in loss of detail, banding, or other artifacts.
HDRs used for lighting purposes are usually slightly convolved to improve on sampling speed and removing specular artefacts. To that extent, 16 bit float HDRIs tend to me most used in CG cycles.

LIGHTING
-
Vahan Sosoyan MakeHDR – an OpenFX open source plug-in for merging multiple LDR images into a single HDRI
Read more: Vahan Sosoyan MakeHDR – an OpenFX open source plug-in for merging multiple LDR images into a single HDRIhttps://github.com/Sosoyan/make-hdr
Feature notes
- Merge up to 16 inputs with 8, 10 or 12 bit depth processing
- User friendly logarithmic Tone Mapping controls within the tool
- Advanced controls such as Sampling rate and Smoothness
Available at cross platform on Linux, MacOS and Windows Works consistent in compositing applications like Nuke, Fusion, Natron.
NOTE: The goal is to clean the initial individual brackets before or at merging time as much as possible.
This means:- keeping original shooting metadata
- de-fringing
- removing aberration (through camera lens data or automatically)
- at 32 bit
- in ACEScg (or ACES) wherever possible
-
Fast, optimized ‘for’ pixel loops with OpenCV and Python to create tone mapped HDR images
Read more: Fast, optimized ‘for’ pixel loops with OpenCV and Python to create tone mapped HDR imageshttps://pyimagesearch.com/2017/08/28/fast-optimized-for-pixel-loops-with-opencv-and-python/
https://learnopencv.com/exposure-fusion-using-opencv-cpp-python/
Exposure Fusion is a method for combining images taken with different exposure settings into one image that looks like a tone mapped High Dynamic Range (HDR) image.
-
Sun cone angle (angular diameter) as perceived by earth viewers
Read more: Sun cone angle (angular diameter) as perceived by earth viewersAlso see:
https://www.pixelsham.com/2020/08/01/solid-angle-measures/
The cone angle of the sun refers to the angular diameter of the sun as observed from Earth, which is related to the apparent size of the sun in the sky.
The angular diameter of the sun, or the cone angle of the sunlight as perceived from Earth, is approximately 0.53 degrees on average. This value can vary slightly due to the elliptical nature of Earth’s orbit around the sun, but it generally stays within a narrow range.
Here’s a more precise breakdown:
-
- Average Angular Diameter: About 0.53 degrees (31 arcminutes)
- Minimum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.52 degrees (when Earth is at aphelion, the farthest point from the sun)
- Maximum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.54 degrees (when Earth is at perihelion, the closest point to the sun)
This angular diameter remains relatively constant throughout the day because the sun’s distance from Earth does not change significantly over a single day.
To summarize, the cone angle of the sun’s light, or its angular diameter, is typically around 0.53 degrees, regardless of the time of day.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angular_diameter
-
-
domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRI
Read more: domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRIWhen collecting hdri make sure the data supports basic metadata, such as:
- Iso
- Aperture
- Exposure time or shutter time
- Color temperature
- Color space Exposure value (what the sensor receives of the sun intensity in lux)
- 7+ brackets (with 5 or 6 being the perceived balanced exposure)
In image processing, computer graphics, and photography, high dynamic range imaging (HDRI or just HDR) is a set of techniques that allow a greater dynamic range of luminances (a Photometry measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle) between the lightest and darkest areas of an image than standard digital imaging techniques or photographic methods. This wider dynamic range allows HDR images to represent more accurately the wide range of intensity levels found in real scenes ranging from direct sunlight to faint starlight and to the deepest shadows.
The two main sources of HDR imagery are computer renderings and merging of multiple photographs, which in turn are known as low dynamic range (LDR) or standard dynamic range (SDR) images. Tone Mapping (Look-up) techniques, which reduce overall contrast to facilitate display of HDR images on devices with lower dynamic range, can be applied to produce images with preserved or exaggerated local contrast for artistic effect. Photography
In photography, dynamic range is measured in Exposure Values (in photography, exposure value denotes all combinations of camera shutter speed and relative aperture that give the same exposure. The concept was developed in Germany in the 1950s) differences or stops, between the brightest and darkest parts of the image that show detail. An increase of one EV or one stop is a doubling of the amount of light.
The human response to brightness is well approximated by a Steven’s power law, which over a reasonable range is close to logarithmic, as described by the Weber�Fechner law, which is one reason that logarithmic measures of light intensity are often used as well.
HDR is short for High Dynamic Range. It’s a term used to describe an image which contains a greater exposure range than the “black” to “white” that 8 or 16-bit integer formats (JPEG, TIFF, PNG) can describe. Whereas these Low Dynamic Range images (LDR) can hold perhaps 8 to 10 f-stops of image information, HDR images can describe beyond 30 stops and stored in 32 bit images.

-
How are Energy and Matter the Same?
Read more: How are Energy and Matter the Same?www.turnerpublishing.com/blog/detail/everything-is-energy-everything-is-one-everything-is-possible/
www.universetoday.com/116615/how-are-energy-and-matter-the-same/
As Einstein showed us, light and matter and just aspects of the same thing. Matter is just frozen light. And light is matter on the move. Albert Einstein’s most famous equation says that energy and matter are two sides of the same coin. How does one become the other?
Relativity requires that the faster an object moves, the more mass it appears to have. This means that somehow part of the energy of the car’s motion appears to transform into mass. Hence the origin of Einstein’s equation. How does that happen? We don’t really know. We only know that it does.
Matter is 99.999999999999 percent empty space. Not only do the atom and solid matter consist mainly of empty space, it is the same in outer space
The quantum theory researchers discovered the answer: Not only do particles consist of energy, but so does the space between. This is the so-called zero-point energy. Therefore it is true: Everything consists of energy.
Energy is the basis of material reality. Every type of particle is conceived of as a quantum vibration in a field: Electrons are vibrations in electron fields, protons vibrate in a proton field, and so on. Everything is energy, and everything is connected to everything else through fields.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
AI Search – Find The Best AI Tools & Apps
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
-
How does Stable Diffusion work?
-
Top 3D Printing Website Resources
-
Advanced Computer Vision with Python OpenCV and Mediapipe
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
-
How do LLMs like ChatGPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) work? Explained by Deep-Fake Ryan Gosling
-
Convert 2D Images to 3D Models
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.









