BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
2DGS – 2D Gaussian Splatting for Geometrically Accurate Radiance Fields
A 2D Gaussian Splats technique for extracting cleaner 3D geometry from 3DGS
https://github.com/hbb1/2d-gaussian-splatting
https://surfsplatting.github.io/
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1qoclD7HJ3-o0O1R8cvV3PxLhoDCMsH8W
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently revolutionized radiance field reconstruction, achieving high quality novel view synthesis and fast rendering speed without baking. However, 3DGS fails to accurately represent surfaces due to the multi-view inconsistent nature of 3D Gaussians. We present 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS), a novel approach to model and reconstruct geometrically accurate radiance fields from multi-view images. Our key idea is to collapse the 3D volume into a set of 2D oriented planar Gaussian disks. Unlike 3D Gaussians, 2D Gaussians provide view-consistent geometry while modeling surfaces intrinsically. To accurately recover thin surfaces and achieve stable optimization, we introduce a perspective-accurate 2D splatting process utilizing ray-splat intersection and rasterization. Additionally, we incorporate depth distortion and normal consistency terms to further enhance the quality of the reconstructions. We demonstrate that our differentiable renderer allows for noise-free and detailed geometry reconstruction while maintaining competitive appearance quality, fast training speed, and real-time rendering.
-
Kiosk – Library Tool for 3D Artists
Kiosk streamlines resource management. With tailored filtering, customizable organization, and seamless integration into Maya, Houdini, Blender and Cinema4D. Maintain one library for them all!
https://fabianstrube.gumroad.com/l/kiosk-library
-
USD cookbook examples and python stubs
This repository is a collection of simple USD projects. Each project shows off a single feature or group of USD features.
https://github.com/ColinKennedy/USD-Cookbook
These stubs are designed to be used with a type checker like
mypyto provide static type checking of python code, as well as to provide analysis and completion in IDEs like PyCharm and VSCode (with Pylance). -
Top 3D Printing Website Resources
The Holy Grail – https://github.com/ad-si/awesome-3d-printing
- Thingiverse – https://www.thingiverse.com/
- Makerworld – https://makerworld.com/
- Printables – https://www.printables.com/
- Cults – https://cults3d.com/
- CG Trader – https://www.cgtrader.com/3d-print-models
- Sketchfab – https://sketchfab.com/store/3d-models/stl
- 3D Export – https://3dexport.com/
- MyMiniFactory – https://www.myminifactory.com/
- Thangs – https://thangs.com/
- Yeggi – https://www.yeggi.com/
- FAB365 – https://fab365.net/
- Gambody – https://www.gambody.com/
- All3DP News – https://all3dp.com/
- TCT Magazine – https://www.tctmagazine.com/topics/3D-printing-news/
- 3DPrint.com – https://3dprint.com/
- NASA 3D Models – https://nasa3d.arc.nasa.gov/models/printable
-
Freepik Mystic – AI image-generator based on Flux
Built on top of a series of fine-tunes of Stable Diffusion, Flux, and Magnific-built models.
https://www.freepik.com/ai/image-generator
-
Generate 3D from ANY Video! │Gaussian Splatting Tutorial w/ Postshot and Blender
After Effects Gaussian Splatting Plugin:
https://aescripts.com/gaussian-splatting/?aff=60Blender Gaussian Splatting Plugin: (kinda buggy)
https://github.com/ReshotAI/gaussian-splatting-blender-addonPostShot
https://www.pixelsham.com/2024/04/03/jawset-postshot-run-gaussian-splatting-with-a-ui-on-your-pc/ -
Artifacts now available for all Claude.ai users across our Free, Pro, and Team plans
https://www.anthropic.com/news/artifacts
Artifacts turn conversations with Claude into a more creative and collaborative experience.
FEATURED POSTS
-
What Is The Resolution and view coverage Of The human Eye. And what distance is TV at best?
https://www.discovery.com/science/mexapixels-in-human-eye
About 576 megapixels for the entire field of view.
Consider a view in front of you that is 90 degrees by 90 degrees, like looking through an open window at a scene. The number of pixels would be:
90 degrees * 60 arc-minutes/degree * 1/0.3 * 90 * 60 * 1/0.3 = 324,000,000 pixels (324 megapixels).At any one moment, you actually do not perceive that many pixels, but your eye moves around the scene to see all the detail you want. But the human eye really sees a larger field of view, close to 180 degrees. Let’s be conservative and use 120 degrees for the field of view. Then we would see:
120 * 120 * 60 * 60 / (0.3 * 0.3) = 576 megapixels.
Or.
7 megapixels for the 2 degree focus arc… + 1 megapixel for the rest.
https://clarkvision.com/articles/eye-resolution.html
Details in the post
-
Survivorship Bias: The error resulting from systematically focusing on successes and ignoring failures. How a young statistician saved his planes during WW2.
A young statistician saved their lives.
His insight (and how it can change yours):
(more…)
During World War II, the U.S. wanted to add reinforcement armor to specific areas of its planes.
Analysts examined returning bombers, plotted the bullet holes and damage on them (as in the image below), and came to the conclusion that adding armor to the tail, body, and wings would improve their odds of survival.
But a young statistician named Abraham Wald noted that this would be a tragic mistake. By only plotting data on the planes that returned, they were systematically omitting the data on a critical, informative subset: The planes that were damaged and unable to return.
-
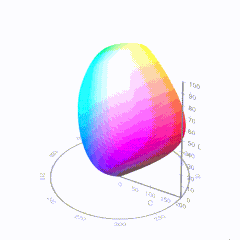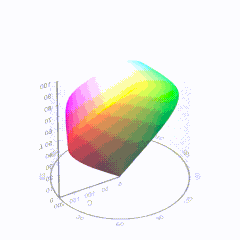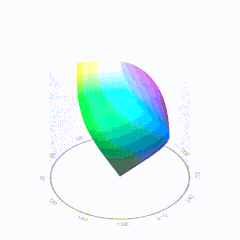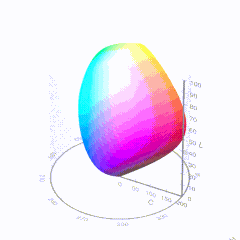
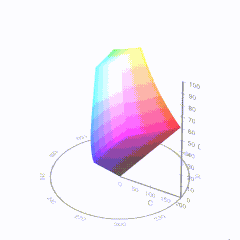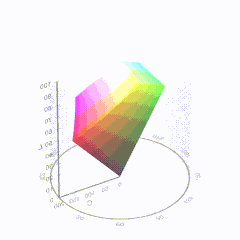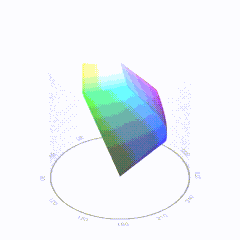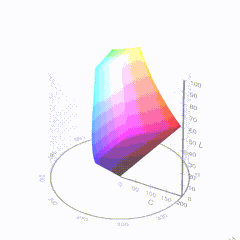
HDR and Color
https://www.soundandvision.com/content/nits-and-bits-hdr-and-color
In HD we often refer to the range of available colors as a color gamut. Such a color gamut is typically plotted on a two-dimensional diagram, called a CIE chart, as shown in at the top of this blog. Each color is characterized by its x/y coordinates.
Good enough for government work, perhaps. But for HDR, with its higher luminance levels and wider color, the gamut becomes three-dimensional.
For HDR the color gamut therefore becomes a characteristic we now call the color volume. It isn’t easy to show color volume on a two-dimensional medium like the printed page or a computer screen, but one method is shown below. As the luminance becomes higher, the picture eventually turns to white. As it becomes darker, it fades to black. The traditional color gamut shown on the CIE chart is simply a slice through this color volume at a selected luminance level, such as 50%.
Three different color volumes—we still refer to them as color gamuts though their third dimension is important—are currently the most significant. The first is BT.709 (sometimes referred to as Rec.709), the color gamut used for pre-UHD/HDR formats, including standard HD.
The largest is known as BT.2020; it encompasses (roughly) the range of colors visible to the human eye (though ET might find it insufficient!).
Between these two is the color gamut used in digital cinema, known as DCI-P3.
sRGB
D65