https://www.uniindia.com/news/entertainment/hollywood-james-cameron/3436702.html





3Dprinting (176) A.I. (756) animation (339) blender (197) colour (229) commercials (49) composition (152) cool (360) design (636) Featured (69) hardware (308) IOS (109) jokes (134) lighting (282) modeling (128) music (186) photogrammetry (177) photography (751) production (1254) python (87) quotes (491) reference (310) software (1336) trailers (296) ves (538) VR (219)
Category: ves
-
AI Creativity – Genius or Gimmick?
7:59-9:50 Justine Bateman:
“I mean first I want to give people, help people have a little bit of a definition of what generative AI is—
think of it as like a blender and if you have a blender at home and you turn it on, what does it do? It depends on what I put into it, so it cannot function unless it’s fed things.
Then you turn on the blender and you give it a prompt, which is your little spoon, and you get a little spoonful—little Frankenstein spoonful—out of what you asked for.
So what is going into the blender? Every but a hundred years of film and television or many, many years of, you know, doctor’s reports or students’ essays or whatever it is.
In the film business, in particular, that’s what we call theft; it’s the biggest violation. And the term that continues to be used is “all we did.” I think the CTO of OpenAI—believe that’s her position; I forget her name—when she was asked in an interview recently what she had to say about the fact that they didn’t ask permission to take it in, she said, “Well, it was all publicly available.”
And I will say this: if you own a car—I know we’re in New York City, so it’s not going to be as applicable—but if I see a car in the street, it’s publicly available, but somehow it’s illegal for me to take it. That’s what we have the copyright office for, and I don’t know how well staffed they are to handle something like this, but this is the biggest copyright violation in the history of that office and the US government” -
Robert Legato joins Stability AI as Chief Pipeline Architect
https://stability.ai/news/introducing-our-new-chief-pipeline-architect-rob-legato
“Joining Stability AI is an incredible opportunity, and I couldn’t be more excited to help shape the next era of filmmaking,” said Legato. “With dynamic leaders like Prem Akkaraju and James Cameron driving the vision, the potential here is limitless. What excites me most is Stability AI’s commitment to filmmakers—building a tool that is as intuitive as it is powerful, designed to elevate creativity rather than replace it. It’s an artist-first approach to AI, and I’m thrilled to be part of it.”

-
Apple TV+ Reportedly Loses $1 Billion on Streaming a Year
https://www.indiewire.com/news/business/apple-tv-reportedly-loses-1-billion-streaming-1235110323
But it supposedly also has 45 million subscribers, and with $124.3 million in revenue.
Per the company’s most recent earnings, the three months ending in January saw Apple bring in $124.3 billion in revenue, $26.3 billion of which came from Services, a record for the division. That’s just for one quarter. For the year, Services brought in more than $96 billion. It can afford to absorb a billion dollars in losses.https://spyglass.org/apple-tv-plus-strategy
It Wasn’t the Apple TV+ Spend, It Was the Apple TV+ Strategy

-
VillageRoadShow production studio files for bankruptcy
Village Roadshow (prod company/financier: Wonka, the Matrix series, and Ocean’s 11) has filed for bankruptcy.
It’s a rough indicator of where we are in 2025 when one of the last independent production companies working with the studios goes under.
Here’s their balance sheet:
$400 M in library value of 100+ films (89 of which they co-own with Warner Bros.)
$500 M – $1bn total debt
$1.4 M in debt to WGA, whose members were told to stop working with Roadshow in December
$794 K owed to Bryan Cranston’s prod company
$250 K owed to Sony Pictures TV
$300 K/month overhead
The crowning expense that brought down this 36-year-old production company is the $18 M in (unpaid) legal fees from a lengthy and currently unresolved arbitration with their long-time partner Warner Bros, who they’ve had a co-financing arrangement since the late 90s.
Roadshow sued when WBD released their Matrix Resurrections (2021) film in theaters and on Max simultaneously, causing Roadshow to withhold their portion of the $190 M production costs.
Due to mounting financial pressures, Village Roadshow’s CEO, Steve Mosko, a veteran film and TV exec, left the company in January.
Now, this all falls on the shoulders of Jim Moore, CEO of Vine, an equity firm that owns Village Roadshow, as well as Luc Besson’s prod company EuropaCorp.
-
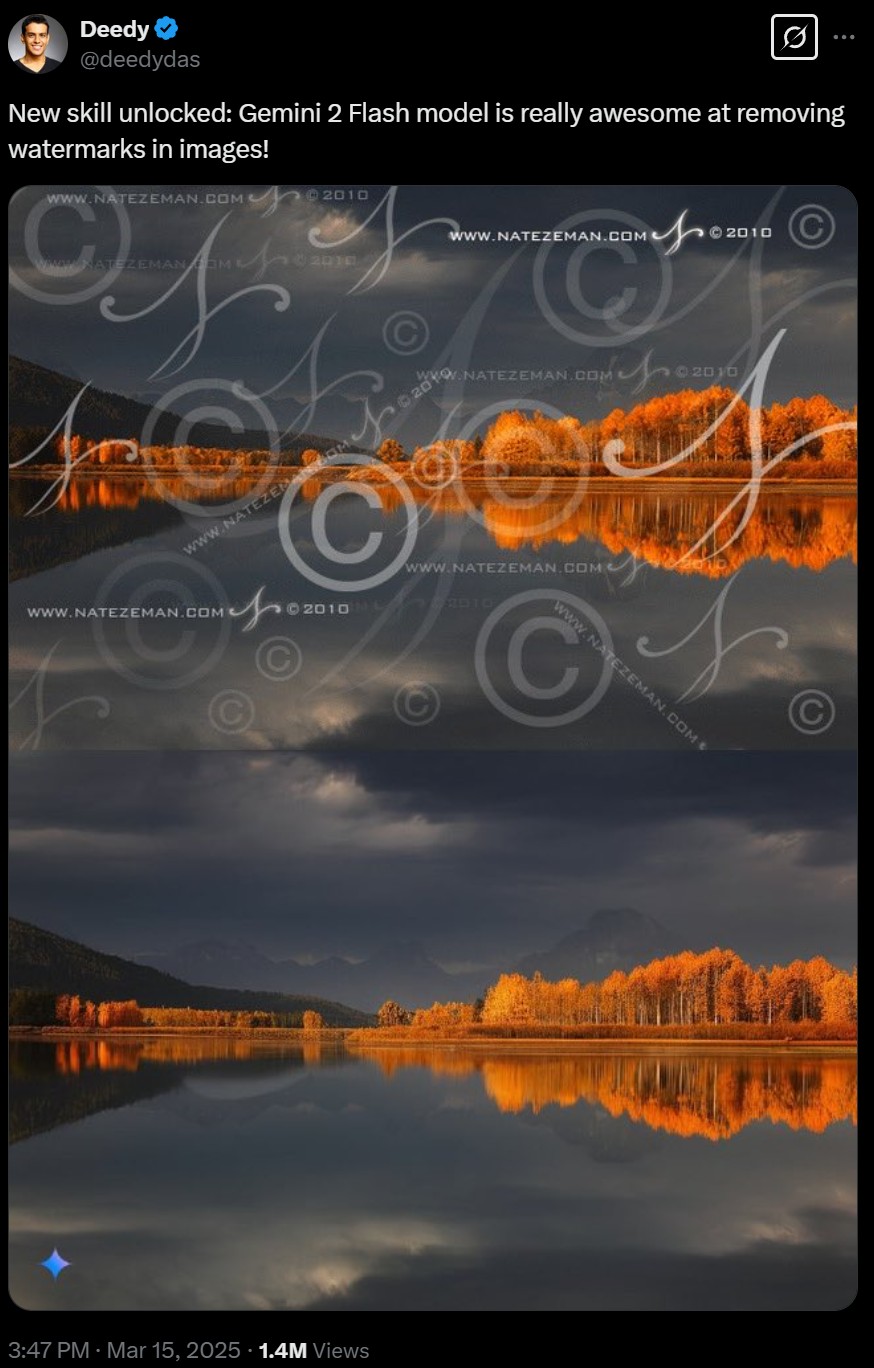
Google Gemini 2.0 Flash new AI model extremely proficient at removing watermarks from images
-
Jellyfish Pictures suspends operations
https://www.broadcastnow.co.uk/post-and-vfx/jellyfish-pictures-suspends-operations/5202847.article
According to a report in Indian news outlet, Animation Xpress, Jellyfish is facing financial struggles and has temporarily suspended its global operations.

-
Judge allows authors AI copyright lawsuit against Meta to move forward
The lawsuit has already provided a few glimpses into how Meta approaches copyright, with court filings from the plaintiffs claiming that Mark Zuckerberg gave the Llama team permission to train the models using copyrighted works and that other Meta team members discussed the use of legally questionable content for AI training.

-
Mike Seymour – Amid Industry Collapses, with guest panelist Scott Ross (ex ILM and DD)
Beyond Technicolor’s specific challenges, the broader VFX industry continues to grapple with systemic issues, including cost-cutting pressures, exploitative working conditions, and an unsustainable business model. VFX houses often operate on razor-thin margins, competing in a race to the bottom due to studios’ demand for cheaper and faster work. This results in a cycle of overwork, burnout, and, in many cases, eventual bankruptcy, as seen with Rhythm & Hues in 2013 and now at Technicolor. The reliance on tax incentives and outsourcing further complicates matters, making VFX work highly unstable. With major vendors collapsing and industry workers facing continued uncertainty, many are calling for structural changes, including better contracts, collective bargaining, and a more sustainable production pipeline. Without meaningful reform, the industry risks seeing more historic names disappear and countless skilled artists move to other fields.

-
Shadow of Mordor’s brilliant Nemesis system is locked away by a Warner Bros patent until 2036, despite studio shutdown
The Nemesis system, for those unfamiliar, is a clever in-game mechanic which tracks a player’s actions to create enemies that feel capable of remembering past encounters. In the studio’s Middle-earth games, this allowed foes to rise through the ranks and enact revenge.
The patent itself – which you can view here – was originally filed back in 2016, before it was granted in 2021. It is dubbed “Nemesis characters, nemesis forts, social vendettas and followers in computer games”. As it stands, the patent has an expiration date of 11th August, 2036.

-
Walt Disney Animation Abandons Longform Streaming Content
https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/business/business-news/tiana-disney-series-shelved-1236153297
A spokesperson confirmed there will be some layoffs in its Vancouver studio as a result of this shift in business strategy. In addition to the Tiana series, the studio is also scrapping an unannounced feature-length project that was set to go straight to Disney+.
Insiders say that Walt Disney Animation remains committed to releasing one theatrical film per year in addition to other shorts and special projects

-
VES Cinematic Color – Motion-Picture Color Management
This paper presents an introduction to the color pipelines behind modern feature-film visual-effects and animation.
Authored by Jeremy Selan, and reviewed by the members of the VES Technology Committee including Rob Bredow, Dan Candela, Nick Cannon, Paul Debevec, Ray Feeney, Andy Hendrickson, Gautham Krishnamurti, Sam Richards, Jordan Soles, and Sebastian Sylwan.
-
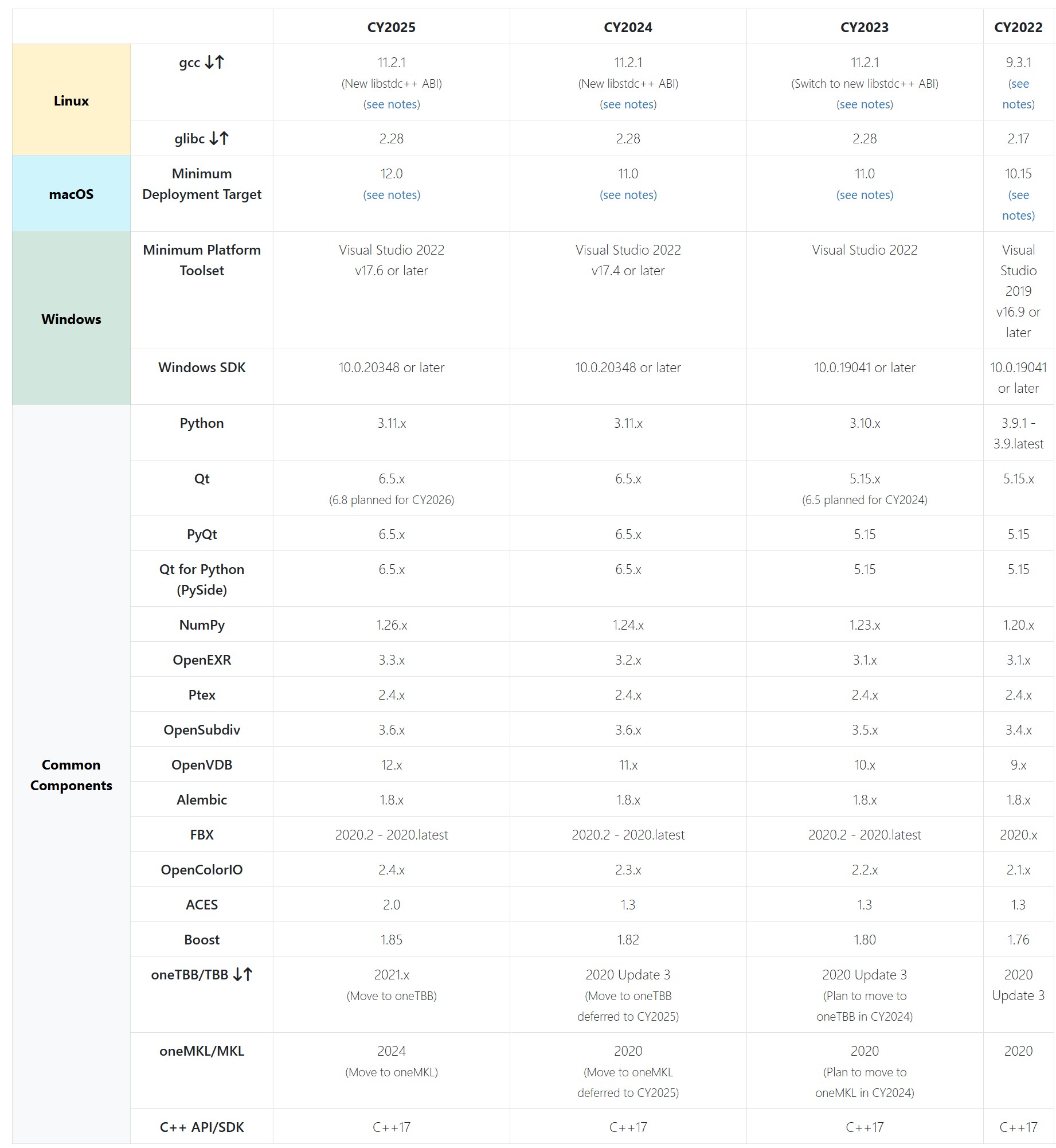
The VFX Reference Platform
The VFX Reference Platform is a set of tool and library versions to be used as a common target platform for building software for the VFX industry. Its purpose is to minimise incompatibilities between different software packages, ease the support burden for integrated pipelines and encourage further adoption of Linux by both studios and software vendors. The Reference Platform is updated annually by a group of software vendors in collaboration with the Visual Effects Society Technology Committee.
Each annual reference platform is designated by the calendar year in which major product releases should be targeting that particular reference.
-
VFX Giant MPC and Parent Company Technicolor Shut Down Amid ‘Severe Financial Challenges
https://variety.com/2025/film/global/technicolor-vfx-mpc-shutter-severe-challenges-1236316354
Shaun Severi, Head of Creative Production at the Mill, claimed in a LinkedIn post that 4,500 had lost their jobs in 24 hours: “The problem wasn’t talent or execution — it was mismanagement at the highest levels…the incompetence at the top was nothing short of disastrous.”
According to Severi, successive company presidents “buried the company under massive debt by acquiring VFX Studios…the second president, after a disastrous merger of the post houses, took us public, artificially inflating the company’s value — only for it to come crashing down when the real numbers were revealed….and the third and final president, who came from a car rental company, had no vision of what she was building, selling or managing.”

-
InvokeAI Got a Copyright for an Image Made Entirely With AI. Here’s How
-
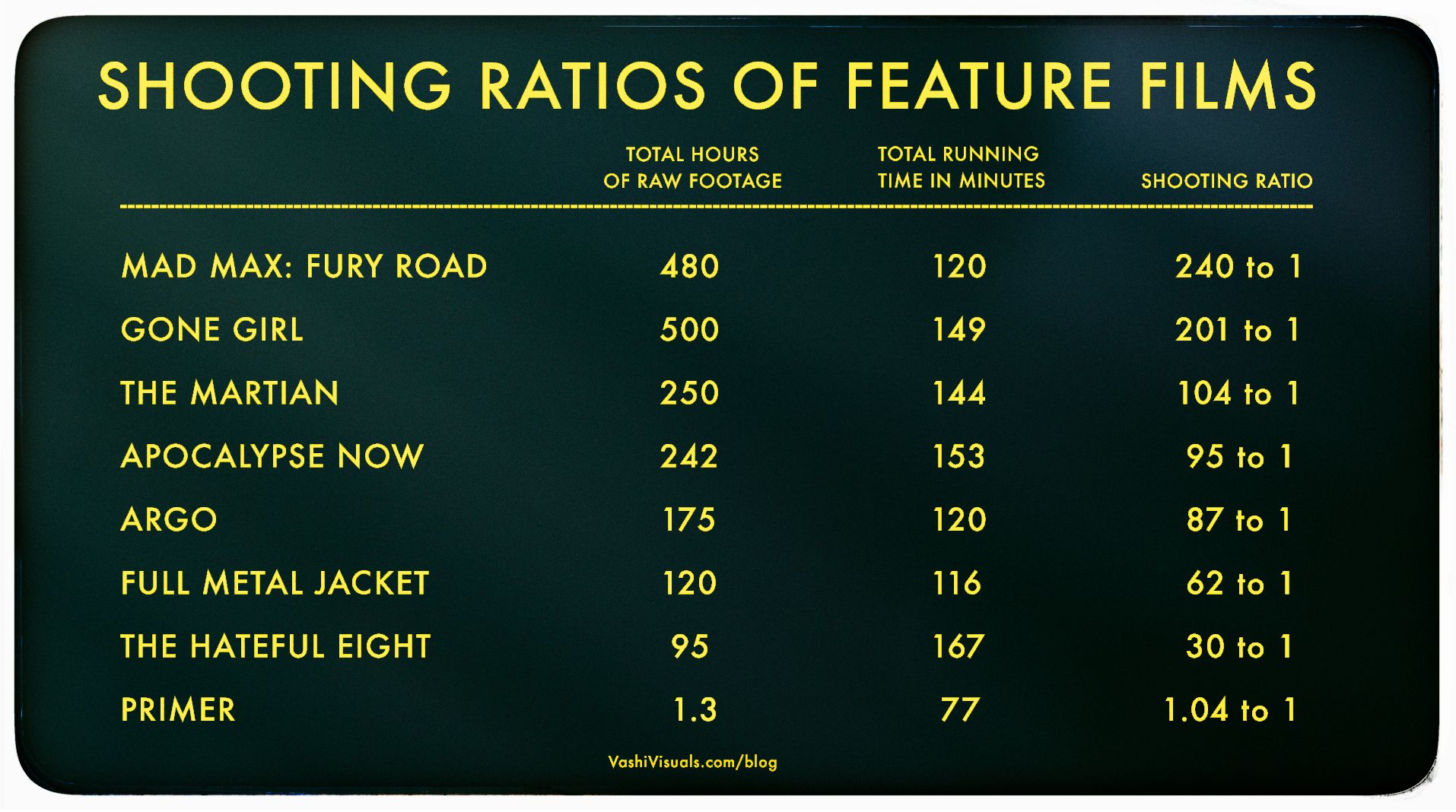
Vashi Nedomansky – Shooting ratios of feature films
In the Golden Age of Hollywood (1930-1959), a 10:1 shooting ratio was the norm—a 90-minute film meant about 15 hours of footage. Directors like Alfred Hitchcock famously kept it tight with a 3:1 ratio, giving studios little wiggle room in the edit.
Fast forward to today: the digital era has sent shooting ratios skyrocketing. Affordable cameras roll endlessly, capturing multiple takes, resets, and everything in between. Gone are the disciplined “Action to Cut” days of film.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shooting_ratio
-
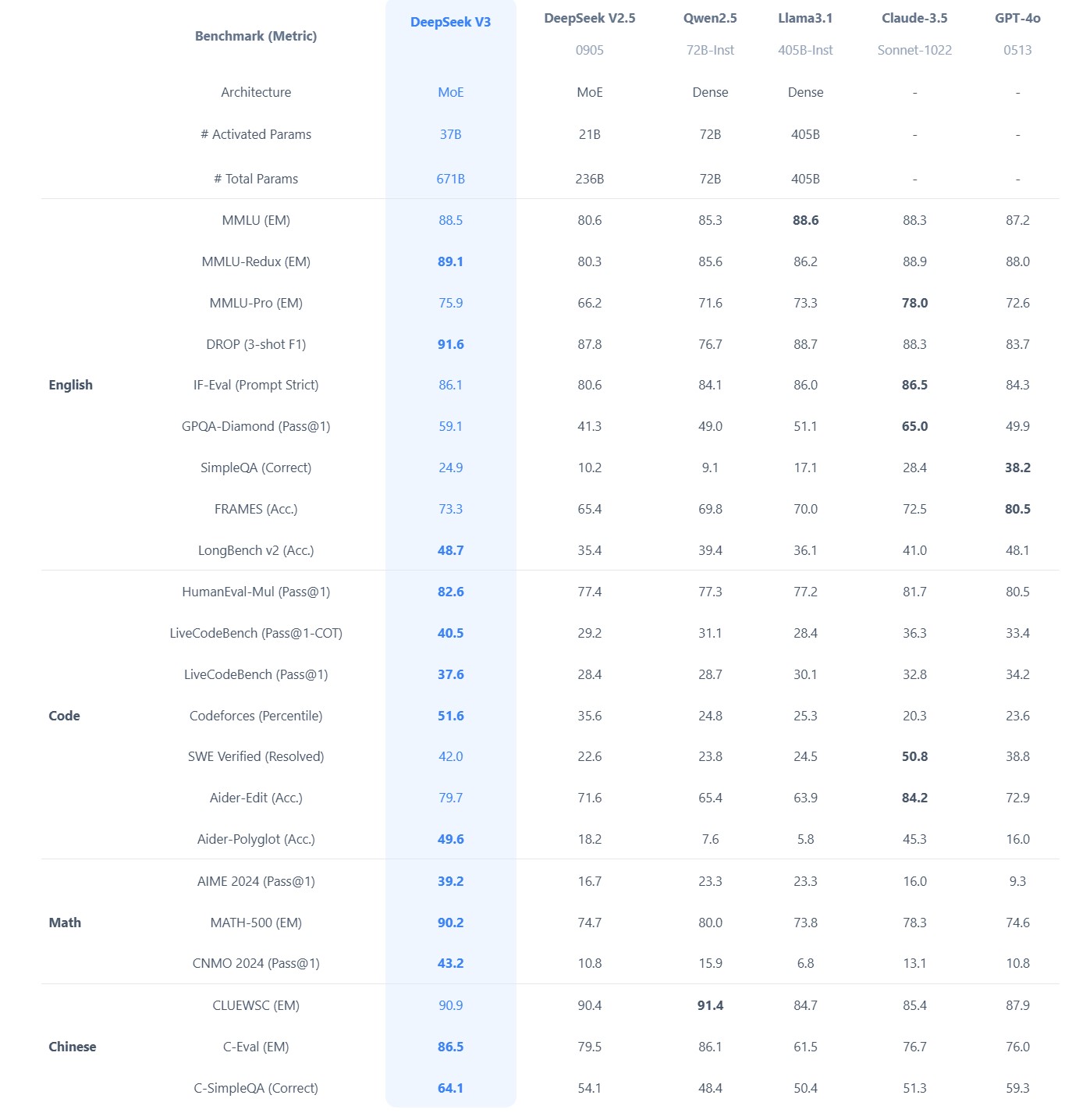
Brian Gallagher – Why Almost Everybody Is Wrong About DeepSeek vs. All the Other AI Companies
Benchmarks don’t capture real-world complexity like latency, domain-specific tasks, or edge cases. Enterprises often need more than raw performance, also needing reliability, ease of integration, and robust vendor support. Enterprise money will support the industries providing these services.
… it is also reasonable to assume that anything you put into the app or their website will be going to the Chinese government as well, so factor that in as well.
-
Jacob Bartlett – Apple is Killing Swift
https://blog.jacobstechtavern.com/p/apple-is-killing-swift
Jacob Bartlett argues that Swift, once envisioned as a simple and composable programming language by its creator Chris Lattner, has become overly complex due to Apple’s governance. Bartlett highlights that Swift now contains 217 reserved keywords, deviating from its original goal of simplicity. He contrasts Swift’s governance model, where Apple serves as the project lead and arbiter, with other languages like Python and Rust, which have more community-driven or balanced governance structures. Bartlett suggests that Apple’s control has led to Swift’s current state, moving away from Lattner’s initial vision.

-
Bloomberg – Sam Altman on ChatGPT’s First Two Years, Elon Musk and AI Under Trump
https://www.bloomberg.com/features/2025-sam-altman-interview
One of the strengths of that original OpenAI group was recruiting. Somehow you managed to corner the market on a ton of the top AI research talent, often with much less money to offer than your competitors. What was the pitch?
The pitch was just come build AGI. And the reason it worked—I cannot overstate how heretical it was at the time to say we’re gonna build AGI. So you filter out 99% of the world, and you only get the really talented, original thinkers. And that’s really powerful. If you’re doing the same thing everybody else is doing, if you’re building, like, the 10,000th photo-sharing app? Really hard to recruit talent.
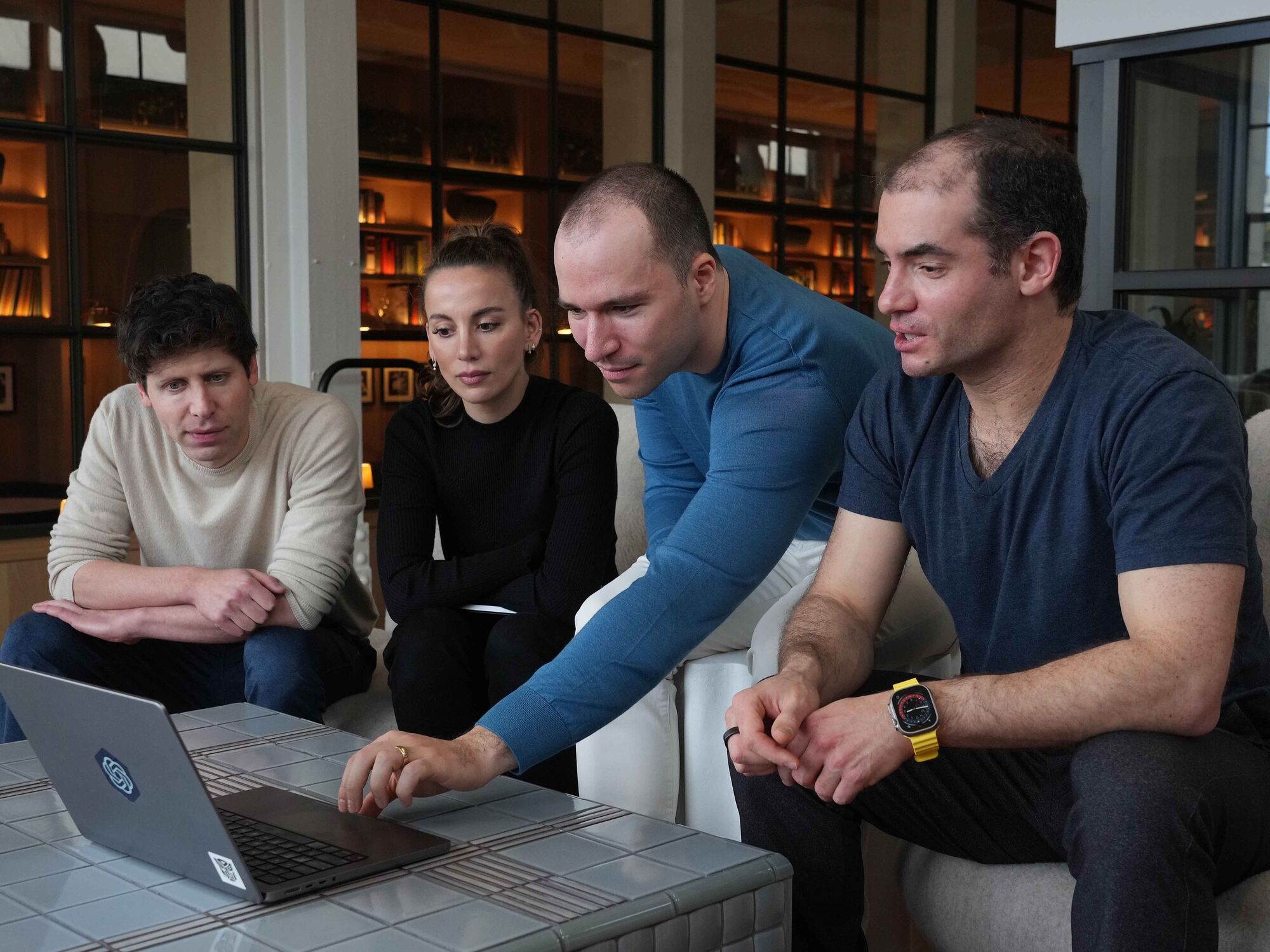

OpenAI senior executives at the company’s headquarters in San Francisco on March 13, 2023, from left: Sam Altman, chief executive officer; Mira Murati, chief technology officer; Greg Brockman, president; and Ilya Sutskever, chief scientist. Photographer: Jim Wilson/The New York Times
-
The AI-Copyright Trap document by Carys Craig
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4905118
“There are many good reasons to be concerned about the rise of generative AI(…). Unfortunately, there are also many good reasons to be concerned about copyright’s growing prevalence in the policy discourse around AI’s regulation. Insisting that copyright protects an exclusive right to use materials for text and data mining practices (whether for informational analysis or machine learning to train generative AI models) is likely to do more harm than good. As many others have explained, imposing copyright constraints will certainly limit competition in the AI industry, creating cost-prohibitive barriers to quality data and ensuring that only the most powerful players have the means to build the best AI tools (provoking all of the usual monopoly concerns that accompany this kind of market reality but arguably on a greater scale than ever before). It will not, however, prevent the continued development and widespread use of generative AI.”
…
“(…) As Michal Shur-Ofry has explained, the technical traits of generative AI already mean that its outputs will tend towards the dominant, likely reflecting ‘a relatively narrow, mainstream view, prioritizing the popular and conventional over diverse contents and narratives.’ Perhaps, then, if the political goal is to push for equality, participation, and representation in the AI age, critics’ demands should focus not on exclusivity but inclusivity. If we want to encourage the development of ethical and responsible AI, maybe we should be asking what kind of material and training data must be included in the inputs and outputs of AI to advance that goal. Certainly, relying on copyright and the market to dictate what is in and what is out is unlikely to advance a public interest or equality-oriented agenda.”
…
“If copyright is not the solution, however, it might reasonably be asked: what is? The first step to answering that question—to producing a purposively sound prescription and evidence-based prognosis, is to correctly diagnose the problem. If, as I have argued, the problem is not that AI models are being trained on copyright works without their owners’ consent, then requiring copyright owners’ consent and/or compensation for the use of their work in AI-training datasets is not the appropriate solution. (…)If the only real copyright problem is that the outputs of generative AI may be substantially similar to specific human-authored and copyright-protected works, then copyright law as we know it already provides the solution.” -
Eddie Yoon – There’s a big misconception about AI creative
You’re being tricked into believing that AI can produce Hollywood-level videos…
We’re far from it.
Yes, we’ve made huge progress.
A video sample like this, created using Kling 1.6, is light-years ahead of what was possible a year ago. But there’s still a significant limitation: visual continuity beyond 5 seconds.
Right now, no AI model can maintain consistency beyond a few seconds. That’s why most AI-generated concepts you’re seeing on your feed rely on 2–5 second cuts – it’s all the tech can handle before things start to fall apart.
This isn’t necessarily a problem for creating movie trailers or spec ads. Trailers, for instance, are designed for quick, attention-grabbing rapid cuts, and AI excels at this style of visual storytelling.
But, making a popular, full-length movie with nothing but 5-second shots? That’s absurd.
There are very few exceptions to this rule in modern cinema (e.g., the Bourne franchise).
To bridge the gap between trailers and full-length cinema, AI creative needs to reach 2 key milestones:
– 5-12 sec average: ASL for slower, non-action scenes in contemporary films – think conversations, emotional moments, or establishing shots
– 30+ sec sequences: Longer, uninterrupted takes are essential for genres that require immersion – drama, romance, thrillers, or any scene that builds tension or atmosphere
Mastering longer cuts is crucial.
30-second continuous shots require a higher level of craftsmanship and visual consistency – you need that 20-30 seconds of breathing room to piece together a variety of scenes and create a compelling movie.
So, where does AI creative stand now?
AI is already transforming industries like auto, fashion, and CPG. These brands can use AI today because short, 2–5 second cuts work perfectly in their visual language. Consumers are accustomed to it, and it simply works. This psychological dynamic is unlikely to change anytime soon.
But for AI to produce true cinema (not just flashy concepts) it needs to extend its visual consistency. And every GenAI company is racing to get there.
The timeline?
Next year, expect breakthroughs in AI-generated content holding consistency for 10+ seconds. By then, full-length commercials, shows, and movies (in that order) will start to feel more crafted, immersive, and intentional, not just stitched together.
If you’re following AI’s impact on creativity, this is the development to watch. The companies that solve continuity will redefine what’s possible in film.

-
Zach Goldberg – The Startup CTO Handbook
https://github.com/ZachGoldberg/Startup-CTO-Handbook
You can buy the book on Amazon or Audible
Hi, thanks for checking out the Startup CTO’s Handbook! This repository has the latest version of the content of the book. You’re welcome and encouraged to contribute issues or pull requests for additions / changes / suggestions / criticisms to be included in future editions. Please feel free to add your name to ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS if you do so.
-
Wyz Borrero – AI-generated “casting”
Guillermo del Toro and Ben Affleck, among others, have voiced concerns about the capabilities of generative AI in the creative industries. They believe that while AI can produce text, images, sound, and video that are technically proficient, it lacks the authentic emotional depth and creative intuition inherent in human artistry—qualities that define works like those of Shakespeare, Dalí, or Hitchcock.
Generative AI models are trained on vast datasets and excel at recognizing and replicating patterns. They can generate coherent narratives, mimic writing or artistic styles, and even compose poetry and music. However, they do not possess consciousness or genuine emotions. The “emotion” conveyed in AI-generated content is a reflection of learned patterns rather than true emotional experience.
Having extensively tested and used generative AI over the past four years, I observe that the rapid advancement of the field suggests many current limitations could be overcome in the future. As models become more sophisticated and training data expands, AI systems are increasingly capable of generating content that is coherent, contextually relevant, stylistically diverse, and can even evoke emotional responses.
The following video is an AI-generated “casting” using a text-to-video model specifically prompted to test emotion, expressions, and microexpressions. This is only the beginning.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Principles of Animation with Alan Becker, Dermot OConnor and Shaun Keenan
-
UV maps
-
Methods for creating motion blur in Stop motion
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
-
Matt Gray – How to generate a profitable business
-
Jesse Zumstein – Jobs in games
-
Convert 2D Images to 3D Models
-
AnimationXpress.com interviews Daniele Tosti for TheCgCareer.com channel
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.